Bubonic plague differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Differential diagnosis== | ==Differential diagnosis== | ||
===Bubonic | ===Bubonic Plague=== | ||
*[[Streptococcal]] or [[staphylococcal]] [[adenitis]] (Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal pyogenes) | *[[Streptococcal]] or [[staphylococcal]] [[adenitis]] (Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal pyogenes) | ||
**Purulent or inflamed [[lesion]] often noted [[distal]] to involved [[nodes]] (i.e., [[pustule]], infected traumatic lesion). | **Purulent or inflamed [[lesion]] often noted [[distal]] to involved [[nodes]] (i.e., [[pustule]], infected traumatic lesion). | ||
Revision as of 20:35, 17 December 2012
There are many diseases that resemble the basic signs and symptoms of bubonic plague. Since bubonic plague has the ability to kill the majority of a population, it is an extremely concerning diagnosis. It is very important to check for these other diseases before a final diagnosis of bubonic plague is made. There are many other bacterial infections that could be mistaken for the bubonic plague.
Differential diagnosis
Bubonic Plague
- Streptococcal or staphylococcal adenitis (Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal pyogenes)
- Purulent or inflamed lesion often noted distal to involved nodes (i.e., pustule, infected traumatic lesion).
- Involved nodes more likely to be fluctuant.
- Associated ascending lymphangitis or cellulitis may be present (generally not seen with plague).
- Tularemia (Francisella tularensis)
- Cat scratch fever (Bartonella henselae)
- Mycobacterial infection, including scrofula (Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other Mycobacterium species)
- With scrofula, adenitis occurs in cervical region.
- Usually painless.
- Indolent clinical course.
- Infections with species other than M. tuberculosis more likely to occur in immunocompromised patients.
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (Chlamydia trachomatis)
- Chancroid (Hemophilus ducreyi)
- Adenitis occurs in the inguinal region.
- Ulcerative lesion present.
- Systemic symptoms uncommon; toxicity does not occur.
- Primary genital herpes
- Herpes lesions present in genital area.
- Adenitis occurs in the inguinal region.
- Although patients may be ill (fever, headache), severe systemic toxicity not present.
- Primary or secondary syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the inguinal region.
- Lymph nodes generally painless.
- Chancre may be noted with primary syphilis.
- Strangulated inguinal hernias
- Evidence of bowel involvement.
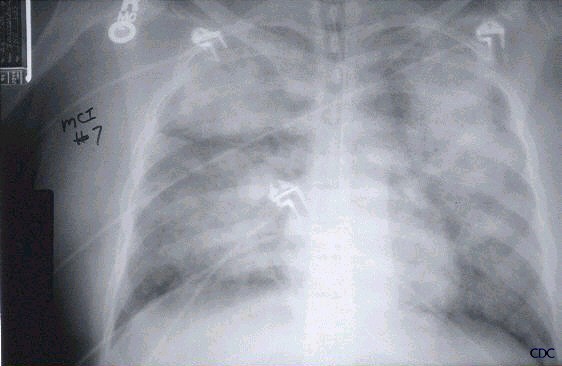
Chest X Ray
Some other infectious diseases can be differentiated by looking at chest x ray images. For example, SARS, Hantavirus syndrome, and Anthrax all need to be ruled out because they do present with some similar Symptoms. An example of a chest x ray for Hantavirus and Anthrax is shown.