Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
FDA on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
CDC on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology in the news |
|
Blogs on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
- Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mahda Alihashemi M.D. [2]
Overview
The exact pathogenesis of [disease name] is not fully understood.
OR
It is thought that [disease name] is the result of / is mediated by / is produced by / is caused by either [hypothesis 1], [hypothesis 2], or [hypothesis 3].
OR
[Pathogen name] is usually transmitted via the [transmission route] route to the human host.
OR
Following transmission/ingestion, the [pathogen] uses the [entry site] to invade the [cell name] cell.
OR
[Disease or malignancy name] arises from [cell name]s, which are [cell type] cells that are normally involved in [function of cells].
OR
The progression to [disease name] usually involves the [molecular pathway].
OR
The pathophysiology of [disease/malignancy] depends on the histological subtype.
Pathophysiology
Physiology
The normal physiology of [name of process] can be understood as follows:
Pathogenesis
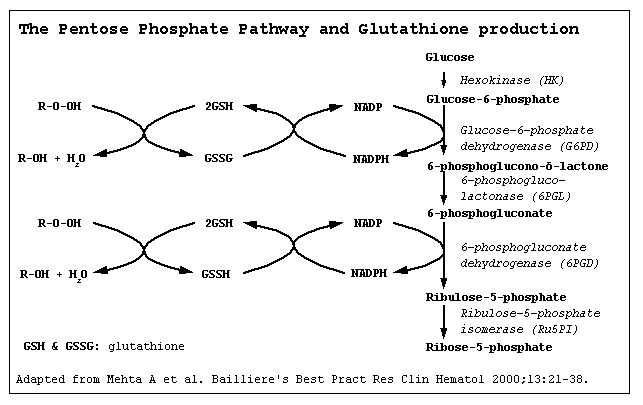
- It is understood that G6PD deficiency is the result of reduced Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme levels. G6PD deficiency is an X-linked disorder. It is the most common enzymatic disorder of red blood cells. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme oxidize glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone in pentose phosphate pathway ( HMP shunt). Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme also reduces nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) to NADPH. NADPH is an important cofactor in glutathione metabolism against oxidative injury in RBC.Reduced glutathione (GSH) convert to oxidized glutathione (GSSG) by glutathione peroxidase enzyme that prevent oxidant accumulation. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of GSSG to GSH by NADPH. In G6PD deficiency, oxidative stresses can denature hemoglobin and intravascular hemolysis in RBC can happen. Infection, some meication and foods with high level of convicine, vicine, divicine and isouramil such as fava beans can cause oxidative stress. Spleen is the organ for sequesteration damaged RBC. The hemoglobin is metabolized to bilirubin and cause jaundice.
- [Pathogen name] is usually transmitted via the [transmission route] route to the human host.
- Following transmission/ingestion, the [pathogen] uses the [entry site] to invade the [cell name] cell.
- [Disease or malignancy name] arises from [cell name]s, which are [cell type] cells that are normally involved in [function of cells].
- The progression to [disease name] usually involves the [molecular pathway].
- The pathophysiology of [disease/malignancy] depends on the histological subtype.
Genetics
G6PD deficiency is transmitted in x-linked disorder pattern. The gene G6PD is located in the distal long arm of the X chromosome at the Xq28 locus. [1]
Heterozygous women are usually normal because of lyonization ( X innactivation)[2]
G6PD B, is the wild type or normal. G6PD has 400 variant enzymes. [3] Caucasians, Asians and majority of blacks has G6PD B.
G6PD A+:In Africa, in 20-30 percent of black. In this variant, asparagine is substitued for aspartate, at amino acid 126. [4] It has normal enzyme activity.
Genes involved in the pathogenesis of G6PD deficency include:
- [Gene1]
- [Gene2]
- [Gene3]The normal wild-type enzyme, G6PD B, is found in most Caucasians, Asians, and a majority of blacks. It has normal catalytic activity and is not associated with hemolysis (class IV). A common variant is G6PD A+ which is found in 20 to 30 percent of blacks from Africa [23]. It differs from G6PD B by the substitution of a single amino acid, an asparagine for aspartate at the amino acid 126 [24], and has much faster electrophoretic mobility (the letters A and B refer to relative electrophoretic mobilities). G6PD A+ has normal catalytic properties and does not cause hemolysis.
OR
The development of G6PD deficency is the result of missense point mutations and also a few deletions. [5]
- G6PD A+:In Africa, in 20-30 percent of black. In this variant, asparagine is substitued for aspartate, at amino acid 126. [4] It has normal enzyme activity.
- G6PD A-: Cause primaquine sensitivity in blacks.
- [Mutation 3]
Associated Conditions
Gross Pathology
On gross pathology, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name].
Microscopic Pathology
On microscopic histopathological analysis, , Heinz bodies can be visualized as a result of denatured hemoglobin in peripheral blood smears with supravital staining. processed with supravital staining (Heinz body prep).
References
- ↑ KIRKMAN HN, HENDRICKSON EM (September 1963). "Sex-linked electrophoretic difference in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 15: 241–58. PMC 1932381. PMID 14033020.
- ↑ BEUTLER E, YEH M, FAIRBANKS VF (January 1962). "The normal human female as a mosaic of X-chromosome activity: studies using the gene for C-6-PD-deficiency as a marker". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 48: 9–16. PMC 285481. PMID 13868717.
- ↑ Beutler E (December 1994). "G6PD deficiency". Blood. 84 (11): 3613–36. PMID 7949118.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Yoshida A (March 1967). "A single amino Acid substitution (asparagine to aspartic Acid) between normal (b+) and the common negro variant (a+) of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 57 (3): 835–40. PMC 335583. PMID 16591538.
- ↑ Beutler E (April 1990). "The genetics of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency". Semin. Hematol. 27 (2): 137–64. PMID 2190319.
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
FDA on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
CDC on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology in the news |
|
Blogs on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [3]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Priyamvada Singh, M.D. [4]
Please help WikiDoc by adding content here. It's easy! Click here to learn about editing.
Overview
Pathophysiology