Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis CT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis}} | {{Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{AL}} | |||
==Overview== | |||
The majority of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis will have abnormal findings in a chest [[CT]], which include micronodules, interlobular septal thickening, [[cavitation]] and consolidation. CT scan is more sensitive than an [[X-ray]] to detect [[lymphadenopathy|lymphadenopathies]]. | |||
==Computed Tomography== | |||
<div style="float:right;"> | |||
[[File:Cavitary tuberculosis - CT scan.jpg|thumb|350px|Chest CT showing a tuberculous cavity in the left lung. <br> Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.]] | |||
</div> | |||
===Pulmonary Tuberculosis=== | |||
*Chest CT abnormalities are seen in the majority of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. | |||
*CT findings include:<ref>{{Cite journal | |||
| author = [[Jeong Min Ko]], [[Hyun Jin Park]] & [[Chi Hong Kim]] | |||
| title = Pulmonary Changes of Pleural Tuberculosis: Up-to-Date CT Imaging | |||
| journal = [[Chest]] | |||
| year = 2014 | |||
| month = June | |||
| doi = 10.1378/chest.14-0196 | |||
| pmid = 25086249 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
:* Micronodules | |||
::*Most commonly located in the subpleural region and peribronchovascular interstitium. | |||
::*CT scan allows an early and accurate detection of micronodules. | |||
:* Interlobular septal thickening | |||
:* Cavitation is the most important finding in secondary tuberculosis | |||
::*Appears as a lesion with thick walls and irregular margins. | |||
::*It may be observed in almost 50% of patients. | |||
::*It is most commonly seen in the upper lung. | |||
::*Cavities in the lower lung can be found in [[diabetes]] and [[HIV]] infection.<ref name="PatelRami2011">{{cite journal|last1=Patel|first1=AnandK|last2=Rami|first2=KiranC|last3=Ghanchi|first3=FerozD|title=Radiological presentation of patients of pulmonary tuberculosis with diabetes mellitus|journal=Lung India|volume=28|issue=1|year=2011|pages=70|issn=0970-2113|doi=10.4103/0970-2113.76308}}</ref><ref name="PadyanaBhat2012">{{cite journal|last1=Padyana|first1=Mahesha|last2=Bhat|first2=RaghavendraV|last3=Dinesha|first3=M|last4=Nawaz|first4=Alam|title=HIV-Tuberculosis: A Study of Chest X-Ray Patterns in Relation to CD4 Count|journal=North American Journal of Medical Sciences|volume=4|issue=5|year=2012|pages=221|issn=1947-2714|doi=10.4103/1947-2714.95904}}</ref> | |||
::*Although it is rare, cavities may be superinfected and an air-fluid level is seen inside the cavity. | |||
::*After the active infection is treated, small cavities with thin walls may remain as a residual finding. | |||
:* Homogeneous and dense consolidation | |||
*CT is more sensitive to detect hiliar lymphadenpathy. | |||
*The "tree-in-bud" sign is a CT finding that may be seen in pulmonary tuberculosis and it is caused by mucus or pus impaction into the small airways that accentuates the branching course of peripheral airways.<ref name="Eisenhuber2002">{{cite journal|last1=Eisenhuber|first1=Edith|title=The Tree-in-Bud Sign1|journal=Radiology|volume=222|issue=3|year=2002|pages=771–772|issn=0033-8419|doi=10.1148/radiol.2223991980}}</ref> | |||
===Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis=== | |||
====Cardiac Tuberculosis==== | |||
*Pericardial thickening may be seen in a CT, specially if it is more than 3 mm.<ref name="BurrillWilliams2007">{{cite journal|last1=Burrill|first1=Joshua|last2=Williams|first2=Christopher J.|last3=Bain|first3=Gillian|last4=Conder|first4=Gabriel|last5=Hine|first5=Andrew L.|last6=Misra|first6=Rakesh R.|title=Tuberculosis: A Radiologic Review1|journal=RadioGraphics|volume=27|issue=5|year=2007|pages=1255–1273|issn=0271-5333|doi=10.1148/rg.275065176}}</ref> | |||
*Lymph node enlargment is also a common CT finding in cardiac tuberculosis.<ref name="BurrillWilliams2007">{{cite journal|last1=Burrill|first1=Joshua|last2=Williams|first2=Christopher J.|last3=Bain|first3=Gillian|last4=Conder|first4=Gabriel|last5=Hine|first5=Andrew L.|last6=Misra|first6=Rakesh R.|title=Tuberculosis: A Radiologic Review1|journal=RadioGraphics|volume=27|issue=5|year=2007|pages=1255–1273|issn=0271-5333|doi=10.1148/rg.275065176}}</ref> | |||
*Pericardial effusion is seen in less than 20% of patients.<ref name="BurrillWilliams2007">{{cite journal|last1=Burrill|first1=Joshua|last2=Williams|first2=Christopher J.|last3=Bain|first3=Gillian|last4=Conder|first4=Gabriel|last5=Hine|first5=Andrew L.|last6=Misra|first6=Rakesh R.|title=Tuberculosis: A Radiologic Review1|journal=RadioGraphics|volume=27|issue=5|year=2007|pages=1255–1273|issn=0271-5333|doi=10.1148/rg.275065176}}</ref> | |||
====Miliary Tuberculosis==== | |||
CT findings include multiple pulmonary nodules with a diameter of 1-2mm, distributed in a random pattern, [[pleural effusion]] may also be present. | |||
{| | |||
|[[Image:Miliary Tuberculosis CT.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Miliary Tuberculosis <br>Image courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, [http://www.Radiopaedia.org Radiopedia]. (original file [http://radiopaedia.org/cases/miliary-tuberculosis-ct here)] [http://radiopaedia.org/licence Creative Commons BY-SA-NC]]] | |||
|[[Image:Miliary Tuberculosis CT 2.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Miliary Tuberculosis <br> Image courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, [http://www.Radiopaedia.org Radiopedia]. (original file [http://radiopaedia.org/cases/miliary-tuberculosis-ct here)] [http://radiopaedia.org/licence Creative Commons BY-SA-NC]]] | |||
|} | |||
===Tuberculous Meningitis=== | |||
* Head CT findings in [[tuberculous meningitis]] include meningeal enhancement consistent with meningeal inflammation and [[Choroid plexus|choroidal]] calcifications.<ref name="KomolafeSunmonu2008">{{cite journal|last1=Komolafe|first1=Morenikeji A|last2=Sunmonu|first2=Taofiki A|last3=Esan|first3=Olufunmi A|title=Tuberculous meningitis presenting with unusual clinical features in Nigerians: Two case reports|journal=Cases Journal|volume=1|issue=1|year=2008|pages=180|issn=1757-1626|doi=10.1186/1757-1626-1-180}}</ref> | |||
* Areas of infarction and hemorrhage may also be seen in cases of miliar tuberculosis. | |||
* Patients with late complications may show hydrocephalus. | |||
[[Image:Tuberculous meningitis.jpg|thumb|none|350px|Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.]] | |||
====Abdominal Tuberculosis==== | |||
* CT findings in a pancreatic and spleen infection with tuberculosis may mimic a [[pancreatic cancer]].<ref name="RongLou2008">{{cite journal|last1=Rong|first1=YF|last2=Lou|first2=WH|last3=Jin|first3=DY|title=Pancreatic tuberculosis with splenic tuberculosis mimicking advanced [[pancreatic cancer]] with [[splenic]] metastasizes: a case report|journal=Cases Journal|volume=1|issue=1|year=2008|pages=84|issn=1757-1626|doi=10.1186/1757-1626-1-84}}</ref> | |||
* Shown below there is CT scan of the [[pancreas]] demonstrating a mass in the pancreatic tail and metastasizes in the [[spleen]]. | |||
{| | |||
|[[Image:Pancreas_and_spleen-tuberculosis.jpg|thumb|none|350px|Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.]] | |||
|[[Image:Pancreas_and_spleen-tuberculosis2.jpg |thumb|none|350px|Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.]] | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | |||
[[Category:Pulmonology]] | |||
[[Category:Needs overview]] | |||
[[Category:Needs content]] | |||
[[Category:Primary care]] | |||
[[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | |||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 26 September 2014
|
Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis CT |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alejandro Lemor, M.D. [2]
Overview
The majority of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis will have abnormal findings in a chest CT, which include micronodules, interlobular septal thickening, cavitation and consolidation. CT scan is more sensitive than an X-ray to detect lymphadenopathies.
Computed Tomography
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Chest CT abnormalities are seen in the majority of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis.
- CT findings include:[1]
- Micronodules
- Most commonly located in the subpleural region and peribronchovascular interstitium.
- CT scan allows an early and accurate detection of micronodules.
- Interlobular septal thickening
- Cavitation is the most important finding in secondary tuberculosis
- Appears as a lesion with thick walls and irregular margins.
- It may be observed in almost 50% of patients.
- It is most commonly seen in the upper lung.
- Cavities in the lower lung can be found in diabetes and HIV infection.[2][3]
- Although it is rare, cavities may be superinfected and an air-fluid level is seen inside the cavity.
- After the active infection is treated, small cavities with thin walls may remain as a residual finding.
- Homogeneous and dense consolidation
- CT is more sensitive to detect hiliar lymphadenpathy.
- The "tree-in-bud" sign is a CT finding that may be seen in pulmonary tuberculosis and it is caused by mucus or pus impaction into the small airways that accentuates the branching course of peripheral airways.[4]
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
Cardiac Tuberculosis
- Pericardial thickening may be seen in a CT, specially if it is more than 3 mm.[5]
- Lymph node enlargment is also a common CT finding in cardiac tuberculosis.[5]
- Pericardial effusion is seen in less than 20% of patients.[5]
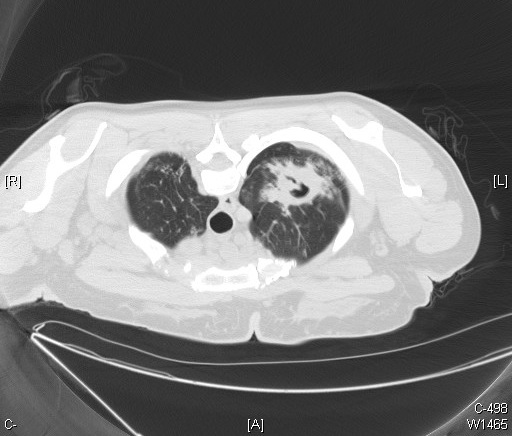
Miliary Tuberculosis
CT findings include multiple pulmonary nodules with a diameter of 1-2mm, distributed in a random pattern, pleural effusion may also be present.
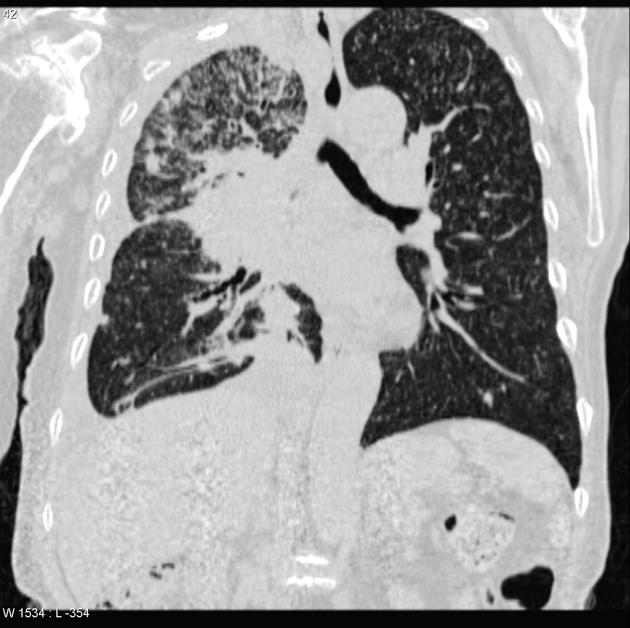 Image courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, Radiopedia. (original file here) Creative Commons BY-SA-NC |
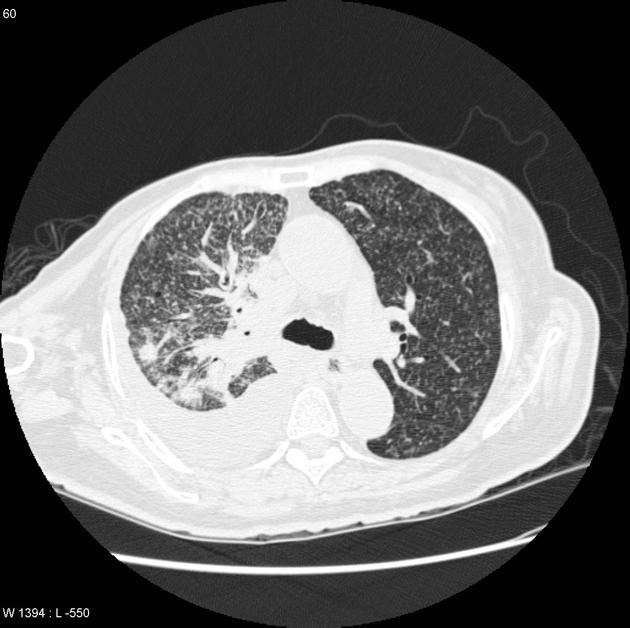 Image courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, Radiopedia. (original file here) Creative Commons BY-SA-NC |
Tuberculous Meningitis
- Head CT findings in tuberculous meningitis include meningeal enhancement consistent with meningeal inflammation and choroidal calcifications.[6]
- Areas of infarction and hemorrhage may also be seen in cases of miliar tuberculosis.
- Patients with late complications may show hydrocephalus.
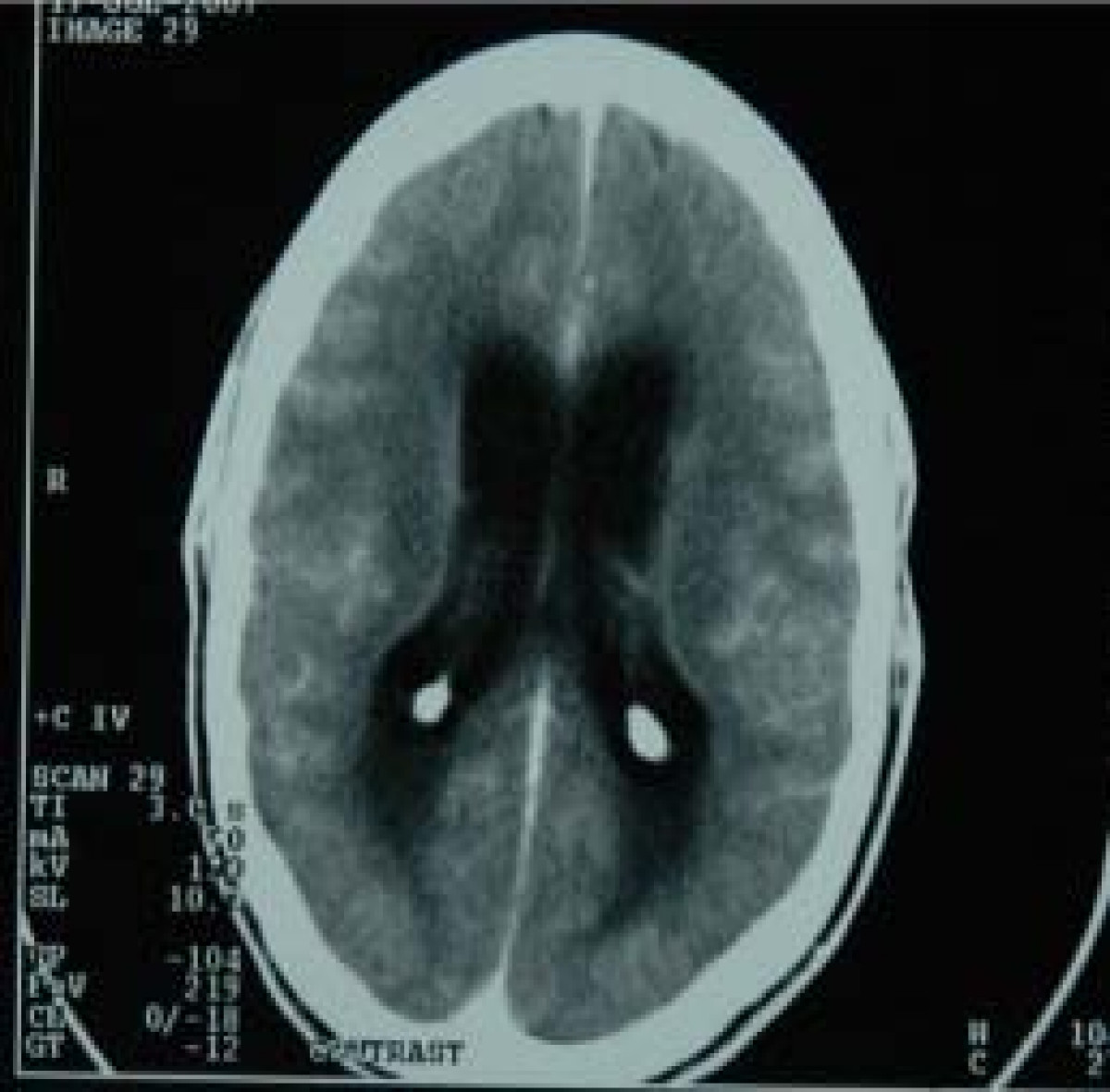
Abdominal Tuberculosis
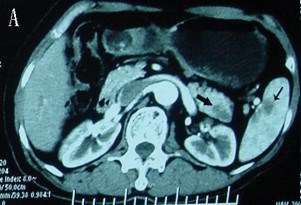
- CT findings in a pancreatic and spleen infection with tuberculosis may mimic a pancreatic cancer.[7]
- Shown below there is CT scan of the pancreas demonstrating a mass in the pancreatic tail and metastasizes in the spleen.
 |
 |
References
- ↑ Jeong Min Ko, Hyun Jin Park & Chi Hong Kim (2014). "Pulmonary Changes of Pleural Tuberculosis: Up-to-Date CT Imaging". Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.14-0196. PMID 25086249. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Patel, AnandK; Rami, KiranC; Ghanchi, FerozD (2011). "Radiological presentation of patients of pulmonary tuberculosis with diabetes mellitus". Lung India. 28 (1): 70. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.76308. ISSN 0970-2113.
- ↑ Padyana, Mahesha; Bhat, RaghavendraV; Dinesha, M; Nawaz, Alam (2012). "HIV-Tuberculosis: A Study of Chest X-Ray Patterns in Relation to CD4 Count". North American Journal of Medical Sciences. 4 (5): 221. doi:10.4103/1947-2714.95904. ISSN 1947-2714.
- ↑ Eisenhuber, Edith (2002). "The Tree-in-Bud Sign1". Radiology. 222 (3): 771–772. doi:10.1148/radiol.2223991980. ISSN 0033-8419.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Burrill, Joshua; Williams, Christopher J.; Bain, Gillian; Conder, Gabriel; Hine, Andrew L.; Misra, Rakesh R. (2007). "Tuberculosis: A Radiologic Review1". RadioGraphics. 27 (5): 1255–1273. doi:10.1148/rg.275065176. ISSN 0271-5333.
- ↑ Komolafe, Morenikeji A; Sunmonu, Taofiki A; Esan, Olufunmi A (2008). "Tuberculous meningitis presenting with unusual clinical features in Nigerians: Two case reports". Cases Journal. 1 (1): 180. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-180. ISSN 1757-1626.
- ↑ Rong, YF; Lou, WH; Jin, DY (2008). "Pancreatic tuberculosis with splenic tuberculosis mimicking advanced pancreatic cancer with splenic metastasizes: a case report". Cases Journal. 1 (1): 84. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-84. ISSN 1757-1626.