WBR0155
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by William J Gibson)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 41-year-old man with Down syndrome is brought to the family's physician for cognitive decline. The family reports that the patient’s memory has been deteriorating for the past year. He cannot recall the names of his brothers and sisters and often has difficulty finding words. He is unable to find his way back home and gets lost when a member of his family does not assist him. Which of the following neuropathologic changes is most likely present in this patient?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Neurofibrillary tangles |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Neurofibrillary tangles are abnormal aggregates of proteins within neurons of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Patient’s with Down syndrome have a high risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease at an early age due to increased gene dosage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) on chromosome 21.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Pick bodies |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Pick bodies are silver-staining, spherical aggregations of tau protein in neurons that are associated with Pick's disease, a subtype of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. While Pick’s disease is characterized by memory loss, it is distinguished from Alzheimer's disease by severe mood and personality changes.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Negri bodies |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Negri bodies are eosinophilic, sharply-outlined inclusion bodies in neurons of patients with rabies virus. Rabies virus is usually transmitted by an animal bite; it causes acute encephalitis and death among patients who develop symptoms.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Lewy bodies |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Lewy bodies are abnormal aggregates of alpha-synuclein protein that develop in neurons. The most common disease associated with the presence of Lewy bodies is Parkinson's disease. Lewy bodies are also present in neurons of patients with Lewy body dementia, a subtype of dementia characterized by symptoms of dementia followed by early parkinsonism (early disability and falls within 1 year of symptoms, in contrast to late disability in parkinson's disease), hallucinations (visual mostly, in contrast to schizophrenia-associated auditory hallucinations), and neuroleptic sensitivity.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Spongioform changes |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Spongioform change in the gray matter is the pathological hallmark of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. It is characterized by a "spongy appearance" of the cerebral cortex due to the presence of many round vacuoles.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
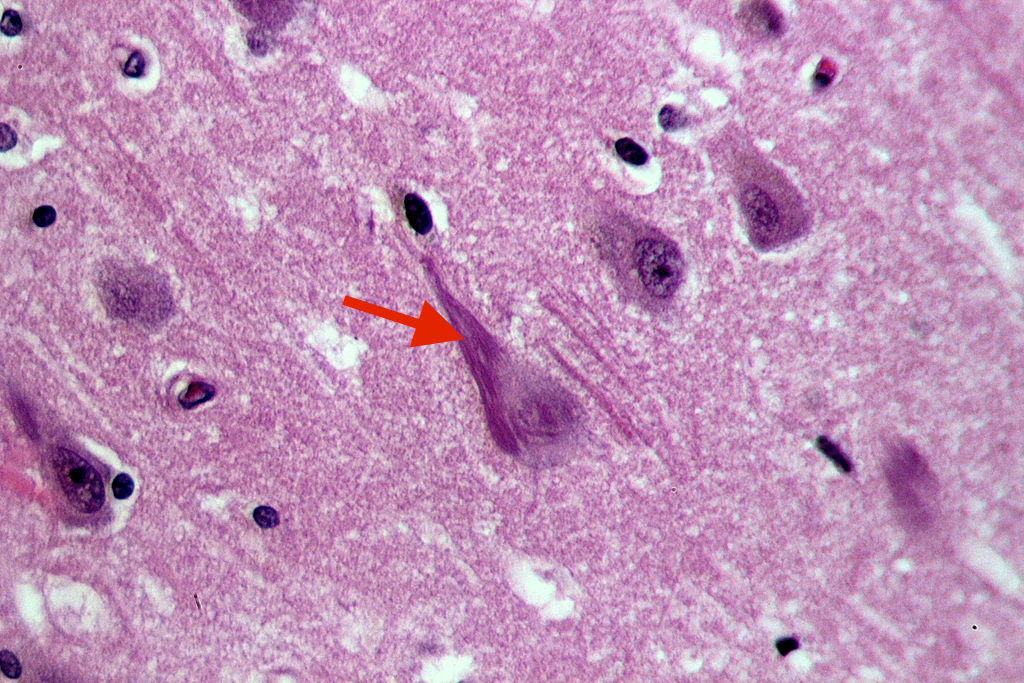
| Explanation | [[Explanation::This patient is most likely diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. Although Alzheimer's disease is most commonly diagnosed in the elderly, patients with Down syndrome are at high risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease at an early age. The presence of an extra chromosome 21 is thought to result in a significant increase in the synthesis of amyloid precursor proteins (APP) that are encoded by chromosome 21. Subsequently, the increase in the amyloidogenic parts leads to early-onset senile plaque formation and Alzheimer's disease. The disease is characterized by the presence of diffuse cortical atrophy with a decrease in acetylcholine (Ach) neutrotransmitter concentration in the brain. Neurofibrillary tangles (shown below) are abnormal proteins present in neurons of patients with Alzheimer's disease. These tangles are formed by hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein, a microtubule-associated protein that causes the tangles to aggregate in an insoluble form. In addition to alterations in APP protein, other proteins are also associated with either early-onset Alzheimer's disease (such as presinilin-1 protein [chromosome 14] and presenilin-2 protein [chromosome 1]) or late-onset Alzheimer's disease (such as ApoE4 [chromosome 19]). On the other hand, ApoE2 protein [chromosome 19] is considered protective against Alzheimer's disease.
|
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Down syndrome, WBRKeyword::Mental retardation, WBRKeyword::Retardation, WBRKeyword::Intellectual disability, WBRKeyword::Neurodegeneration, WBRKeyword::Alzheimer's disease, WBRKeyword::Alzheimer, WBRKeyword::Dementia, WBRKeyword::Alzheimer disease, WBRKeyword::Cognitive, WBRKeyword::Cognitive decline, WBRKeyword::Tau protein, WBRKeyword::Tau, WBRKeyword::APP, WBRKeyword::Amyloid, WBRKeyword::Amyloidosis, WBRKeyword::Amyloid precursor protein, WBRKeyword::Neuropathology, WBRKeyword::Brain, WBRKeyword::Neurofibrillary tangles, WBRKeyword::Chromosome, WBRKeyword::Memory, WBRKeyword::Memory loss |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |