COVID-19 x ray: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Removed protection from "COVID-19 x ray") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{COVID-19}} | {{COVID-19}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}};{{AE}}{{sab}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
The [[Chest X-ray|chest x ray]] findings in a suspected case of coronavirus [[infection]] can mimic the findings in [[pneumonia]]. | |||
==X Ray== | |||
*The [[Chest X-ray|chest x ray]] findings in a suspected case of coronavirus [[infection]] can mimic the findings in [[pneumonia]], which can include: | |||
:*[[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]]<ref name="pmid31986264">{{cite journal |vauthors=Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B |title=Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China |journal=Lancet |volume= |issue= |pages= |date=January 2020 |pmid=31986264 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 |url=}}</ref> | |||
:*[[Interstitial]] [[Infiltration (medical)|infiltration]] | |||
* [[Chest X-ray|Chest x ray]] findings in [[Patient|patients]] infected with MERS-CoV include: | |||
** Ground-glass opacity (the most common finding)<ref name="pmid26102309">{{cite journal |vauthors=Das KM, Lee EY, Al Jawder SE, Enani MA, Singh R, Skakni L, Al-Nakshabandi N, AlDossari K, Larsson SG |title=Acute Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: Temporal Lung Changes Observed on the Chest Radiographs of 55 Patients |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=205 |issue=3 |pages=W267–74 |date=September 2015 |pmid=26102309 |doi=10.2214/AJR.15.14445 |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] | |||
** [[Pneumothorax]] | |||
** Involvement of all [[lung]] zones in advanced [[disease]] | |||
===Images=== | |||
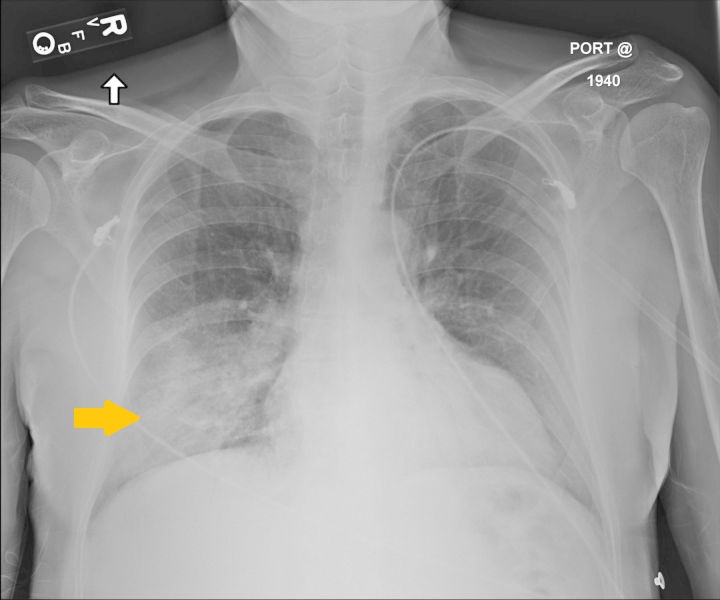
[[File:Coronavirus xray.jpg |300px|thumb|left| Chest x ray of a patient infected with MERS-CoV. <ref>By US government employee - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/core/lw/2.0/html/tileshop_pmc/tileshop_pmc_inline.html?title=Click%20on%20image%20to%20zoom&p=PMC3&id=4650772_ciu63501.jpg, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=68221821</ref>]] | |||
<br style="clear:left"> | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
Revision as of 14:44, 31 March 2020
|
COVID-19 Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
COVID-19 x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of COVID-19 x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sabawoon Mirwais, M.B.B.S, M.D.[2]
Overview
The chest x ray findings in a suspected case of coronavirus infection can mimic the findings in pneumonia.
X Ray
- The chest x ray findings in a suspected case of coronavirus infection can mimic the findings in pneumonia, which can include:
- Chest x ray findings in patients infected with MERS-CoV include:
- Ground-glass opacity (the most common finding)[2]
- Consolidation
- Pneumothorax
- Involvement of all lung zones in advanced disease
Images
References
- ↑ Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B (January 2020). "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China". Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. PMID 31986264.
- ↑ Das KM, Lee EY, Al Jawder SE, Enani MA, Singh R, Skakni L, Al-Nakshabandi N, AlDossari K, Larsson SG (September 2015). "Acute Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: Temporal Lung Changes Observed on the Chest Radiographs of 55 Patients". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 205 (3): W267–74. doi:10.2214/AJR.15.14445. PMID 26102309.
- ↑ By US government employee - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/core/lw/2.0/html/tileshop_pmc/tileshop_pmc_inline.html?title=Click%20on%20image%20to%20zoom&p=PMC3&id=4650772_ciu63501.jpg, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=68221821