Hepatitis B MRI: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Hepatitis B}} | {{Hepatitis B}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{ | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{JS}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
The [[MRI]] may be used to diagnose/monitor [[biliary]] obstruction, [[cirrhosis]], and [[hepatocellular carcinoma]] in hepatitis B patients. [[MRI]] findings in these patients may include [[nodular]] appearance and signs of [[portal hypertension]], such as [[ascites]] and [[splenomegaly]].<ref name="pmid18333158">{{cite journal| author=Bialecki ES, Di Bisceglie AM| title=Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. | journal=HPB (Oxford) | year= 2005 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= 26-34 | pmid=18333158 | doi=10.1080/13651820410024049 | pmc=PMC2023919 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18333158 }} </ref> | |||
==MRI== | ==MRI== | ||
In patients with hepatitis B, an [[MRI]] may be performed to: | |||
*Exclude biliary obstruction | *Exclude [[biliary]] obstruction | ||
* | *Diagnose/monitor [[hepatic cirrhosis]] and [[hepatocellular carcinoma]]<ref name="pmid18333158">{{cite journal| author=Bialecki ES, Di Bisceglie AM| title=Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. | journal=HPB (Oxford) | year= 2005 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= 26-34 | pmid=18333158 | doi=10.1080/13651820410024049 | pmc=PMC2023919 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18333158 }} </ref> | ||
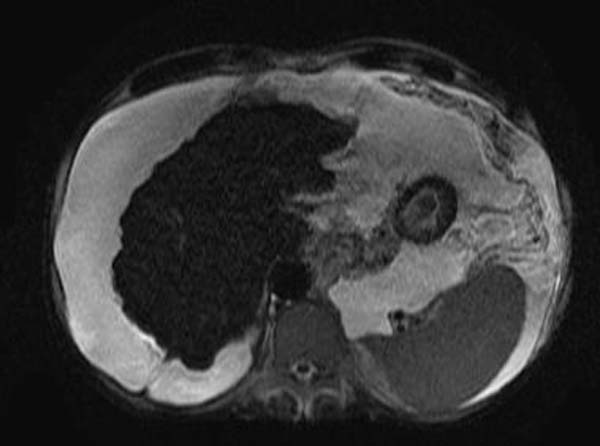
The MRI findings may include nodular appearance | The [[MRI]] findings in patients with [[hepatic cirrhosis]] may include a shrunken [[liver]] with a [[nodular]] appearance and signs of [[portal hypertension]], such as [[splenomegaly]] and [[ascites]]. | ||
[[File:Cirrhosis-001.jpg|thumb| | [[File:Cirrhosis-001.jpg|thumb|250px|center|Shrunken and nodular liver that is consistent with cirrhosis-T2 weighted image - Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11317]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:FinalQCRequired]] | |||
[[Category:Emergency mdicine]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | |||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:05, 29 July 2020
|
Hepatitis B |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hepatitis B MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatitis B MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: João André Alves Silva, M.D. [2]
Overview
The MRI may be used to diagnose/monitor biliary obstruction, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B patients. MRI findings in these patients may include nodular appearance and signs of portal hypertension, such as ascites and splenomegaly.[1]
MRI
In patients with hepatitis B, an MRI may be performed to:
- Exclude biliary obstruction
- Diagnose/monitor hepatic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[1]
The MRI findings in patients with hepatic cirrhosis may include a shrunken liver with a nodular appearance and signs of portal hypertension, such as splenomegaly and ascites.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bialecki ES, Di Bisceglie AM (2005). "Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma". HPB (Oxford). 7 (1): 26–34. doi:10.1080/13651820410024049. PMC 2023919. PMID 18333158.