Brugada syndrome: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 04:00, 31 August 2012
| Brugada syndrome | |
 | |
|---|---|
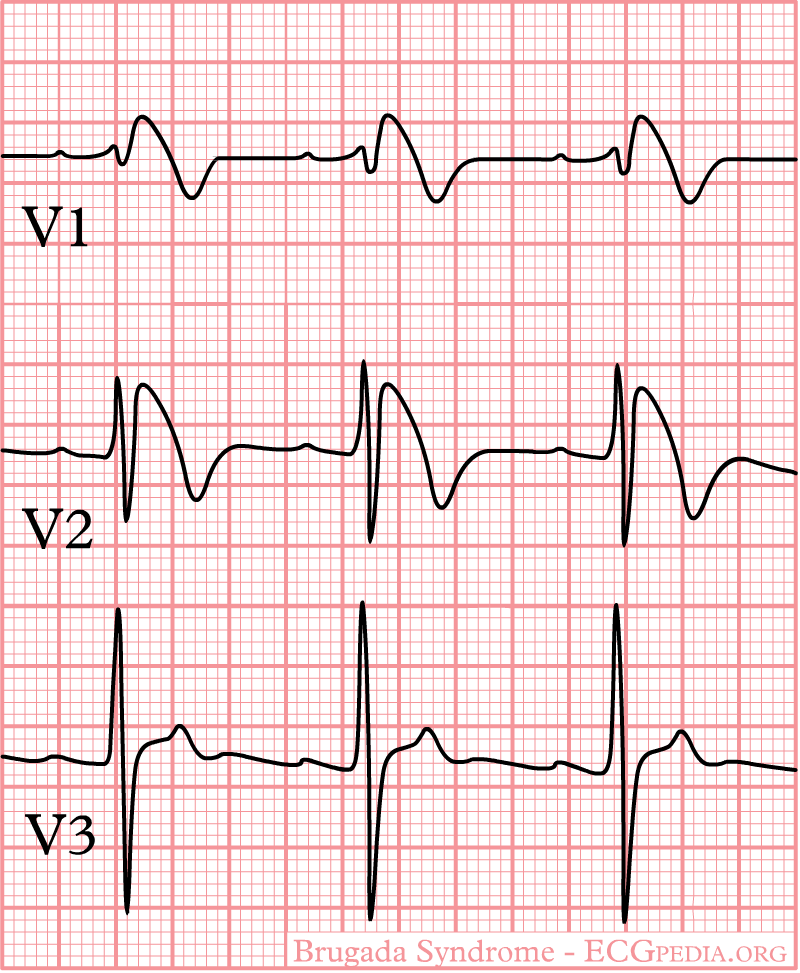
| ECG findings of Brugada Syndrome | |
| ICD-10 | I42.8 |
| ICD-9 | 746.89 |
| OMIM | 601144 |
| DiseasesDB | 31999 |
| MeSH | D053840 |
|
Brugada syndrome Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Brugada syndrome On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Brugada syndrome |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Sudden unexpected death syndrome; SUDS
Differential Diagnosis
Characteristics
- Characterized by a coved-type ST-segment elevation in the right precordial leads
- The Brugada ECG is often concealed, but can be unmasked or modulated by a number of drugs and pathophysiological states including sodium channel blockers, a febrile state, vagotonic agents, tricyclic antidepressants, as well as cocaine and Propranolol intoxication.
Diagnosis
See also
References
External links
- GeneReviews: Brugada syndrome
- Algado et al: http://www.medspain.com/ant/n13_jun00/Brugada.htm
- Behr: http://www.c-r-y.org.uk/long_qt_syndrome.htm
- The Ramon Brugada Senior Foundation
- http://digilander.libero.it/martini_syndrome/
de:Brugada-Syndrom
it:Sindrome di Brugada
he:תסמונת ברוגדה
fi:Brugadan oireyhtymä