Sparsentan
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kosar Doraghi[2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
*Hepatotoxicity
For all patients, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the FILSPARI REMS because of the risk of hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity
|
Overview
Sparsentan is an endothelin and angiotensin II receptor antagonist that is FDA approved for the treatment of proteinuria(reduce) in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) at risk of rapid disease progression, generally a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5 g/g. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include Hepatotoxicity, Embryo-Fetal Toxicity, Hypotension, Acute Kidney Injury, Hyperkalemia, Fluid Retention.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Prior to initiating treatment with FILSPARI, discontinue use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs), and aliskiren.
- Initiate treatment with FILSPARI at 200 mg orally once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily, as tolerated. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI after an interruption, consider titration of FILSPARI, starting at 200 mg once daily. After 14 days, increase to the recommended dose of 400 mg once daily
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
The safety and efficacy of FILSPARI in pediatric patients have not been established
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Do not coadminister FILSPARI with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), ERAs, or aliskiren
Warnings
|
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
*Hepatotoxicity
For all patients, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the FILSPARI REMS because of the risk of hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity
|
- Hepatotoxicity
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- FILSPARI REMS
For all patients, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the FILSPARI REMS because of the risk of hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity Hypotension, Acute Kidney Injury, Hyperkalemia, Fluid Retention
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Hepatotoxicity
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Hypotension
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Hyperkalemia
- Fluid Retention
Postmarketing Experience
The safety of FILSPARI was assessed in a clinical trial called PROTECT (NCT03762850), involving adults with IgAN. Data from 202 patients with a median duration of 73 weeks (up to 110 weeks) of FILSPARI exposure were analyzed. Adverse reactions observed in the trial are outlined.
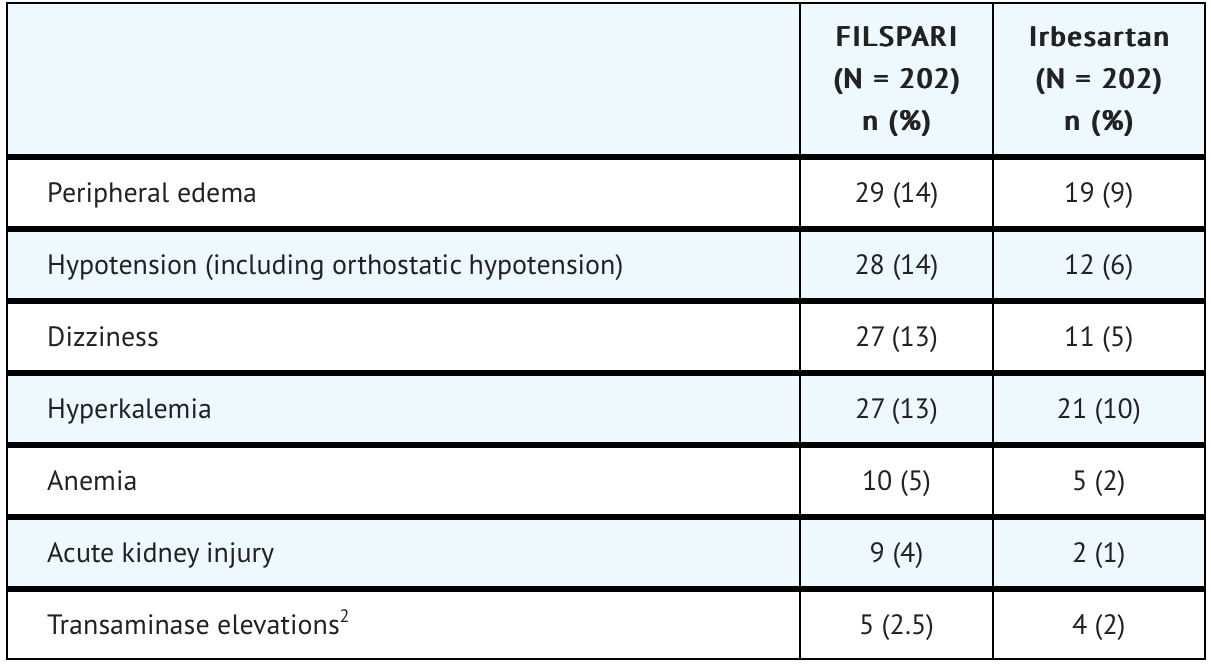 Initiation of FILSPARI may cause an initial small decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that occurs within the first 4 weeks of starting therapy and then stabilizes.
The incidence of a hemoglobin decrease >2 g/dL compared to baseline and below the lower limit of normal was greater for the FILSPARI arm (11%) compared to the irbesartan arm (5%). This decrease is thought to be in part due to hemodilution. There were no treatment discontinuations due to anemia or hemoglobin decrease in the PROTECT study.
Initiation of FILSPARI may cause an initial small decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that occurs within the first 4 weeks of starting therapy and then stabilizes.
The incidence of a hemoglobin decrease >2 g/dL compared to baseline and below the lower limit of normal was greater for the FILSPARI arm (11%) compared to the irbesartan arm (5%). This decrease is thought to be in part due to hemodilution. There were no treatment discontinuations due to anemia or hemoglobin decrease in the PROTECT study.
Drug Interactions
- Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Inhibitors and ERAs
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
- Strong CYP3A Inducers
- Antacids and Acid Reducing Agents
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs), Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors
- CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 Substrates
- P-gp and BCRP Substrates
- Agents Increasing Serum Potassium
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
FILSPARI can cause fetal harm, including birth defects and fetal death, when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Sparsentan in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Sparsentan during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use of FILSPARI in patients with any hepatic impairment
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sparsentan in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Sparsentan in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Instruct patient to swallow tablets whole with water prior to the morning or evening meal. Maintain the same dosing pattern in relationship to meals. If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. Do not take double or extra doses. Dosage Modification for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with FILSPARI. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt treatment with FILSPARI
Monitoring
Treatment and monitoring recommendations
- 3x and ≤8x ULN
- Confirm elevation with a repeat measure.
- If confirmed, interrupt treatment, and monitor aminotransferase levels and bilirubin at least weekly, and INR as needed, until the levels return to pretreatment values and the patient is asymptomatic.
- Do not resume treatment if any of the following occurs without other cause found:
- ALT or AST >3x ULN and total bilirubin >2x ULN or INR >1.5
- ALT or AST >3x ULN, with symptoms of fatigue, nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain or tenderness, fever, rash, and/or eosinophilia (>5% eosinophils)
- ALT or AST >5x ULN for more than 2 weeks
- If treatment is resumed, initiate FILSPARI at 200 mg once daily, with reassessment of hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin within 3 days. Close monitoring is required in these patients.
- 8x ULN
Stop treatment permanently if no other cause found.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Sparsentan and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Sparsentan overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Sparsentan Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Sparsentan is a single molecule with antagonism of the endothelin type A receptor (ETAR) and the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R). Sparsentan has high affinity for both the ETAR (Ki= 12.8 nM) and the AT1R (Ki=0.36 nM), and greater than 500-fold selectivity for these receptors over the endothelin type B and angiotensin II subtype 2 receptors. Endothelin-1 and angiotensin II are thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of IgAN via the ETAR and AT1R, respectively.
Structure
Sparsentan is a white to off-white powder, which is practically insoluble in water. Sparsentan has pH-dependent solubility, with intrinsic solubility of 1.48 and 0.055 mg/mL under pH 1.2 and 6.8, respectively. Sparsentan has a molecular weight of 592.76 g/mol, a molecular formula of C32H40N4O5S, and the following structure:

Pharmacodynamics
In a randomized, positive-, and placebo-controlled study in healthy subjects, sparsentan caused QTcF prolongation with maximal mean effect of 8.8 msec (90% CI: 5.9, 11.8) at 800 mg and 8.1 msec (90% CI: 5.2, 11.0) at 1600 mg. The underlying mechanism behind the observed QTc prolongation is unknown but is unlikely to be mediated via direct inhibition of hERG channels. At the recommended dose, no clinically relevant QTc prolongation (i.e., > 20 msec) is expected.
Pharmacokinetics
Following a single oral dose of 400 mg sparsentan, the median (minimum to maximum) time to peak plasma concentration is approximately 3 hours (2 to 8 hours). The apparent volume of distribution at steady state is 61.4 L at the approved recommended dosage. Sparsentan is >99% bound to human plasma proteins. The half-life of sparsentan is estimated to be 9.6 hours at steady state. Metabolism
Cytochrome P450 3A is the major isozyme responsible for the metabolism of sparsentan.
- Excretion
After a single dose of radiolabeled sparsentan 400 mg to healthy subjects, approximately 80% of the dose was recovered in feces (9% unchanged) and 2% in urine (negligible amount unchanged). 82% of the dosed radioactivity was recovered within a 10-day collection period.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Sparsentan Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
In a study (PROTECT, NCT03762850), the impact of FILSPARI on proteinuria was evaluated in adults with biopsy-proven IgAN, eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2, and total urine protein ≥1.0 g/day on stable RAS inhibitor treatment. Patients with certain conditions were excluded. Patients were randomized to FILSPARI or irbesartan. Rescue immunosuppressive treatment was allowed at the investigator’s discretion, but SGLT2 inhibitors were prohibited. Of the 281 patients who reached week 36, the mean age was 46 years; 69% were male, with majority being White or Asian, and most had a history of hypertension.
percent change from baseline over time is displayed in Figure 1:

How Supplied
200 mg tablets are film-coated, modified oval, white to off-white, debossed with “105” on one side and plain on the other side, available in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant caps (NDC 68974-200-30). 400 mg tablets are film-coated, modified oval, white to off-white, debossed with “021” on one side and plain on the other side, available in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant caps (NDC 68974-400-30).
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store FILSPARI in its original container.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Sparsentan |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
NDC 68974-200-30 30 Tablets
FILSPARI™ (sparsentan) tablets
200 mg
Rx Only
 {{#ask: Label Page::Sparsentan
|?Label Name
|format=template
|template=DrugLabelImages
|mainlabel=-
|sort=Label Page
}}
{{#ask: Label Page::Sparsentan
|?Label Name
|format=template
|template=DrugLabelImages
|mainlabel=-
|sort=Label Page
}}
Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Sparsentan interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Sparsentan Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Sparsentan Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.