Tinidazole adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Zaghw, M.D. [2]
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
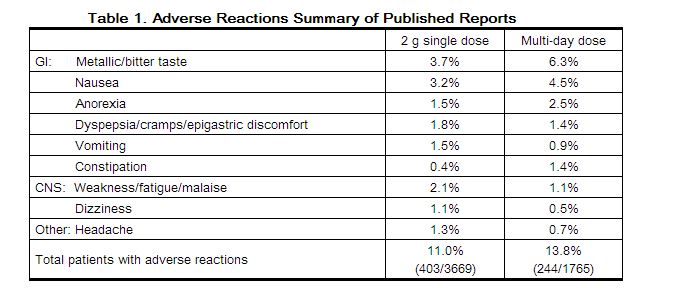
Among 3669 patients treated with a single 2 g dose of tinidazole, in both controlled and uncontrolled trichomoniasis and giardiasis clinical studies, adverse reactions were reported by 11.0% of patients. For multi-day dosing in controlled and uncontrolled amebiasis studies, adverse reactions were reported by 13.8% of 1765 patients. Common (≥ 1% incidence) adverse reactions reported by body system are as follows. (Note: Data described in Table 1 below are pooled from studies with variable designs and safety evaluations.)
Other adverse reactions reported with tinidazole include:
- Central Nervous System: Two serious adverse reactions reported include convulsions and transient peripheral neuropathy including numbness and paresthesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Other CNS reports include vertigo, ataxia, giddiness, insomnia, drowsiness.
- Gastrointestinal: tongue discoloration, stomatitis, diarrhea
- 'Hypersensitivity: urticaria, pruritis, rash, flushing, sweating, dryness of mouth, fever, burning sensation, thirst, salivation, angioedema
- Renal: darkened urine
- Cardiovascular: palpitations
- Hematopoietic: transient neutropenia, transient leukopenia
- Other: Candida overgrowth, increased vaginal discharge, oral candidiasis, hepatic abnormalities including raised transaminase level, arthralgias, myalgias, and arthritis.
 |
Rare reported adverse reactions include bronchospasm, dyspnea, coma, confusion, depression, furry tongue, pharyngitis and reversible thrombocytopenia.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients: In pooled pediatric studies, adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients taking tinidazole were similar in nature and frequency to adult findings including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, taste change, anorexia, and abdominal pain.
Bacterial vaginosis: The most common adverse reactions in treated patients (incidence >2%), which were not identified in the trichomoniasis, giardiasis and amebiasis studies, are gastrointestinal: decreased appetite, and flatulence; renal: urinary tract infection, painful urination, and urine abnormality; and other reactions including pelvic pain, vulvo-vaginal discomfort, vaginal odor, menorrhagia, and upper respiratory tract infection [See Clinical Studies (14.5)].
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified and reported during post-approval use of Tindamax. Because the reports of these reactions are voluntary and the population is of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency of the reaction or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions have been reported on initial or subsequent exposure to tinidazole. Hypersensitivity reactions may include urticaria, pruritis, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme.[1]
References
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.