Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Overview
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) are any of several autosomal recessive diseases resulting from mutations of genes for enzymes mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol from cholesterol by the adrenal glands (steroidogenesis).[1] Most of these conditions involve excessive or deficient production of sex steroids and can alter development of primary or secondary sex characteristics in some affected infants, children, or adults.[2] Congenital adrenal hyperplasia may be classified according to biochemical enzyme deficiency into commonly five subtypes: lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia, congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency, and congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
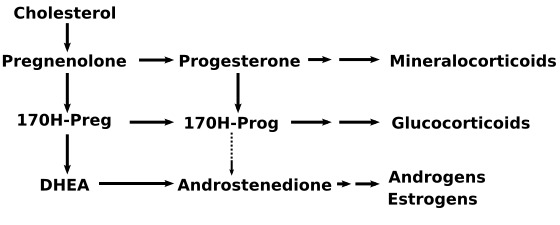
Classification
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia may be classified according to biochemical enzyme deficiency into commonly the following types.
Biochemistry
| Common medical term | OMIM no. | Enzyme(s) | Gene location | Substrate(s) | Product(s) |
| 21-hydroxylase CAH | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 201910 | P450c21 | 6p21.3 | 17OH-progesterone→ progesterone→ |
11-deoxycortisol DOC |
| lipoid CAH (20,22-desmolase) |
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 201710 | StAR P450scc |
8p11.2 15q23-q24 |
transport of cholesterol cholesterol→ |
into mitochondria pregnenolone |
| 17α-hydroxylase CAH | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 202110 | P450c17 | 10q24.3 | pregnenolone→ progesterone→ 17OH-pregnenolone→ |
17OH-pregnenolone 17OH-progesterone DHEA |
| 3β-HSD CAH | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 201810 | 3βHSD II | 1p13 | pregnenolone→ 17OH-pregnenolone→ DHEA→ |
progesterone 17OH-progesterone androstenedione |
| 11β-hydroxylase CAH | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 202010 | P450c11β | 8q21-22 | 11-deoxycortisol→ DOC→ |
cortisol corticosterone |
Reference
- ↑ David A. Warrell (2005). Oxford textbook of medicine: Sections 18-33. Oxford University Press. pp. 261–. ISBN 978-0-19-856978-7. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ↑ Aubrey Milunsky; Jeff Milunsky (29 January 2010). Genetic Disorders and the Fetus: Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 600–. ISBN 978-1-4051-9087-9. Retrieved 14 June 2010.