Dofetilide
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
{{{blackBoxWarningTitle}}}
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
To minimize the risk of induced arrhythmia, patients initiated or re-initiated on TIKOSYN should be placed for a minimum of 3 days in a facility that can provide calculations of creatinine clearance, continuous electrocardiographic monitoring, and cardiac resuscitation. For detailed instructions regarding dose selection, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. TIKOSYN is available only to hospitals and prescribers who have received appropriate TIKOSYN dosing and treatment initiation education; see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
|
Overview
Dofetilide is {{{aOrAn}}} Antiarrhythmic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of Maintenance of Normal Sinus Rhythm (Delay in AF/AFl Recurrence), Conversion of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include chest pain, dizziness , headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
<h4>Condition 1</h4>
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Contraindications
TIKOSYN is contraindicated in patients with congenital or acquired long QT syndromes. TIKOSYN should not be used in patients with a baseline QT interval or QTc >440 msec (500 msec in patients with ventricular conduction abnormalities). TIKOSYN is also contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (calculated creatinine clearance <20 mL/min). The concomitant use of verapamil or the cation transport system inhibitors cimetidine, trimethoprim (alone or in combination with sulfamethoxazole), or ketoconazole with TIKOSYN is contraindicated (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions), as each of these drugs cause a substantial increase in dofetilide plasma concentrations. In addition, other known inhibitors of the renal cation transport system such as prochlorperazine, dolutegravir and megestrol should not be used in patients on TIKOSYN. The concomitant use of hydrochlorothiazide (alone or in combinations such as with triamterene) with TIKOSYN is contraindicated (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions) because this has been shown to significantly increase dofetilide plasma concentrations and QT interval prolongation. TIKOSYN is also contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug.
Warnings
|
{{{blackBoxWarningTitle}}}
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
To minimize the risk of induced arrhythmia, patients initiated or re-initiated on TIKOSYN should be placed for a minimum of 3 days in a facility that can provide calculations of creatinine clearance, continuous electrocardiographic monitoring, and cardiac resuscitation. For detailed instructions regarding dose selection, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. TIKOSYN is available only to hospitals and prescribers who have received appropriate TIKOSYN dosing and treatment initiation education; see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
|
Ventricular Arrhythmia TIKOSYN (dofetilide) can cause serious ventricular arrhythmias, primarily Torsade de Pointes (TdP) type ventricular tachycardia, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation. QT interval prolongation is directly related to dofetilide plasma concentration. Factors such as reduced creatinine clearance or certain dofetilide drug interactions will increase dofetilide plasma concentration. The risk of TdP can be reduced by controlling the plasma concentration through adjustment of the initial dofetilide dose according to creatinine clearance and by monitoring the ECG for excessive increases in the QT interval. Treatment with dofetilide must therefore be started only in patients placed for a minimum of three days in a facility that can provide electrocardiographic monitoring and in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious ventricular arrhythmias. Calculation of the creatinine clearance for all patients must precede administration of the first dose of dofetilide. For detailed instructions regarding dose selection, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. The risk of dofetilide induced ventricular arrhythmia was assessed in three ways in clinical studies: 1) by description of the QT interval and its relation to the dose and plasma concentration of dofetilide; 2) by observing the frequency of TdP in TIKOSYN-treated patients according to dose; 3) by observing the overall mortality rate in patients with atrial fibrillation and in patients with structural heart disease. Relation of QT Interval to Dose The QT interval increases linearly with increasing TIKOSYN dose (see Figures 1 and 2 in CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and Dose-Response and Concentration Response for Increase in QT Interval). Frequency of Torsade de Pointes In the supraventricular arrhythmia population (patients with AF and other supraventricular arrhythmias), the overall incidence of Torsade de Pointes was 0.8%. The frequency of TdP by dose is shown in Table 4. There were no cases of TdP on placebo.
As shown in Table 5, the rate of TdP was reduced when patients were dosed according to their renal function (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations, Renal Impairment and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
The majority of the episodes of TdP occurred within the first three days of TIKOSYN therapy (10/11 events in the studies of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias; 19/25 and 4/7 events in DIAMOND CHF and DIAMOND MI, respectively; 2/4 events in the DIAMOND AF subpopulation).
Mortality
In a pooled survival analysis of patients in the supraventricular arrhythmia population (low prevalence of structural heart disease), deaths occurred in 0.9% (12/1346) of patients receiving TIKOSYN and 0.4% (3/677) in the placebo group. Adjusted for duration of therapy, primary diagnosis, age, gender, and prevalence of structural heart disease, the point estimate of the hazard ratio for the pooled studies (TIKOSYN/placebo) was 1.1 (95% CI: 0.3, 4.3). The DIAMOND CHF and MI trials examined mortality in patients with structural heart disease (ejection fraction ≤35%). In these large, double-blind studies, deaths occurred in 36% (541/1511) of TIKOSYN patients and 37% (560/1517) of placebo patients. In an analysis of 506 DIAMOND patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter at baseline, one year mortality on TIKOSYN was 31% vs. 32% on placebo (see CLINICAL STUDIES). Because of the small number of events, an excess mortality due to TIKOSYN cannot be ruled out with confidence in the pooled survival analysis of placebo-controlled trials in patients with supraventricular arrhythmias. However, it is reassuring that in two large placebo-controlled mortality studies in patients with significant heart disease (DIAMOND CHF/MI), there were no more deaths in TIKOSYN-treated patients than in patients given placebo (see CLINICAL STUDIES).
Drug-Drug Interactions
(see CONTRAINDICATIONS) Because there is a linear relationship between dofetilide plasma concentration and QTc, concomitant drugs that interfere with the metabolism or renal elimination of dofetilide may increase the risk of arrhythmia(Torsade de Pointes). TIKOSYN is metabolized to a small degree by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme of the cytochrome P450 system and an inhibitor of this system could increase systemic dofetilide exposure. More important, dofetilide is eliminated by cationic renal secretion, and three inhibitors of this process have been shown to increase systemic dofetilide exposure. The magnitude of the effect on renal elimination by cimetidine, trimethoprim, and ketoconazole (all contraindicated concomitant uses with dofetilide) suggests that all renal cation transport inhibitors should be contraindicated.
Hypokalemia and Potassium-Depleting Diuretics
Hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia may occur with administration of potassium-depleting diuretics, increasing the potential for Torsade de Pointes. Potassium levels should be within the normal range prior to administration of TIKOSYN and maintained in the normal range during administration of TIKOSYN (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Use with Drugs that Prolong QT Interval and Antiarrhythmic Agents
The use of TIKOSYN in conjunction with other drugs that prolong the QT interval has not been studied and is not recommended. Such drugs include phenothiazines, cisapride, bepridil, tricyclic antidepressants, certain oral macrolides, and certain fluoroquinolones. Class I or Class III antiarrhythmic agents should be withheld for at least three half-lives prior to dosing with TIKOSYN. In clinical trials, TIKOSYN was administered to patients previously treated with oral amiodarone only if serum amiodarone levels were below 0.3 mg/L or amiodarone had been withdrawn for at least three months.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Dofetilide in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Dofetilide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Dofetilide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dofetilide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Dofetilide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Dofetilide and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
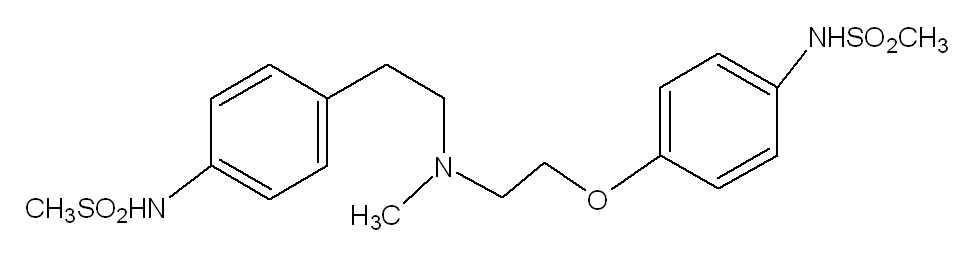
Structure
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Dofetilide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Dofetilide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Dofetilide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Dofetilide Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 96% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 60% -70% |
| Elimination half-life | 10 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27N3O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 441.567 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Dofetilide |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Dofetilide |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Dofetilide at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Dofetilide at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Dofetilide
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Dofetilide Discussion groups on Dofetilide Patient Handouts on Dofetilide Directions to Hospitals Treating Dofetilide Risk calculators and risk factors for Dofetilide
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Dofetilide |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [3]
For patient information, click here
Dofetilide is a class III antiarrhythmic agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the maintenance of sinus rhythm in individuals prone to the formation of atrial fibrillation and flutter, and for the chemical cardioversion to sinus rhythm from atrial fibrillation and flutter.
The chemical name for dofetilide is N-[4-(2-{2-[4-(methanesulphonamido) phenoxyl]-N-methylethylamino}ethyl)phenyl]- methanesulphonamide. It is marketed under the trade name Tikosyn® by Pfizer, and is available in the United States in capsules containing 125, 250, and 500 µg of dofetilide. Due to the pro-arrhythmic potential of dofetilide, it is only available by prescription by physicians who have undergone specific training in the risks of treatment with dofetilide. In addition, it is only available by mail order or through specially trained local pharmacies to individuals who are prescribed dofetilide by a physician who is registered as being able to prescribe the pharmaceutical.
The elimination half-life of dofetilide is roughly 10 hours, however this is variable based on many physiologic factors (most significantly creatinine clearance), and ranges from 4.8 to 13.5 hours.
Mechanism of action
Dofetilide works by selectively blocking the rapid component of the delayed rectifier outward potassium current (IKr).
This causes prolongation of the effective refractory period of accessory pathways (both anterograde and retrograde conduction in the accessory pathway). It is this selective action on accessory pathways that makes dofetilide effective in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and flutter.
Dofetilide does not effect Vmax (The slope of the upstroke of phase 0 depolarization), conduction velocity, or the resting membrane potential.
There is a dose-dependent increase in the QT interval and the corrected QT interval (QTc). Because of this, many practitioners will initiate dofetilide therapy only on individuals under telemetry monitoring or if serial EKG measurements of QT and QTc can be performed.
Metabolism
A steady-state plasma level of dofetilide is achieved in 2-3 days.
80% of dofetilide is excreted by the kidneys, so the dose of dofetilide should be adjusted in individuals with renal insufficiency, based on creatinine clearance.
In the kidneys, dofetilide is eliminated via cation exchange (secretion). Agents that interfere with the renal cation exchange system, such as verapamil, cimetidine, hydrochlorothiazide, itraconazole, ketoconazole, prochlorperazine, and trimethoprim should not be administered to individuals taking dofetilide.
About 20 percent of dofetilide is metabolized in the liver via the CYP3A4 isoenzyme of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Drugs that interfere with the activity of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme can increase serum dofetilide levels. If the renal cation exchange system is interfered with (as with the medications listed above), a larger percentage of dofetilide is cleared via the CYP3A4 isoenzyme system.
Side effects
Torsades de pointes is the most serious side effect of dofetilide therapy. The incidence of torsades de pointes is dose-related, and is 0.3-10.5%. The risk appears to be dose-dependent, with an increased incidence of torsades de pointes associated with higher doses of dofetilide administered.
The risk of inducing torsades de pointes can be decreased by taking precautions when initiating therapy, such as hospitalizing individuals for a minimum of three days for serial creatinine measurement, continuous telemetry monitoring and availability of cardiac resuscitation.
Clinical use
Based on the results of the Danish Investigations of Arrhythmias and Mortality on Dofetilide (DIAMOND) study, dofetilide does not affect mortality in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction with left ventricular dysfunction.3 Because of the results of the DIAMOND study, many physicians use dofetilide in the suppression of atrial fibrillation in individuals with LV dysfunction.
See also
References
- Thomas L. Lenz, Pharm.D., and Daniel E. Hilleman, Pharm.D., Department of Cardiology, Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska. Dofetilide, a New Class III Antiarrhythmic Agent. Pharmacotherapy 20(7):776-786, 2000. (Medline abstract)
- Lenz TL, Hilleman DE. Dofetilide: A new antiarrhythmic agent approved for conversion and/or maintenance of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter. Drugs Today (Barc). 2000 Nov;36(11):759-71. (Medline abstract)
- Torp-Pedersen C, Moller M, Bloch-Thomsen PE, Kober L, Sandoe E, Egstrup K, Agner E, Carlsen J, Videbaek J, Marchant B, Camm AJ. Dofetilide in patients with congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction. Danish Investigations of Arrhythmia and Mortality on Dofetilide Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1999 Sep 16;341(12):857-65. (Medline abstract)
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Antiarrhythmic agents
- Drugs