Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Associate Editors-in-Chief:''' [[User:Ujjwal Rastogi|Ujjwal Rastogi, MBBS]] [mailto:urastogi@perfuse.org] | '''Associate Editors-in-Chief:''' [[User:Ujjwal Rastogi|Ujjwal Rastogi, MBBS]] [mailto:urastogi@perfuse.org] | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
ECG abnormalities exist in both patients with<ref name="pmid15863641">{{cite journal| author=Geibel A, Zehender M, Kasper W, Olschewski M, Klima C, Konstantinides SV| title=Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism. | journal=Eur Respir J | year= 2005 | volume= 25 | issue= 5 | pages= 843-8 | pmid=15863641 |doi=10.1183/09031936.05.00119704 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15863641 }} </ref> and without<ref name="pmid11018210">{{cite journal| author=Rodger M, Makropoulos D, Turek M, Quevillon J, Raymond F, Rasuli P et al.| title=Diagnostic value of the electrocardiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism. | journal=Am J Cardiol | year= 2000 | volume= 86 | issue= 7 | pages= 807-9, A10 |pmid=11018210 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11018210 }} </ref> PE who do not have preexisting cardiovascular disease thus limiting the diagnostic usefullness. ECG findings may be normal as well. | |||
Stein et al.<ref name="pmid1746481">{{cite journal| author=Stein PD, Saltzman HA, Weg JG| title=Clinical characteristics of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. | journal=Am J Cardiol | year= 1991 | volume= 68 | issue= 17 | pages= 1723-4 | pmid=1746481 | doi= |pmc= | url= }} </ref>, in there prospective study, reported 70% of the patients with acute PE had ECG abnormalities, most commonly nonspecific ST-segment and T-wave changes. | |||
=== Electrocardiogram === | |||
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on patients with chest pain to quickly diagnose [[myocardial infarctions]] (heart attacks). An ECG may show signs of right heart strain or acute [[cor pulmonale]] in cases of large PEs - the classic signs are a large S wave in lead I, a large Q wave in lead III and an inverted T wave in lead III ('''S1Q3T3'''). | An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on patients with chest pain to quickly diagnose [[myocardial infarctions]] (heart attacks). An ECG may show signs of right heart strain or acute [[cor pulmonale]] in cases of large PEs - the classic signs are a large S wave in lead I, a large Q wave in lead III and an inverted T wave in lead III ('''S1Q3T3'''). | ||
* The most common ECG finding is anterior T-wave inversion. | * The most common ECG finding is anterior T-wave inversion. | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 22 November 2011
|
Pulmonary Embolism Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Pulmonary Embolism Assessment of Probability of Subsequent VTE and Risk Scores |
|
Treatment |
|
Follow-Up |
|
Special Scenario |
|
Trials |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editors-in-Chief: Ujjwal Rastogi, MBBS [2]
Overview
ECG abnormalities exist in both patients with[1] and without[2] PE who do not have preexisting cardiovascular disease thus limiting the diagnostic usefullness. ECG findings may be normal as well. Stein et al.[3], in there prospective study, reported 70% of the patients with acute PE had ECG abnormalities, most commonly nonspecific ST-segment and T-wave changes.
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on patients with chest pain to quickly diagnose myocardial infarctions (heart attacks). An ECG may show signs of right heart strain or acute cor pulmonale in cases of large PEs - the classic signs are a large S wave in lead I, a large Q wave in lead III and an inverted T wave in lead III (S1Q3T3).
- The most common ECG finding is anterior T-wave inversion.
- This likely represents reciprocal changes reflecting infero-posterior ischemia due to compression of the right coronary artery (RCA) as a result of pressure overload in the right ventricle (RV).
- Sinus tachycardia, right bundle branch block (RBBB) are also frequently seen, but again are not sensitive or specific
- There may be an S wave in lead 1, a Q wave in lead 3, and a flipped T wave in lead 3 (S1Q3T3 pattern).
An ECG may show signs of right heart strain or acute cor pulmonale in cases of large PEs - the classic signs are a large S wave in lead I, a large Q wave in lead III and an inverted T wave in lead III ("S1Q3T3").[4] This is present in upto 20% patient, but may also occur in other acute lung conditions and has therefore limited diagnostic value; the most commonly seen sign in the ECG is sinus tachycardia.
-
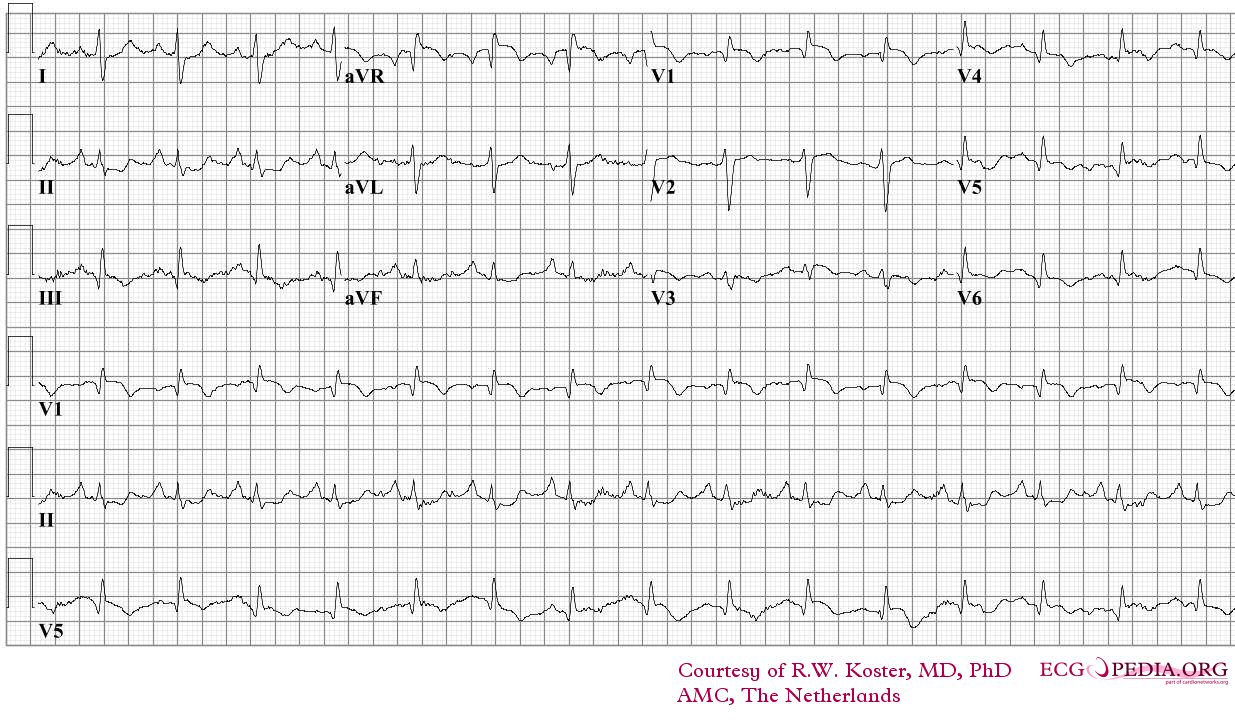
ECG of a patient with pulmonary embolism Image courtesy of ecgpedia
-
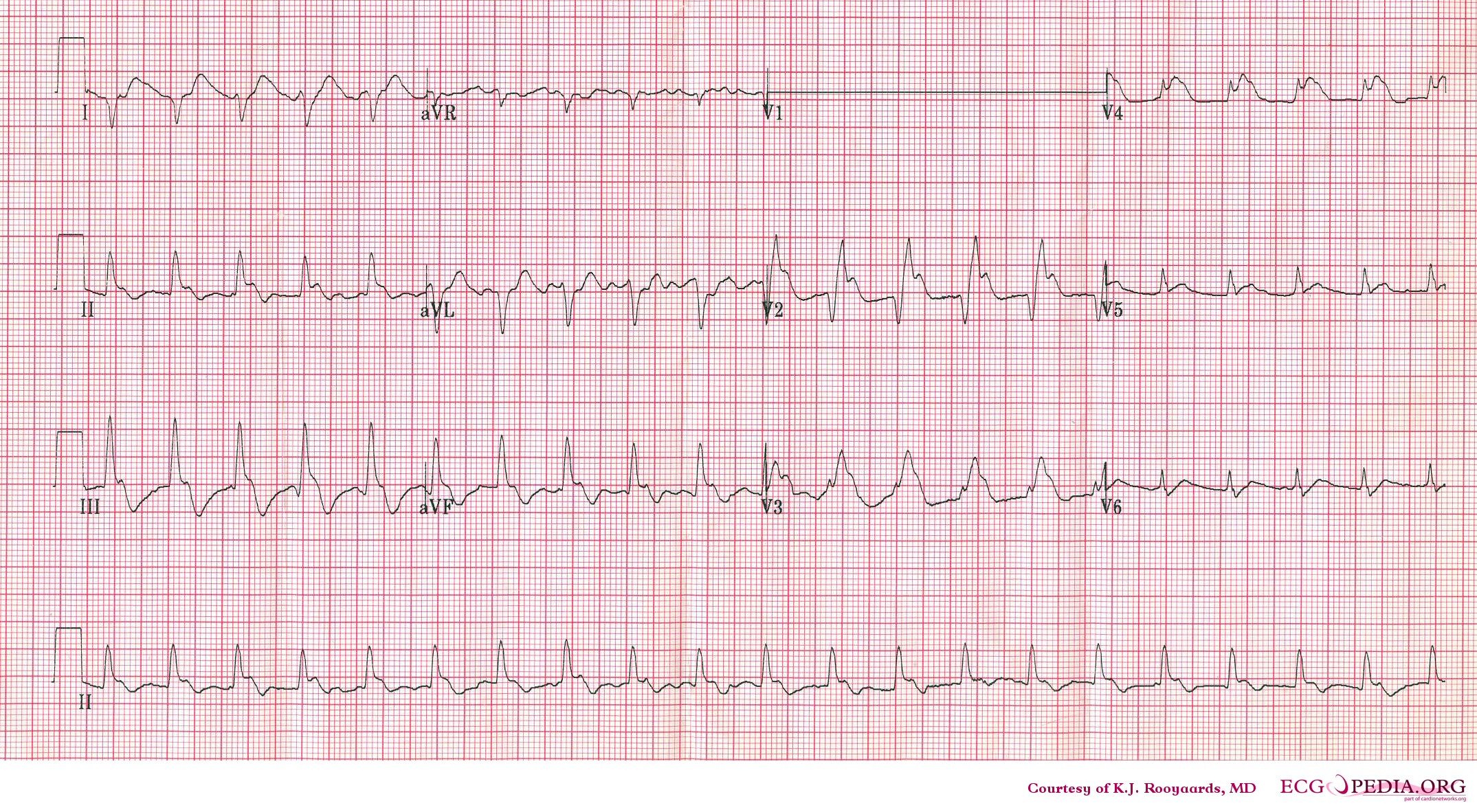
Another example; a patient with pulmonary embolism. Note the tachycardia and right axis.Image courtesy of ecgpedia
-
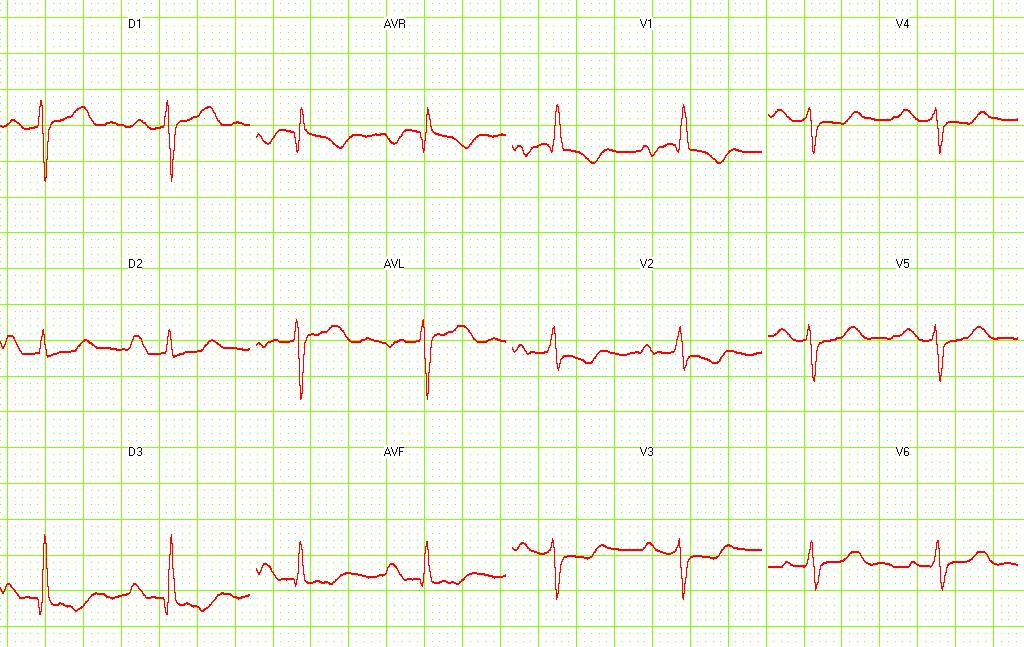
Pulmonary embolism. S1-Q3 and signs of right frontal axis are shown. Image courtesy of Dr Jose Ganseman Dr Ganseman's webpage: An ultimate source of EKG
References
- ↑ Geibel A, Zehender M, Kasper W, Olschewski M, Klima C, Konstantinides SV (2005). "Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism". Eur Respir J. 25 (5): 843–8. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00119704. PMID 15863641.
- ↑ Rodger M, Makropoulos D, Turek M, Quevillon J, Raymond F, Rasuli P; et al. (2000). "Diagnostic value of the electrocardiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism". Am J Cardiol. 86 (7): 807–9, A10. PMID 11018210.
- ↑ Stein PD, Saltzman HA, Weg JG (1991). "Clinical characteristics of patients with acute pulmonary embolism". Am J Cardiol. 68 (17): 1723–4. PMID 1746481.
- ↑ McGinn S, White PD. Acute cor pulmonale resulting from pulmonary embolism. J Am Med Assoc 1935;104:1473–1480.