Vertebral column

|
WikiDoc Resources for Vertebral column |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Vertebral column Most cited articles on Vertebral column |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Vertebral column |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Vertebral column at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Vertebral column Clinical Trials on Vertebral column at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Vertebral column NICE Guidance on Vertebral column
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Vertebral column Discussion groups on Vertebral column Patient Handouts on Vertebral column Directions to Hospitals Treating Vertebral column Risk calculators and risk factors for Vertebral column
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Vertebral column |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
In human anatomy, the vertebral column (backbone or spine) is a column of 33 vertebrae, the sacrum, intervertebral discs, and the coccyx situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by spinal discs. It houses the spinal cord in its spinal canal.
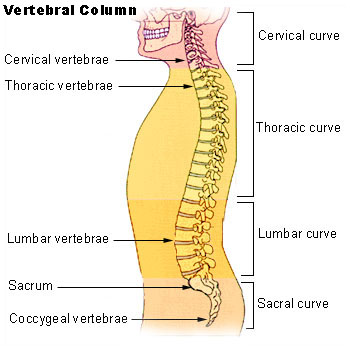
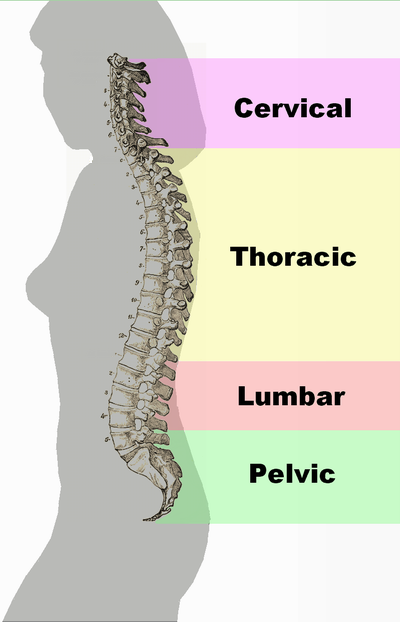
Curves
Viewed laterally the vertebral column presents several curves, which correspond to the different regions of the column, and are called cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and pelvic.
The cervical curve, convex forward, begins at the apex of the odontoid (tooth-like) process, and ends at the middle of the second thoracic vertebra; it is the least marked of all the curves.
The thoracic curve, concave forward, begins at the middle of the second and ends at the middle of the twelfth thoracic vertebra. Its most prominent point behind corresponds to the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra. This curve is known as a tt curve.
The lumbar curve is more marked in the female than in the male; it begins at the middle of the last thoracic vertebra, and ends at the sacrovertebral angle. It is convex anteriorly, the convexity of the lower three vertebrae being much greater than that of the upper two. This curve is described as a lordotic curve.
The pelvic curve begins at the sacrovertebral articulation, and ends at the point of the coccyx; its concavity is directed downward and forward.
The thoracic and pelvic curves are termed primary curves, because they alone are present during fetal life. In the early embryo, the vertebral column is C-shaped, and the cervical and lumbar curvatures are not yet present in a newborn infant. The cervical and lumbar curves are compensatory or secondary, and are developed after birth, the former when the child is able to hold up its head (at three or four months) and to sit upright (at nine months), the latter at twelve or eighteen months, when the child begins to walk.
The thoracic portion of the vertebral column also has a slight lateral curvature, the convexity of which is directed toward the right side. This may be produced by muscular action, most persons using the right arm in preference to the left, especially in making long-continued efforts, when the body is curved to the right side. In support of this explanation it has been found that in one or two individuals who were left-handed, the convexity was to the left side. This curvature is regarded by others as being produced by the aortic arch and upper part of the descending thoracic aorta – a view which is supported by the fact that in cases of situs inversus where the viscera are transposed and the aorta is on the right side, the convexity of the curve is directed to the left side.
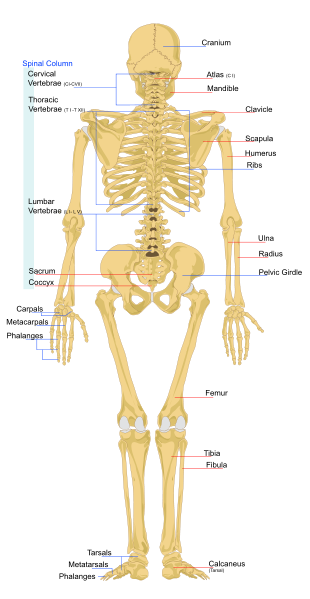
Names of individual vertebrae
Individual vertebrae named according to region and position, from superior to inferior
- Cervical – 7 vertebrae (C1-C7)
- C1 is known as "atlas" and supports the head, C2 is known as "axis"
- Possesses bifid spinous processes, which is absent in C7
- Small-bodied
- Thoracic – 12 vertebrae (T1-T12)
- Distinguished by the presence of costal facets for the articulation of the heads of ribs
- Body is intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae
- Lumbar – 5 vertebrae (L1-L5)
- Has a large body
- Does not have costal facets nor transverse process foramina
- Sacral – 5 (fused) vertebrae (S1-S5)
- Coccygeal – 4 (fused) vertebrae (Co1-Co4)
Surfaces
Anterior surface
When viewed from in front, the width of the bodies of the vertebrae is seen to increase from the second cervical to the first thoracic; there is then a slight diminution in the next three vertebrae; below this there is again a gradual and progressive increase in width as low as the sacrovertebral angle. From this point there is a rapid diminution, to the apex of the coccyx.
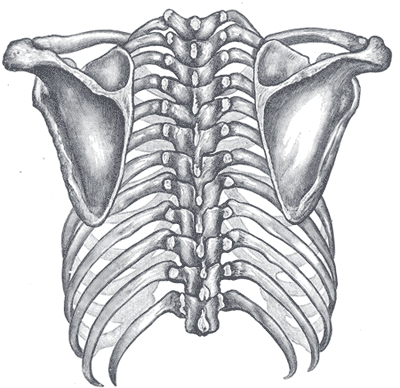
Posterior surface
The posterior surface of the vertebral column presents in the median line the spinous processes. In the cervical region (with the exception of the second and seventh vertebrae) these are short and horizontal, with bifid extremities. In the upper part of the thoracic region they are directed obliquely downward; in the middle they are almost vertical, and in the lower part they are nearly horizontal. In the lumbar region they are nearly horizontal. The spinous processes are separated by considerable intervals in the lumbar region, by narrower intervals in the neck, and are closely approximated in the middle of the thoracic region. Occasionally one of these processes deviates a little from the median line — a fact to be remembered in practice, as irregularities of this sort are attendant also on fractures or displacements of the vertebral column. On either side of the spinous processes is the vertebral groove formed by the laminae in the cervical and lumbar regions, where it is shallow, and by the laminae and transverse processes in the thoracic region, where it is deep and broad; these grooves lodge the deep muscles of the back. Lateral to the vertebral grooves are the articular processes, and still more laterally the transverse processes. In the thoracic region, the transverse processes stand backward, on a plane considerably behind that of the same processes in the cervical and lumbar regions. In the cervical region, the transverse processes are placed in front of the articular processes, lateral to the pedicles and between the intervertebral foramina. In the thoracic region they are posterior to the pedicles, intervertebral foramina, and articular processes. In the lumbar region they are in front of the articular processes, but behind the intervertebral foramina.
Lateral surfaces
The lateral surfaces are separated from the posterior surface by the articular processes in the cervical and lumbar regions, and by the transverse processes in the thoracic region. They present, in front, the sides of the bodies of the vertebrae, marked in the thoracic region by the facets for articulation with the heads of the ribs. More posteriorly are the intervertebral foramina, formed by the juxtaposition of the vertebral notches, oval in shape, smallest in the cervical and upper part of the thoracic regions, and gradually increasing in size to the last lumbar. They transmit the spinal nerves and are situated between the transverse processes in the cervical region, and in front of them in the thoracic and lumbar regions.

T3 is at level of medial part of spine of scapula. T7 is at inferior angle of the scapula. L4 is at highest point of iliac crest. S2 is at the level of posterior superior iliac spine. T12 can be found by identifying the lowest pair of ribs and tracing them to their thoracic attachment.[1] Furthermore, C7 is easily localized as a prominence at the lower part of the neck. [2]
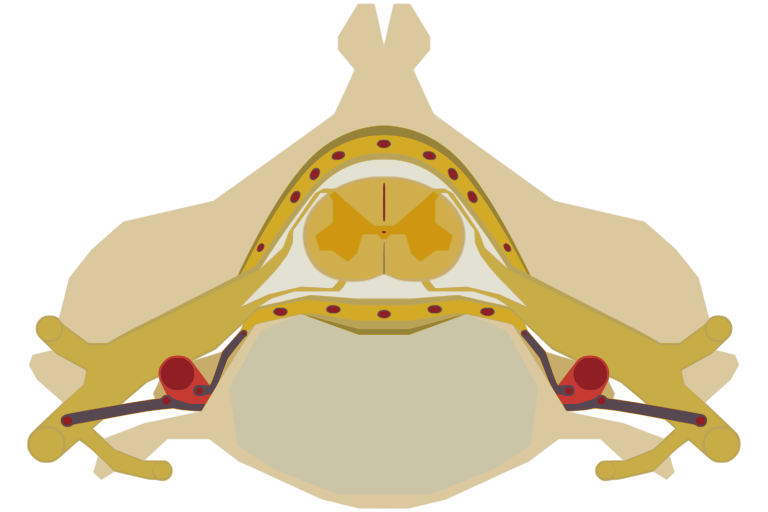
Vertebral canal
The vertebral canal follows the different curves of the column; it is large and triangular in those parts of the column which enjoy the greatest freedom of movement, such as the cervical and lumbar regions; and is small and rounded in the thoracic region, where motion is more limited.
Abnormalities
Occasionally the coalescence of the laminae is not completed, and consequently a cleft is left in the arches of the vertebrae, through which a protrusion of the spinal membranes (dura mater and arachnoid), and generally of the spinal cord (medulla spinalis) itself, takes place, constituting the malformation known as spina bifida. This condition is most common in the lumbosacral region, but it may occur in the thoracic or cervical region, or the arches throughout the whole length of the canal may remain incomplete.
The following abnormal curvatures may occur in some people:
- Kyphosis is an exaggerated kyphotic (posterior) curvature in the thoracic region. This produces the so-called "humpback" or "dowager's hump", a condition commonly observed in osteoporosis.
- Lordosis is an exaggerated lordotic (anterior) curvature of the lumbar region, "swayback". Temporary lordosis is common among pregnant women.
- Scoliosis, lateral curvature, is the most common abnormal curvature, occurring in 0.5% of the population. It is more common among females and may result from unequal growth of the two sides of one or more vertebrae. It can also be caused by pulmonary atelectasis (partial or complete deflation of one or more lobes of the lungs) as observed in asthma or pneumothorax.
Additional images
-
Vertebral column.
-
The spinal cord nested in the vertebral column.
-
Human skeleton back
-
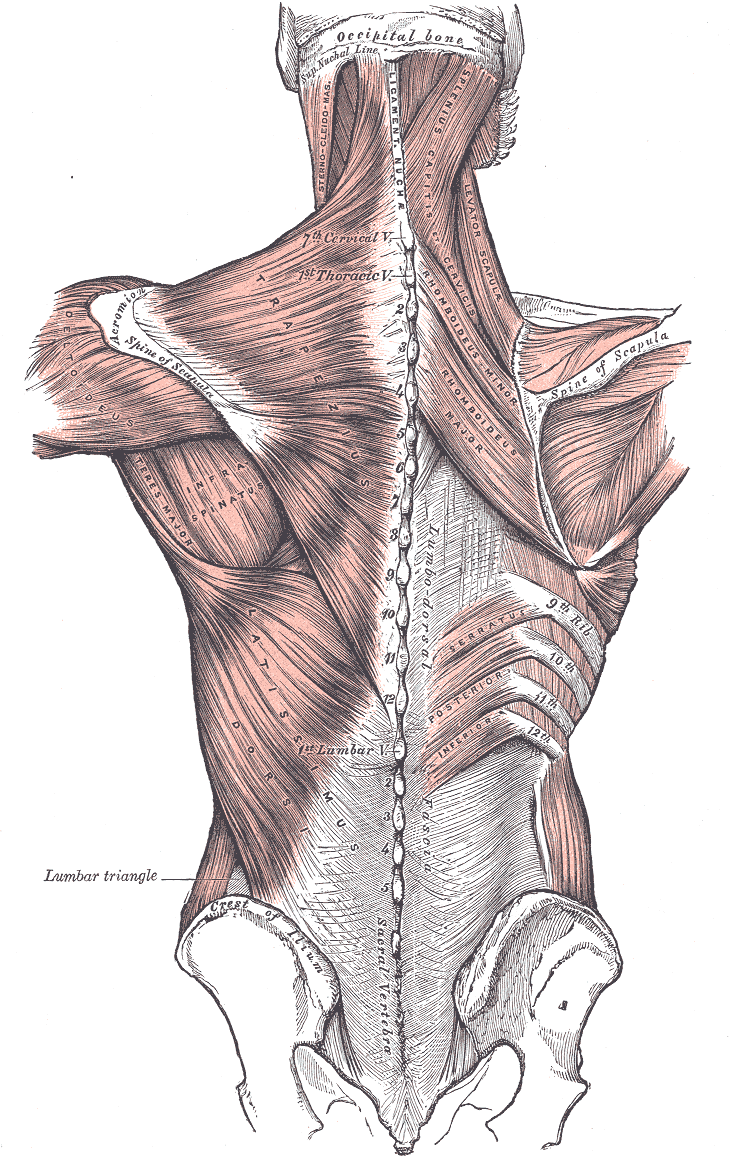
Relation of the vertebral column to the surrounding muscles.
References
See also
External links
- North American Spine Society is a multidisciplinary medical organization that advances quality spine care through education, research and advocacy.
- Spinal Cord Injuries Australia (formerly Australian Quadriplegic Association AQA, established 1967) provides information about the disability and services for affected people, advocacy, accommodation, employment, peer support.
- Spinal Cord Injury Peer SupportPeer support for those living with spinal injuries.
- Vertebral column basics
- Spinal Term Glossary
Template:Vertebral column and spinal cord Template:Human anatomical features
ar:عمود فقري
ay:Jikhani k'ili
br:Gwalenn ar c'hein
bg:Гръбначен стълб
ca:Columna vertebral
cs:Páteř
cy:Asgwrn cefn
da:Rygsøjlen
de:Wirbelsäule
eo:Vertebraro
fa:ستون مهرهها
ko:등뼈
is:Hryggsúla
it:Colonna vertebrale
he:עמוד השדרה
ku:Masiya piştê
la:Columna vertebralis
lv:Mugurkauls
lt:Stuburas
ln:Mokesa
nl:Wervelkolom
no:Ryggsøyle
nn:Ryggsøyle
scn:Cutruzzu
simple:Vertebral column
sk:Chrbtica
sl:Hrbtenica
su:Tulang tonggong
fi:Selkäranka
sv:Ryggrad
tl:Gulugod
te:వెన్నెముక
th:กระดูกสันหลัง
uk:Хребет
fiu-vro:Sälgruuts
yi:רוקן ביין