WBR1015
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Physiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Cardiology |
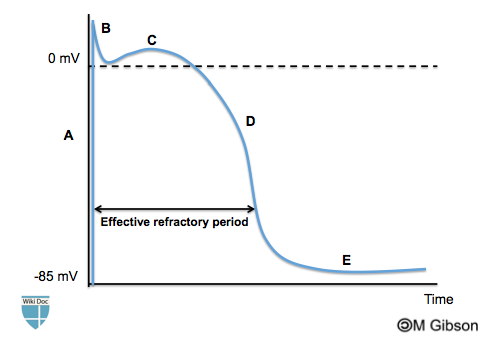
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A pharmaceutical company develops a new anti-arrhythmic drug that targets the slow voltage gated potassium channels. Shown below is an image depicting the ventricular action potential. Which of the following phases of the action potential, labelled from A to E, correspond to the target of the new drug? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::A |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::A corresponds to phase 0 of the ventricular action potential. Phase 0 is characterized by a depolarization caused by the abrupt opening of the voltage gated sodium channel.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::B |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::B corresponds to phase 1 of the ventricular action potential. Phase 1 is characterized by an early repolarization caused by the closure of the sodium channels and the opening of voltage gated potassium channels.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::C |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::C corresponds to phase 2 of the ventricular action potential. Phase 2 is characterized by a plateau. The plateau results from the opening of the voltage gated calcium channels leading to an influx of calcium that balances the potassium efflux.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::D |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::D corresponds to phase 3 of the ventricular action potential. Phase 3 is characterized by a rapid repolarization caused by the closure of the calcium channels and opening of the slow voltage gated potassium channel.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::E |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::E corresponds to phase 4 of the ventricular action potential. Phase 4 is characterized by a resting potential which is caused by the high potassium permeability through the potassium channels.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
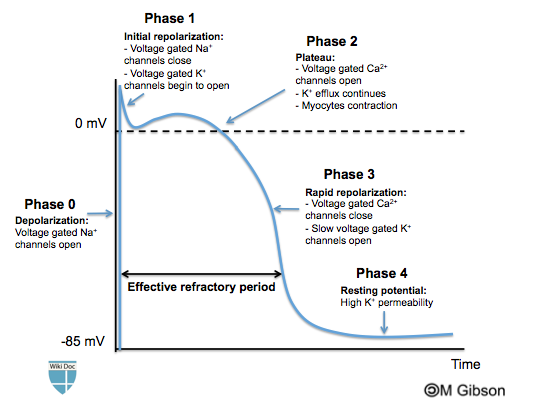
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The ventricular action potential is composed of four phases: - Phase 0 (depolarization): abrupt opening of the voltage gated sodium channel Education objective: The phase 3 of the ventricular action potential is characterized by a rapid repolarization caused by the closure of the calcium channels and opening of the slow voltage gated potassium channel. Reference:
First aid for USMLE step 1, 2014. Page 274. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Action potential |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |