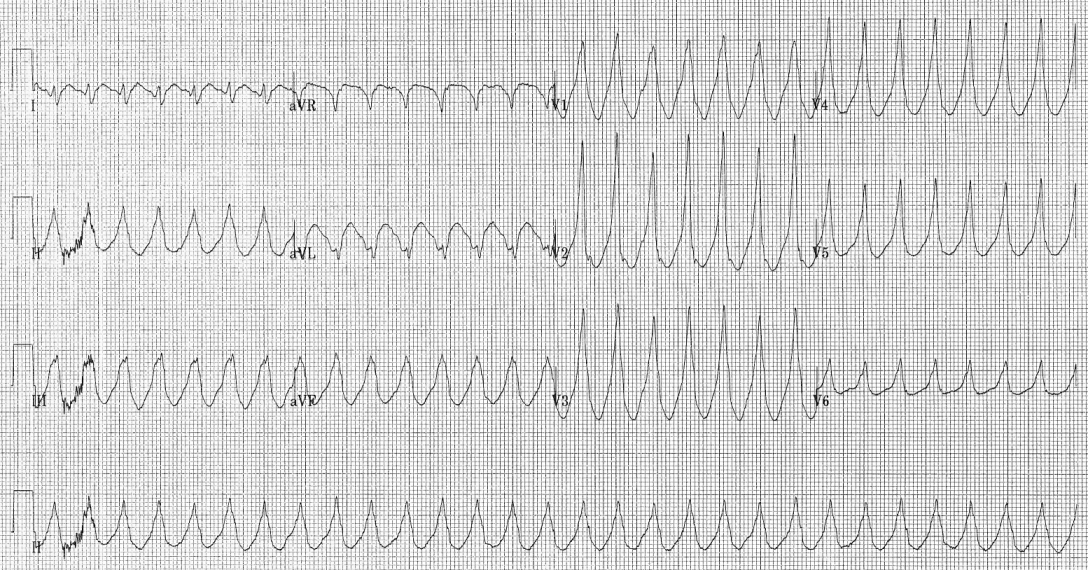
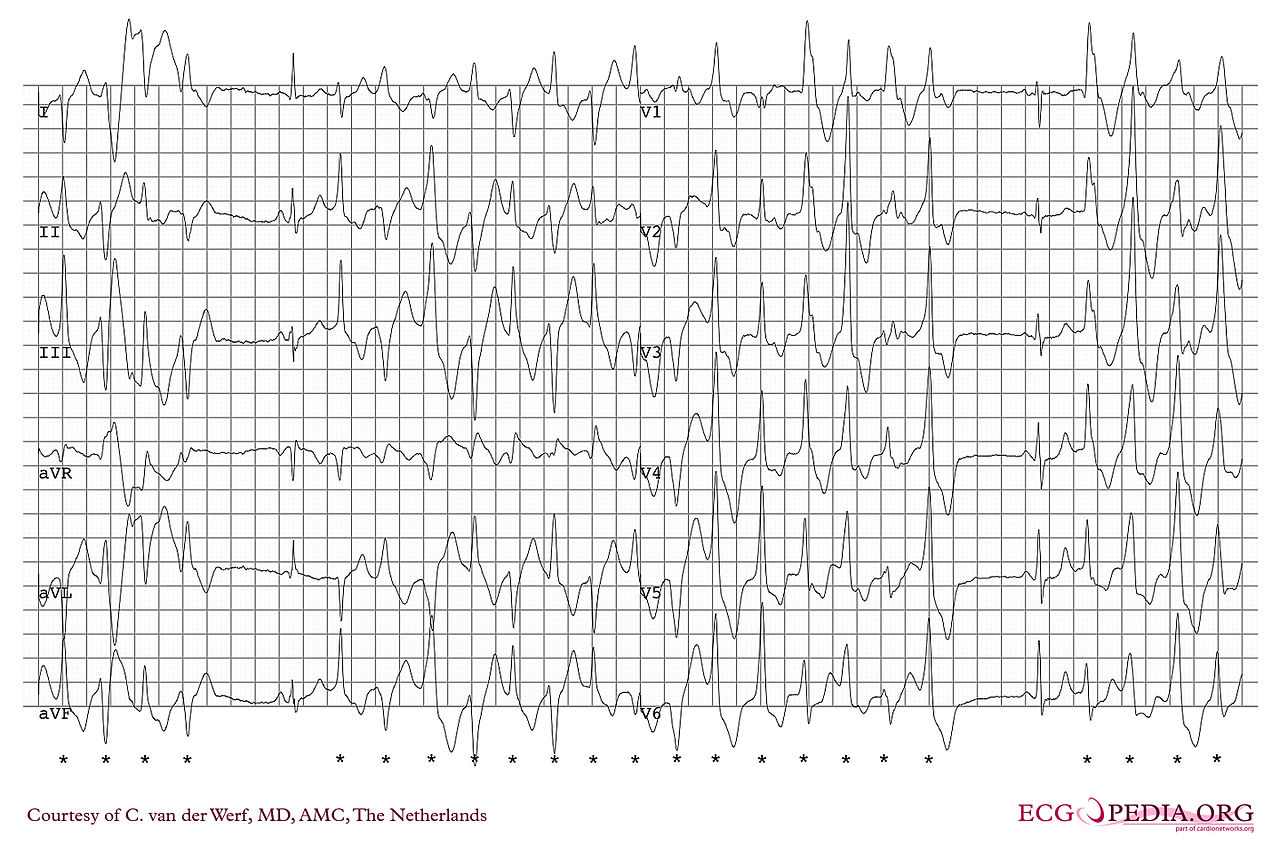
Ventricular tachycardia classification
|
Ventricular tachycardia Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Ventricular Tachycardia from other Disorders |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ventricular tachycardia classification On the Web |
|
to Hospitals Treating Ventricular tachycardia classification |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ventricular tachycardia classification |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Sara Zand, M.D.[2] Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [3]
Overview
Ventricular tachycardia refers to a rhythm with a heart rate in excess of 100 (and in some definitions 120) beats per minute that arises distal to the bundle of His. Ventricular tachycardia can be classified based on morphology and duration of tachyarrhythmia. The morphology of the QRS complexes on the ECG maybe (monomorphic ventricular tachycardiaor polymorphic ventricular tachycardia). In sustained VT duration of VT lasts > 30 sec or VT< 30 sec that needs to termination due to compromised hemodynamic. Nonsustained, or unsustained VT is more than 3 consecutive premature ventricular complexes with spontaneously termination. Bidirectional VT is a type of VT with beat to beat changing QRS frontal plane axis indicating of digoxin toxicity or catecholaminergic polymorphic VT.Torsades de pointed is a type of polymorphic VT in the setting of long QT interval which is characterized by twisting of the points, waxing and waning QRS amplitude, Long-short sequence with long-coupling interval to the first VT beat, maybe initiated after bradycardia such as high grade AV block.Ventricular flutter is explained as a regular ventricular arrhythmia with rate about 300 beat per minute (bpm), or cycle length 200 ms, sinusoidal monophorphic QRS complexes, Without any isoelecterical interval between successive QRS complexes. Ventricular fibrillation is a rapid, grossly irregular electrical activity with variation in morphologic waveforms by ventricular rate >300bpm, cycle length <200 ms. VT/ VF storm is an electerical storm or cardiac instability due to ≥ 3 episodes of sustained VT, VF or shock delivery from ICD within 24 hours.
Classification Based Upon Morphology of the QRS Complexes
Classification of ventriculat arrhythmia:
| Term | Definition | Feature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ventricular tachycardia[1] | Presence of ≥ 3 consecutive premature ventricular complexes with the rate of >100 beats per minute or cycle length< 600 ms | 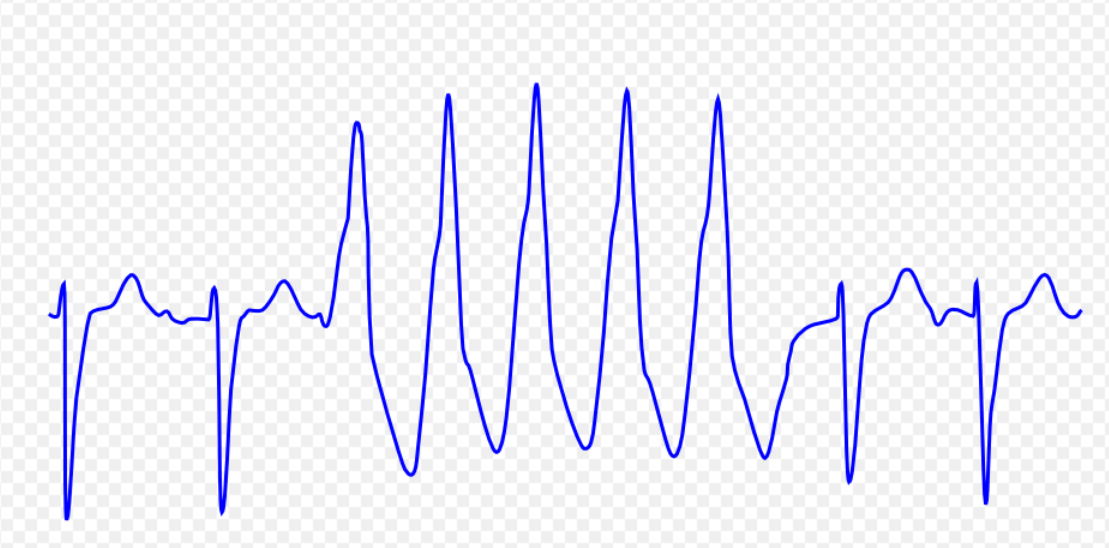 |
|
| Sustained VT |
|
||
| Nonsustained, or unsustained VT |
|
||
| Monomorphic VT |
|
||
| Polymorphic VT | |||
| Bidirectional VT |
|
||
| Torsades de pointes |
|
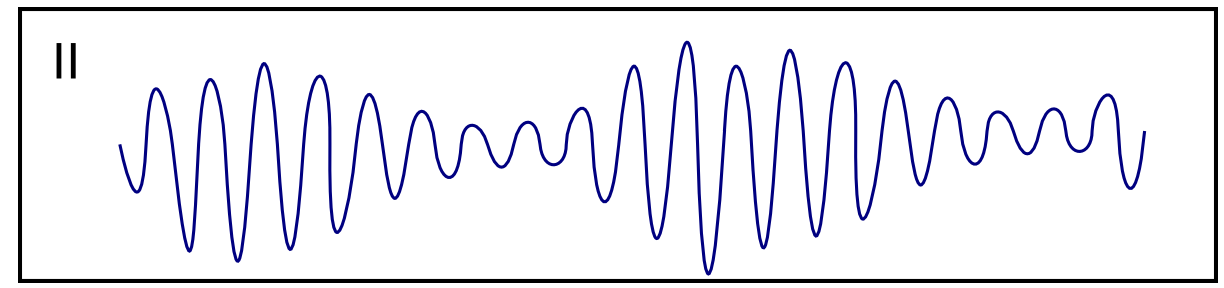 |
|
| Ventricular flutter |
|
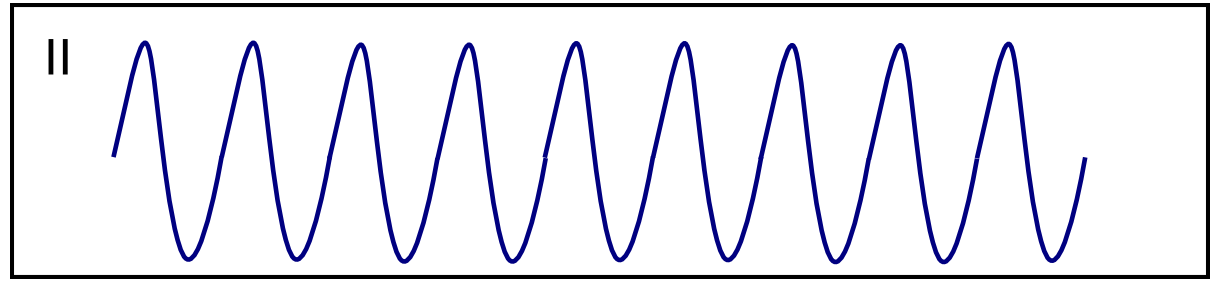 |
|
| Ventricular fibrillation |
|
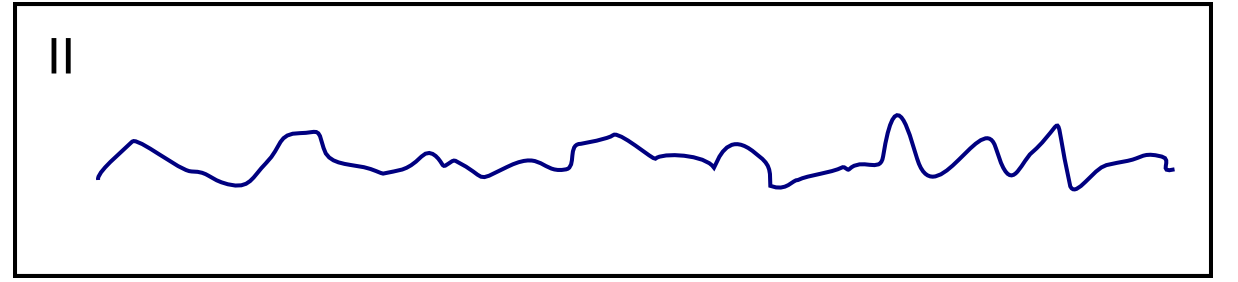 |
|
| VT, VF storm |
References
- ↑ "ACC/AHA/HRS 2006 Key Data Elements and Definitions for Electrophysiological Studies and Procedures". Circulation. 114 (23): 2534–2570. 2006. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.180199. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ ECG found in of https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
- ↑ ECG found in https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
- ↑ ECG found in https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
- ↑ ECG found in https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Main_Page