Lymph vessel
|
WikiDoc Resources for Lymph vessel |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Lymph vessel Most cited articles on Lymph vessel |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Lymph vessel |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Lymph vessel at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Lymph vessel at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Lymph vessel
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Lymph vessel Discussion groups on Lymph vessel Patient Handouts on Lymph vessel Directions to Hospitals Treating Lymph vessel Risk calculators and risk factors for Lymph vessel
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Lymph vessel |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
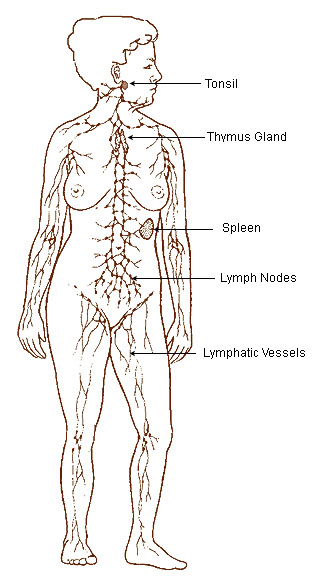
In anatomy, lymph vessels are thin walled, valved structures that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complimentary with the vascular system. In contrast to the vascular system, which carries blood under pressure to the entire body, lymph is not under pressure and is propelled in a passive fashion, assisted by the aforementioned valves. Fluid that leaks from the vascular system is returned to general circulation via lymphatic vessels.
Generally, lymph flows away from the tissues to lymph nodes and eventually to either the right lymphatic duct or the largest lymph vessel in the body, the thoracic duct. These vessels drain into the right and left subclavian veins respectively.
Function
Lymph vessels act as a reservoir from plasma and other substances including cells that leaked from the vascular system and transport lymph fluid back from the tissues to the circulatory system. Without functioning lymph vessels, lymph cannot be effectively drained and edema typically results.
Additional images
-
Lymphatic system
-
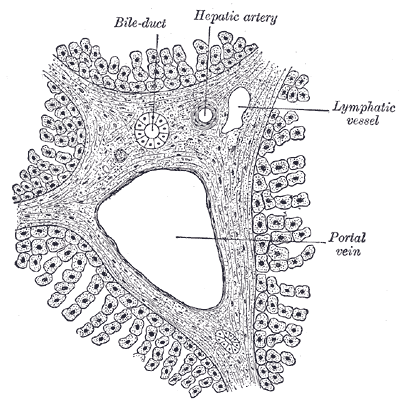
Section across portal canal of pig. X 250.
External links
- Lymphatic+Vessels at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Template:BiowebUW
- Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 3/3ch9/s3ch9_5.