Trophoblast
|
WikiDoc Resources for Trophoblast |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Trophoblast Most cited articles on Trophoblast |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Trophoblast |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Trophoblast at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Trophoblast at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Trophoblast
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Trophoblast Discussion groups on Trophoblast Patient Handouts on Trophoblast Directions to Hospitals Treating Trophoblast Risk calculators and risk factors for Trophoblast
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Trophoblast |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Trophoblasts (from Greek threphein: to feed) are cells forming the outer layer of a blastocyst, which provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They are formed during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg.
Function
Trophoblasts are invasive, eroding, and metastasizing cells of the placenta.
Trophoblasts mediate the implantation of the embryo into the endometrium, but they are never incorporated into the mother's body or the fetus. They are not "fetal" cells.
Trophoblasts become inert during pregnancy and are completely rejected by the fetus and mother at delivery. They can be seen as the thin membrane covering the fetus at birth, the caul.[1]
Differentiation
The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into 2 cell layers:
| Layer | Location | Description |
| cytotrophoblast | inner layer | Single celled layer adjacent to trophoblast. |
| syncytiotrophoblast | outer layer | Thick layer that lacks cell boundaries and grows into the endometrial stroma. It secretes hCG in order to maintain progesterone secretion and sustain a pregnancy. |
Pathology
The invasion of a specific type of trophoblast (extravillous trophoblast) into the maternal uterus is a vital stage in the establishment of pregnancy:
- Failure of the trophoblast to invade sufficiently may be important in the development of some cases of pre-eclampsia.
- Too firm an attachment may lead to placenta accreta.
Additional images
-
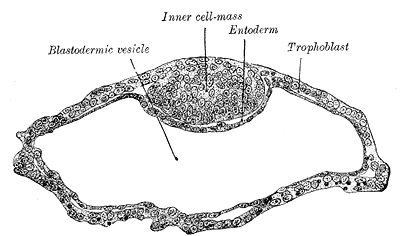
Blastodermic vesicle of Vespertilio murinus.
-
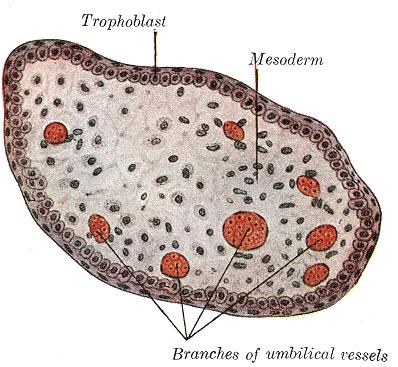
Section through embryonic disk of Vespertilio murinus.
-
Transverse section of a chorionic villus.
-
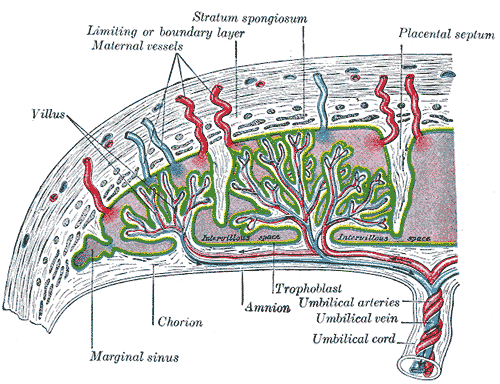
Scheme of placental circulation.
See also
References
External links