Dental porcelain
|
WikiDoc Resources for Dental porcelain |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Dental porcelain Most cited articles on Dental porcelain |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Dental porcelain |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Dental porcelain at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Dental porcelain Clinical Trials on Dental porcelain at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Dental porcelain NICE Guidance on Dental porcelain
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Dental porcelain Discussion groups on Dental porcelain Patient Handouts on Dental porcelain Directions to Hospitals Treating Dental porcelain Risk calculators and risk factors for Dental porcelain
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Dental porcelain |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
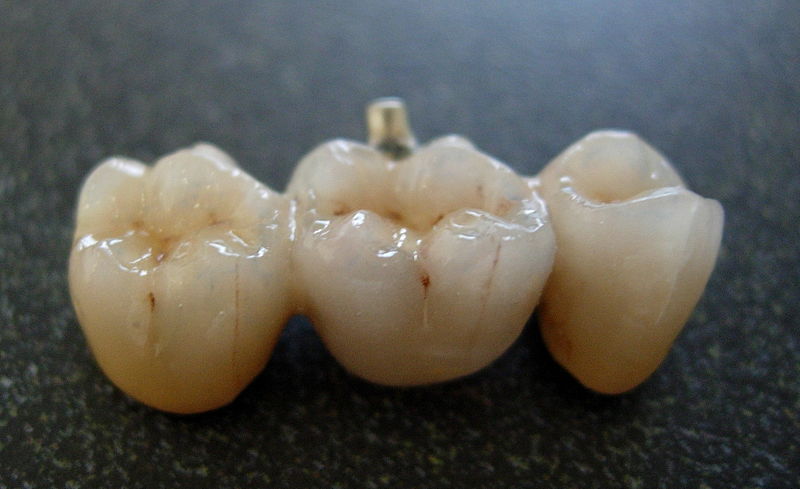
Dental porcelain (also known as dental ceramic) is a porcelain used by a dental technician to create biocompatible lifelike crowns and bridges for the dentist.
The dentist will usually specify a shade of porcelain, corresponding to a set of bottles in the lab containing the porcelain powder. A common shade system used is the Vita guide. The powder corresponding to the dentine base is mixed with water, and then fired. Further layers are built up to mimic the natural translucency of the enamel of the tooth. Often the porcelain is fused to a semi-precious metal or precious metal such as gold, for extra strength. Many new systems use an aluminium oxide or zirconium oxide; zirconia core.
Recent developments in dental CAD-CAM technology have required specialized porcelains formed into sintered blocks.
Dental porcelain is generally regarded as biologically inert. However, other toxicities may exist from some of the accessory materials, and the fillings may increase wear on opposing teeth.[1]
References
- The National Association of Dental Laboratories http://www.nadl.org/
- Napier, Bennett. Letter to the Food and Drug Administration. "Dear Interagency Working Group on Import Safety," National Association of Dental Laboratories, September 10, 2007. http://www.nadl.org/pdfs/NADLLettertoFDA09102007.pdf
Footnotes
- ↑ Mackert JR (1992). "Side-effects of dental ceramics". Adv. Dent. Res. 6: 90–3. PMID 1337968. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)