Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies: Difference between revisions
m (→Overview) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*[[High resolution Ultrasound]]: assess for [[birth defects]] that may have been overlooked in initial [[Ultrasound|ultrasounds]]; often done at 18-22 weeks <ref name="“CDC”">{{cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/diagnosis.html}}</ref> | *[[High resolution Ultrasound]]: assess for [[birth defects]] that may have been overlooked in initial [[Ultrasound|ultrasounds]]; often done at 18-22 weeks <ref name="“CDC”">{{cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/diagnosis.html}}</ref> | ||
*[[Chorionic villus sampling]]: collecting a sample of placenta tissues to determine the presence or absence of [[genetic]] or [[chromosomal disorders]]; performed between 10-12 weeks[[File:ChorionicVillus.png|alt=BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons|none|thumb|300x300px|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ChorionicVillus.png Chorionic Villus Sampling]]] | *[[Chorionic villus sampling]]: collecting a sample of [[placenta]] tissues to determine the presence or absence of [[genetic]] or [[chromosomal disorders]]; performed between 10-12 weeks[[File:ChorionicVillus.png|alt=BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons|none|thumb|300x300px|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ChorionicVillus.png Chorionic Villus Sampling]]] | ||
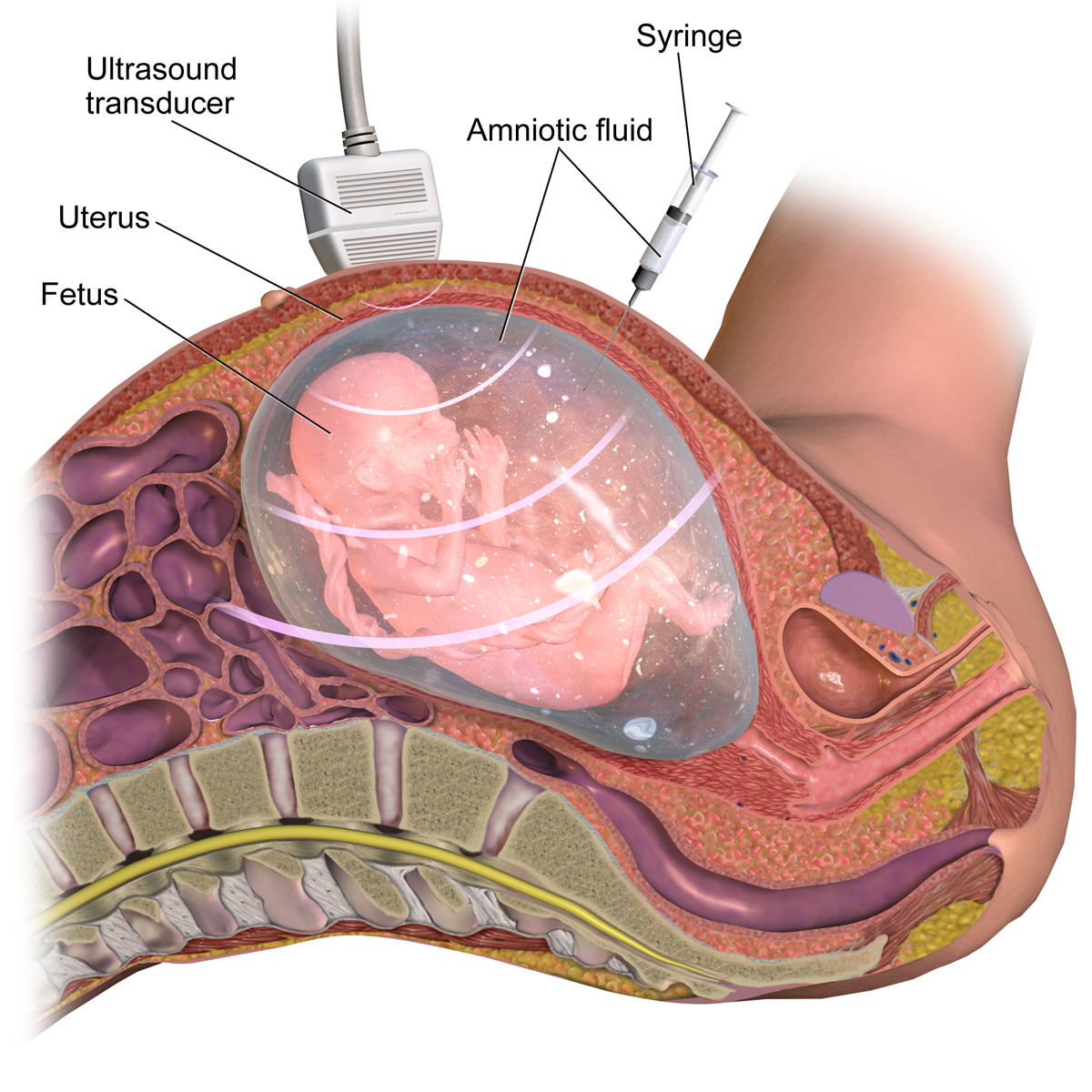
*[[Amniocentesis]]: process by which fluid containing cells surrounding the baby is collected. These cells can then be tested for [[genetic defects]]. Due to the higher risk carried by this procedure, it is not a routine one and is performed only when indicated after other abnormal tests; often | *[[Amniocentesis]]: process by which fluid containing cells surrounding the baby is collected. These cells can then be tested for [[genetic defects]]. Due to the higher risk carried by this procedure, it is not a routine one and is performed only when indicated after other abnormal tests; often performed between 15-18 weeks of gestation | ||
**[[AFP]] | **[[AFP]] | ||
**[[Acetylcholinesterase]][[File:Amniocentesis.png|alt=BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons|none|thumb|300x300px|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Amniocentesis.png Amniocentesis]]] | **[[Acetylcholinesterase]][[File:Amniocentesis.png|alt=BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons|none|thumb|300x300px|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Amniocentesis.png Amniocentesis]]] | ||
Revision as of 11:31, 24 April 2022
|
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Congenital diaphragmatic hernia from Other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies |
|
FDA on Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies |
|
CDC on Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies |
|
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies in the news |
|
Blogs on Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Congenital diaphragmatic hernia |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Congenital diaphragmatic hernia other diagnostic studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Arooj Naz, M.B.B.S
Overview
Diagnostic studied that can be utilized include high resolution ultrasound, chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, microarray analysis, and karyotyping. Although these studies are not necessarily diagnostic for CDH, they help identify underlying genetic defects which have a high correlation rate with diaphragmatic hernia's.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- High resolution Ultrasound: assess for birth defects that may have been overlooked in initial ultrasounds; often done at 18-22 weeks [1]
- Chorionic villus sampling: collecting a sample of placenta tissues to determine the presence or absence of genetic or chromosomal disorders; performed between 10-12 weeks
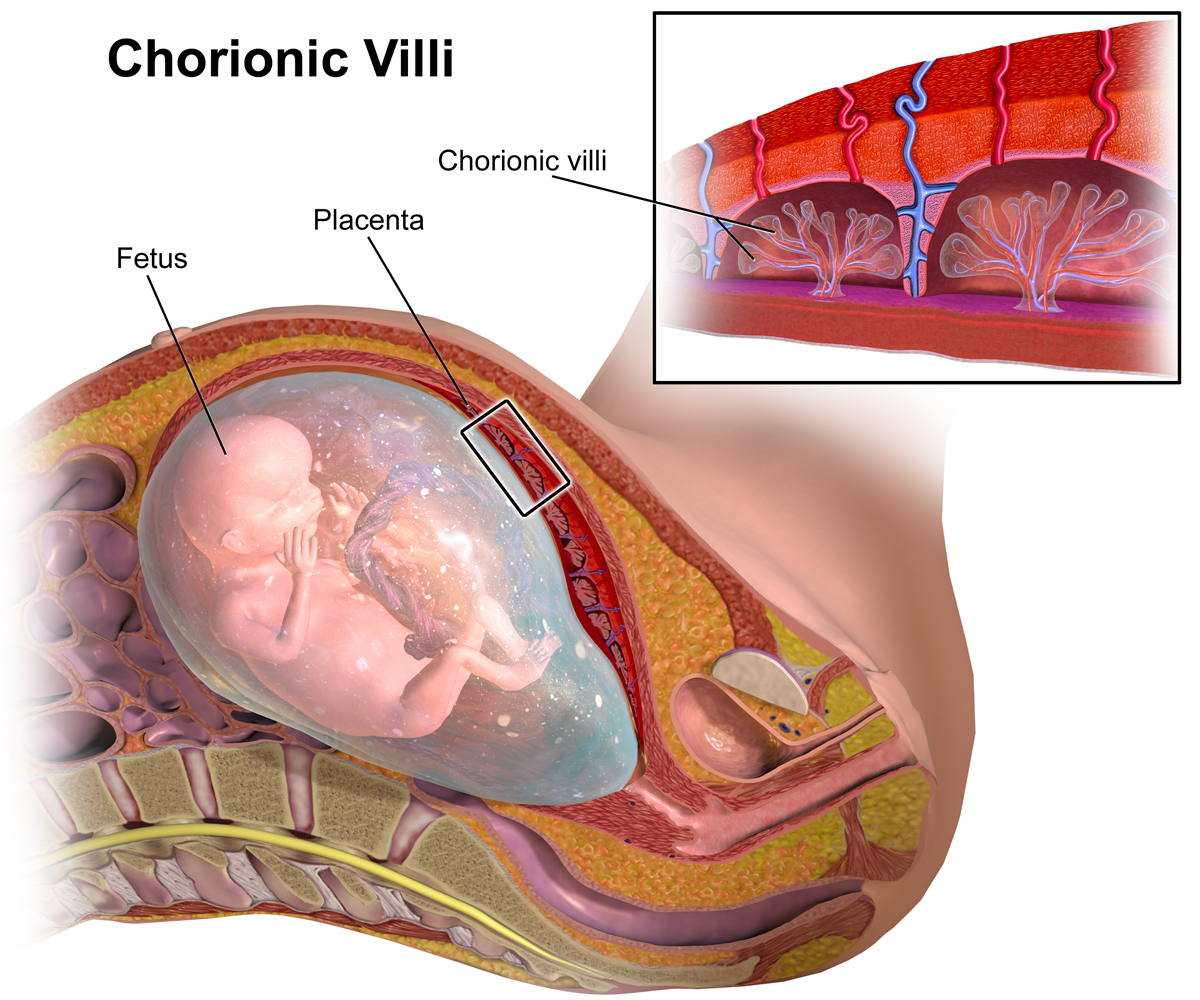
Chorionic Villus Sampling - Amniocentesis: process by which fluid containing cells surrounding the baby is collected. These cells can then be tested for genetic defects. Due to the higher risk carried by this procedure, it is not a routine one and is performed only when indicated after other abnormal tests; often performed between 15-18 weeks of gestation
- Chromosomal microarray analysis: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) can detect microdeletions and microduplications
- Karyotyping: a process by which chromosomes are identified and sorted [2]
References
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/diagnosis.html. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Shemilt L, Verbanis E, Schwenke J, Estandarte AK, Xiong G, Harder R; et al. (2015). "Karyotyping human chromosomes by optical and X-ray ptychography methods". Biophys J. 108 (3): 706–13. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3456. PMC 4317545. PMID 25650937.