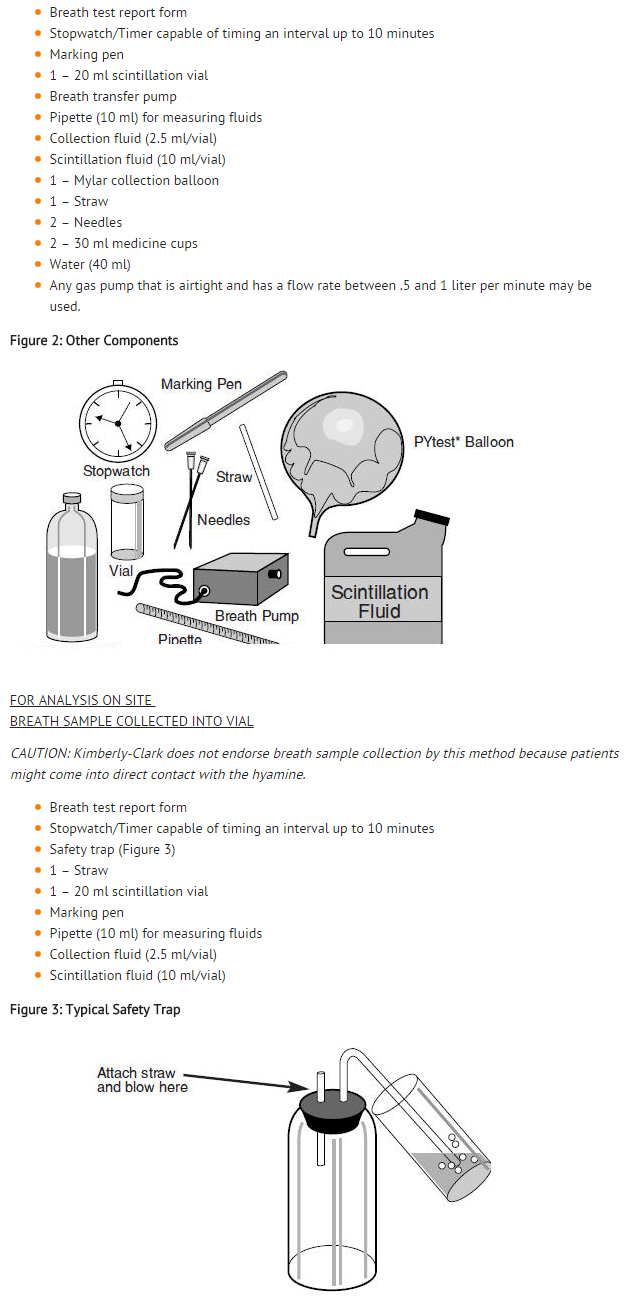
14C-Urea
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
14C-Urea is a diagnostic agent that is FDA approved for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection in the human stomach. Common adverse reactions include none.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- 14C-Urea breath test is indicated for use in the detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of H. pylori infection in the human stomach. The test utilizes a liquid scintillation counter for the measurement of 14CO2 in breath samples.
Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of 14C-Urea in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of 14C-Urea in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of 14C-Urea in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of 14C-Urea in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
None
Warnings
None
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
None
Postmarketing Experience
None
Drug Interactions
- Antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, sucralfate, and bismuth preparations are known to suppress H. pylori. Ingestion of antibiotics or bismuth within 4 weeks and proton pump inhibitors or sucralfate within 2 weeks prior to performing the test may give false negative results.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with 14C-urea. It is also not known whether 14C-urea can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of 14C-Urea in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of 14C-Urea during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when 14C-urea is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Clinical studies in children have not been conducted. However, 14C-urea is expected to work the same in children as in adults. While the dose (1 capsule) does not need to be adjusted, the child must be able to swallow the intact capsule and blow into a straw.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of 14C-Urea in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of 14C-Urea in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
- The performance characteristics of the test have not been established for monitoring the efficacy of antimicrobial therapies for the treatment of H. pylori infection.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of 14C-Urea and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- Risk from radiation is negligible even with a 1000 capsule overdose (0.3 rem). If overdose occurs, the patient may drink one glass of water (150 ml) every hour to hasten excretion of the isotope. Maximum excretion of urea is achieved at a urine output of ≥ 2.0 ml/min.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- The urease enzyme is not present in mammalian cells, so the presence of urease in the stomach is evidence that bacteria are present. The presence of urease is not specific for H. pylori, but other bacteria are not usually found in the stomach. The principle of the breath test is shown in Figure 1.
- To detect H. pylori, urea labeled with 14C is swallowed by the patient. If gastric urease from H. pylori is present, urea is split to form CO2 and NH3 at the interface between the gastric epithelium and lumen and 14CO2 is absorbed into the blood and exhaled in the breath.
- Following ingestion of the capsule by a patient with H. pylori, 14CO2 excretion in the breath peaks between 10 and 15 minutes and declines thereafter with a biological half-life of about 15 minutes. 14C-urea that is not hydrolyzed by H. pylori is excreted in the urine with a half-life of approximately 12 hours. About 10% of the 14C remains in the body at 72 hours and is gradually excreted with a biological half-life of 40 days.
Clinical Studies
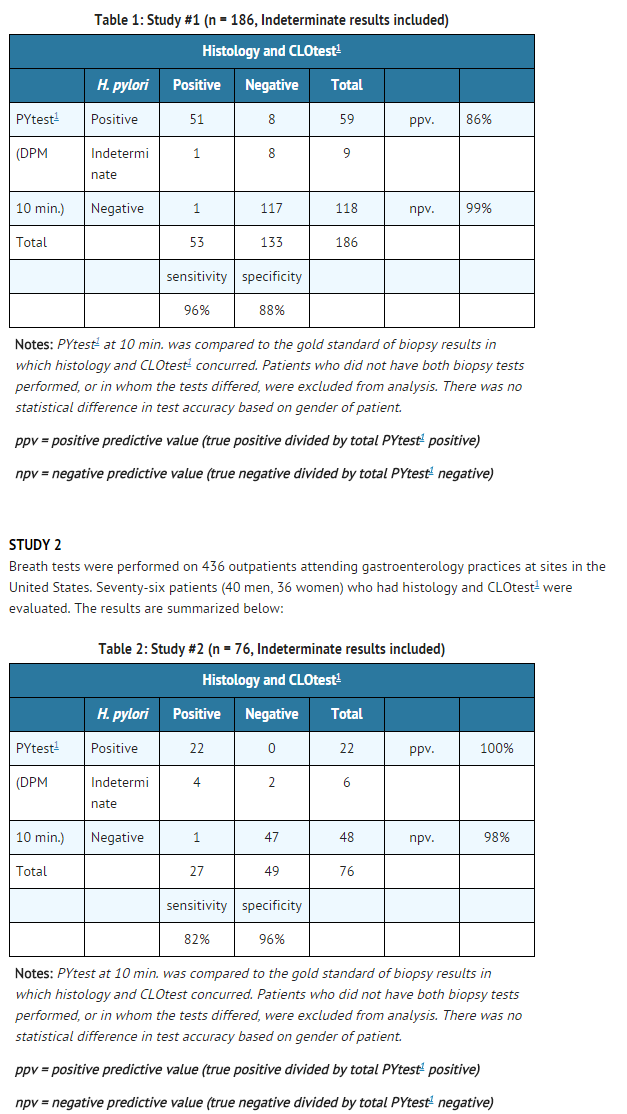
- Two studies were performed. In both studies, patients with gastrointestinal symptoms underwent the breath test and an endoscopy. During the endoscopy, biopsy samples were taken from the antral gastric mucosa for histological analysis (2 samples, Giemsa stain) and rapid urease test (1 sample, CLOtest1). Breath samples were mailed to the TRI-MED lab where they were read in a liquid scintillation counter.
- Results were reported as disintegrations per minute (DPM). Analysis for accuracy used the ten minute breath sample. A breath sample DPM <50 was defined as a negative result. DPM ≥ 200 was defined as a positive result. DPM in the range of 50–199 was classified as indeterminate.
STUDY 1
- Of 186 patients who had histopathology and CLOtest1 (80 men, 106 women), 53 were infected with H. pylori as determined by agreement between histology and CLOtest1. The study results are summarized below:
Structure
- 14C-urea is intended for use in the detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in the human stomach. The test utilizes a liquid scintillation counter for the measurement of 14CO2 in breath samples. The capsules are to be used when analysis is planned at the site where the sample is taken.
- 14C-urea capsule is a gelatin capsule for oral administration containing 1 µCi of 14C labeled urea. The urea is adsorbed on sugar spheres and colored yellow with fluorescein.
- 1 Registered Trademark or Trademark of Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc.
- Data on 14C-urea
- Structural Formula (14C-urea): NH2 14CONH2
- Radiation emission: beta-emission, 49 keVmean, 156 keVmax, no other emissions
- External emission: No external radiation hazard. Low-energy beta emissions only.
Maximum range of 0.3 mm in water.
- Radiological Half-life: 5730 years
- Maximum effective dose equivalent (EDE) : 0.3 mrem/µCi.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
- 14C-urea Capsules, clear gelatin capsules each containing 1 μCi of 14C-urea in unit dose packages of 1, 10 and 100.
- 14C-urea Kit (14C-urea breath test) is also supplied as a kit containing a 14C-urea Capsule and breath collection equipment.
- The 14C-urea Capsule has a shelf life of two years. The expiration date is printed on the capsule label.
Storage
- 14C-urea Capsules and Kit should be stored at 15–30 °C (59–86 °F) in an area designated by each individual institution's regulations.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::14C-Urea |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

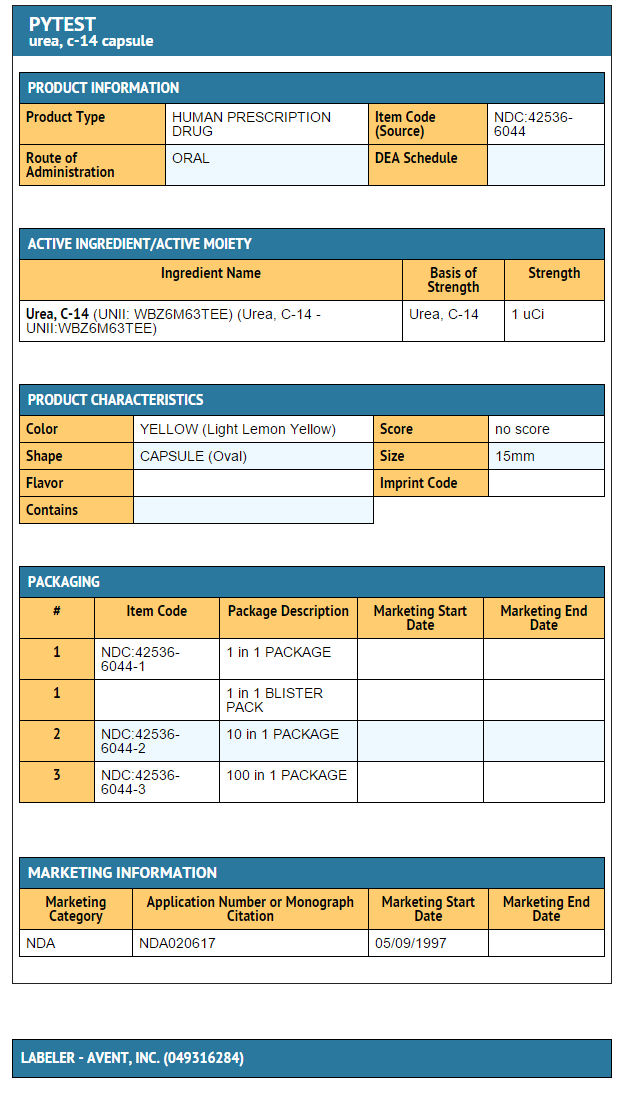
{{#ask: Label Page::14C-Urea |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-14C-Urea interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- PYTEST®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding 14C-Urea Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.