DIGOXIN tablet description: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Digoxin}} {{CMG}}; {{AE}}:{{AK}} '''''For patient information about Digoxin, click here.''''' ==11 DESCRIPTION== Digoxin is one...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''''For patient information about Digoxin, click [[Digoxin (patient information)|here]].''''' | '''''For patient information about Digoxin, click [[Digoxin (patient information)|here]].''''' | ||
== | == Description== | ||
Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or [[digitalis]]) [[glycosides]], a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”). | Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or [[digitalis]]) [[glycosides]], a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”). | ||
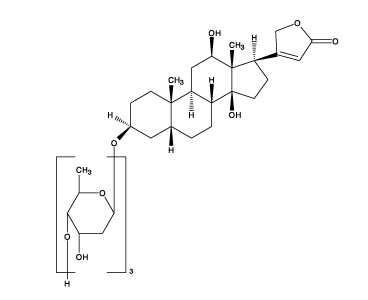
Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is: | Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is: | ||
{| | |||
[[image:diginj9.png]] | |[[image:diginj9.png|600px|thumb]] | ||
|} | |||
Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in [[pyridine]]. | Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in [[pyridine]]. | ||
Revision as of 05:17, 13 March 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: :Abdurahman Khalil, M.D. [2]
For patient information about Digoxin, click here.
Description
Digoxin is one of the cardiac (or digitalis) glycosides, a closely related group of drugs having in common specific effects on the myocardium. These drugs are found in a number of plants. Digoxin is extracted from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. The term “digitalis” is used to designate the whole group of glycosides. The glycosides are composed of 2 portions: a sugar and a cardenolide (hence “glycosides”).
Digoxin is described chemically as (3β,5β,12β)-3-[(O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12,14-dihydroxy-card-20(22)-enolide. Its molecular formula is C41H64O14, its molecular weight is 780.95, and its structural formula is:
 |
Digoxin exists as clear to white odorless crystals or white, odorless crystalline powder that melts with decomposition above 230°C. The drug is practically insoluble in water and in ether; slightly soluble in diluted (50%) alcohol and in chloroform; and freely soluble in pyridine.
Digoxin Tablets, USP are supplied as 125 mcg (0.125 mg) or 250 mcg (0.25 mg) tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains the labeled amount of Digoxin, USP and the following inactive ingredients:
125 mcg (0.125 mg): anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C yellow #6 aluminum lake, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and starch 1500.
250 mcg (0.25 mg): anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and starch 1500.