Premature Ventricular Contraction EKG Examples: Difference between revisions
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Shown below is an EKG showing a trigeminal rhythm where wide complex beats are interpolated between normal QRS complexes. Note that the PR interval is prolonged after the wide complex beat. The wide complex beats are probably ventricular beats. As a rule interpolated wide beats are usually ventricular. In most cases the P wave after the PVC is not conducted and a compensatory pause is created instead of an interpolated beat. | Shown below is an EKG showing a trigeminal rhythm where wide complex beats are interpolated between normal QRS complexes. Note that the PR interval is prolonged after the wide complex beat. The wide complex beats are probably ventricular beats. As a rule interpolated wide beats are usually ventricular. In most cases the P wave after the PVC is not conducted and a compensatory pause is created instead of an interpolated beat. | ||
[[File:Premature_Ventricular_Contractions_with_trigeminal_rhythm.jpg|center|800px]] | [[File:Premature_Ventricular_Contractions_with_trigeminal_rhythm.jpg|center|800px]] | ||
---- | |||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
Revision as of 17:42, 16 October 2012
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
For the main page on premature ventricular contraction, click here.
Premature Ventricular Contraction EKG Examples
Shown below is an EKG showing premature ventricular contractions.
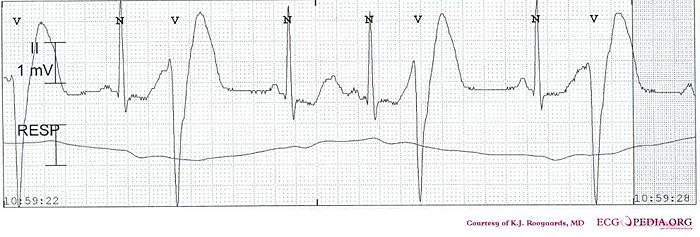
Shown below is an EKG showing a Premature Ventricular Contractions.

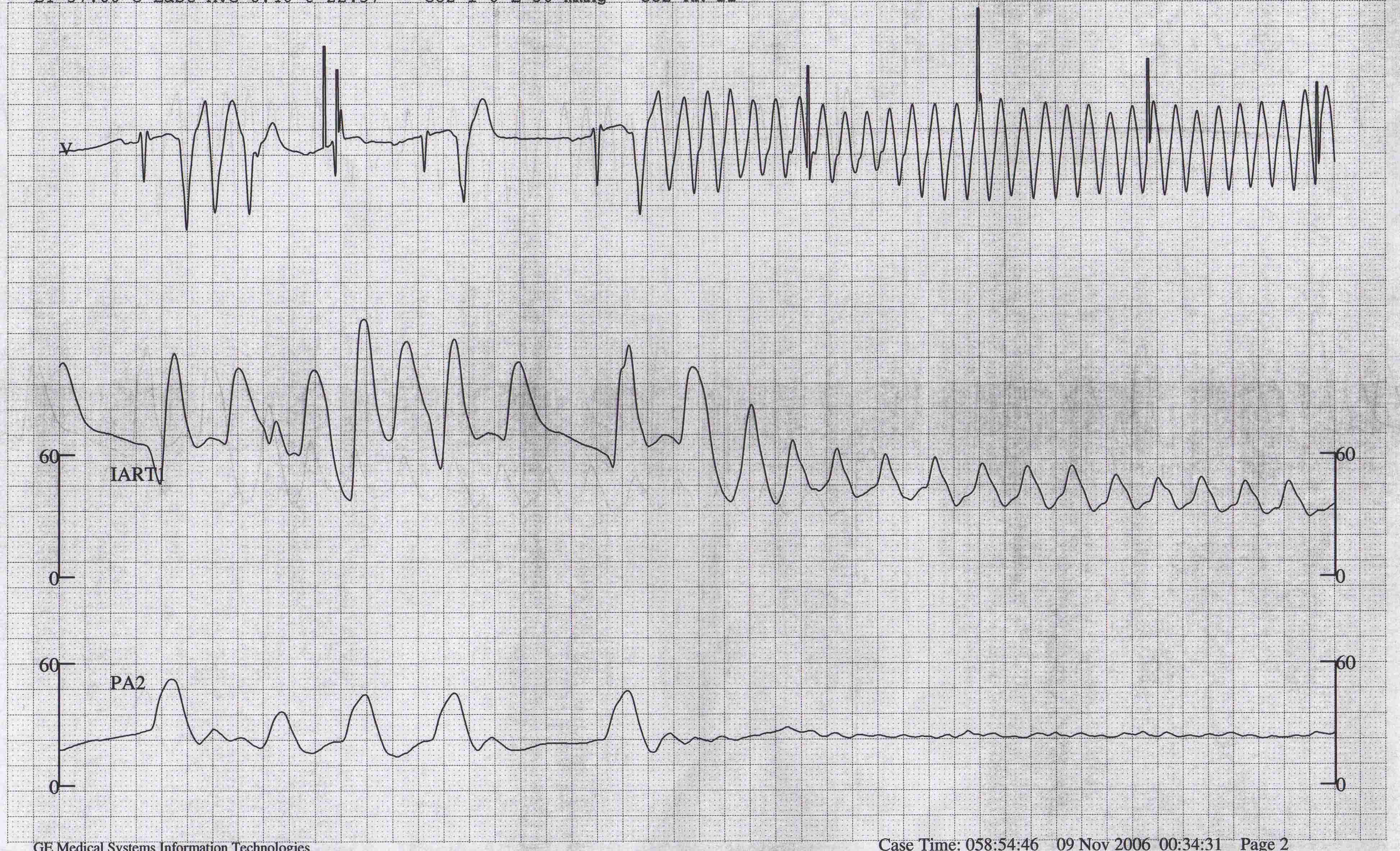
Shown below is an EKG showing a Premature Ventricular Contractions triggering ventricular flutter.
Shown below is an EKG showing a sinus rhythm with ventricular bigemini.

Shown below is an EKG showing a sinus rhythm with ventricular bigemini. Every sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole.

Shown below is an EKG image of premature ventricular contraction. The arrow indicates a ventricular extrasystole (VES).

Shown below is an EKG showing a trigeminal rhythm where wide complex beats are interpolated between normal QRS complexes. Note that the PR interval is prolonged after the wide complex beat. The wide complex beats are probably ventricular beats. As a rule interpolated wide beats are usually ventricular. In most cases the P wave after the PVC is not conducted and a compensatory pause is created instead of an interpolated beat.

Sources
Copyleft images obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Special:NewFiles&offset=&limit=500
References