Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Pathophysiology == | == Pathophysiology == | ||
* The exact [[pathogenesis]] of Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome is not completely understood. | * The exact [[pathogenesis]] of Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome is not completely understood. | ||
* It is understood that Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome | * It is understood that Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome may be caused by [[Genetics|genetic]] factors but which are involved are difficult to say. | ||
* It is understood that Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome is also may be caused by [[anomaly]] in [[organogenesis]]. | |||
* Origin of [[Cell (biology)|cells]] of the [[Blood vessel|vessel wall]]<nowiki/>s in the cephalic region in the brain, and their migration may explain the connection between [[Lesion|lesions]] looks alike but at different locations in the body. | |||
* | |||
== Signs and symptoms == | == Signs and symptoms == | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 7 June 2019
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vamsikrishna Gunnam M.B.B.S [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Wyburn mason's syndrome; Retinoencephalofacial angiomatosis
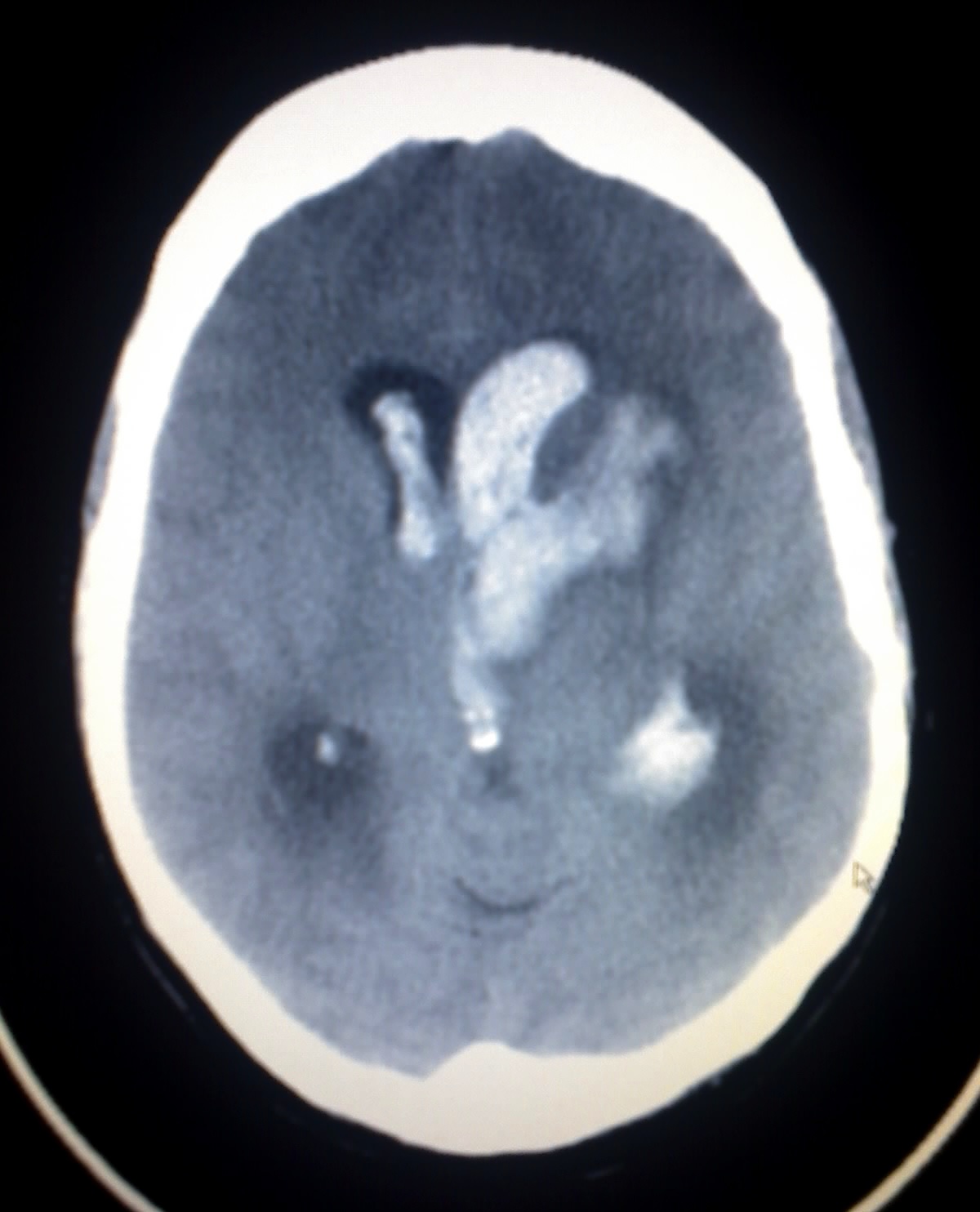
Overview
Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome or Wyburn mason's syndrome or Retinoencephalofacial angiomatosis is a rare arteriovenous malformation (AVMs) condition. In The United States of America in order to categorise a condition as a rare disease it should affect fewer than 200,000 people. Rare diseases also called as orphan diseases. Orphan Drug Act was passed on 1983 by congress for the rare diseases. Today an average of 25-30 million americans have been reported with rare diseases. The number of people with individual rare disease may be less but overall the number of people with rare diseases are large in number.
Historical Perspective
- Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome was first discovered by Magnus, in 1874.[1]
- In 1932, Yates and Payne was the first to discover retinal and cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVMs) in patients with Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome.[2]
- In 1937, Bonnet, Dechaume and Blanc was the first to discover arteriovenous malformations in face, retina, and brain.[3][4]
Pathophysiology
- The exact pathogenesis of Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome is not completely understood.
- It is understood that Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome may be caused by genetic factors but which are involved are difficult to say.
- It is understood that Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome is also may be caused by anomaly in organogenesis.
- Origin of cells of the vessel walls in the cephalic region in the brain, and their migration may explain the connection between lesions looks alike but at different locations in the body.
Signs and symptoms
Causes
Mechanism
Epidemiology
Diagnosis
Treatment
References
- ↑ Magnus, Hugo (1874). "Aneurysma arterioso-venosum retinale". Archiv für Pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für Klinische Medicin. 60 (1): 38–45. doi:10.1007/BF01938766. ISSN 0945-6317.
- ↑ Yates, A. Gurney; Paine, C. G. (1930). "A CASE OF ARTERIOVENOUS ANEURYSM WITHIN THE BRAIN". Brain. 53 (1): 38–46. doi:10.1093/brain/53.1.38. ISSN 0006-8950.
- ↑ Bhattacharya, J.J.; Luo, C.B.; Suh, D.C.; Alvarez, H.; Rodesch, G.; Lasjaunias, P. (2016). "Wyburn-Mason or Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc as Cerebrofacial Arteriovenous Metameric Syndromes (CAMS)". Interventional Neuroradiology. 7 (1): 5–17. doi:10.1177/159101990100700101. ISSN 1591-0199.
- ↑ Wyburn-Mason, R. (1943). "ARTERIOVENOUS ANEURYSM OF MID-BRAIN AND RETINA, FACIAL NÆVI AND MENTAL CHANGES". Brain. 66 (3): 163–203. doi:10.1093/brain/66.3.163. ISSN 0006-8950.