WBR0979: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|SubCategory=General Principles | |SubCategory=General Principles | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|SubCategory=General Principles | |SubCategory=General Principles | ||
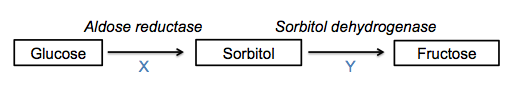
|Prompt=Sorbitol | |Prompt=Sorbitol concentration is measured in hepatocytes of normal rats and mutant rats with glucose intolerance. The aim of the experiment is to establish the association between the concentration of glucose in blood and the concentration of sorbitol in hepatocytes. Shown below is a figure that illustrates sorbitol metabolism. Which compounds correspond to the cofactors X and Y, respectively?<br> | ||
[[Image:WBR0979.png|600px]] | |||
[[ | |Explanation=NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+ whereas NAD+ is the oxidized form of NADH. Both NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors are electron carriers and donors in the redox reactions of sorbitol metaolism. [[Glucose]] is converted to sorbitol by the action of [[aldose reductase]] (requires NADPH), and sorbitol is then converted to fructose by the action of sorbitol dehydrogenase (requires NAD+). While some cells are lacking sorbitol dehydrogenase (cells of the retina, Schwann cells, and kidney cells), other cells (e.g. hepatocytes and cells of the ovaries and seminal vesicles) have both enzymes to metabolize glucose into fructose.<br> | ||
|Explanation=NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+ | Shown below is a figure that illustrates sorbitol metabolism<br> | ||
[[Image:Sorbitol pathway illustration.png|700px]] | |||
[[ | |AnswerA=X=NADPH and Y=NAD+ | ||
|AnswerAExp=NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. | |||
|AnswerB=X=NAD+ and Y=NADPH | |||
|AnswerBExp=While both NAD+ and NADPH are needed for sorbitol metabolism, X corresponds to NADPH and Y corresponds to NAD+, and the order by which the enzymes and their cofactors function in the sorbitol pathway is important. | |||
|AnswerC=X=ATP and Y=NAD+ | |||
|AnswerCExp=NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ATP is not a cofactor in either reaction. | |||
|AnswerD=X=NADPH and Y=ADP | |||
|AnswerA=NADPH and NAD+ | |AnswerDExp=NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ADP is not a cofactor in either reaction. | ||
|AnswerAExp=NADPH and NAD+ are | |AnswerE=X=NAD+ and Y=ATP | ||
|AnswerB=NAD+ and NADPH | |AnswerEExp=NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ATP is not a cofactor in either reaction. | ||
|AnswerBExp= | |EducationalObjectives=NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. | ||
|AnswerC=ATP and NAD+ | |References=First Aid 2014 page 107 | ||
|AnswerCExp= | |||
|AnswerD=NADPH and ADP | |||
|AnswerDExp= | |||
|AnswerE=NAD+ and ATP | |||
|AnswerEExp= | |||
|RightAnswer=A | |RightAnswer=A | ||
|WBRKeyword=NADPH, NAD+, | |WBRKeyword=NADPH, NAD+, Fructose, Cofactor, Sorbitol, Sorbitol metabolism, Sorbitol pathway, Diabetes, Rat. Experiment, Hepatocyte | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 21:33, 10 March 2015
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biochemistry |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::General Principles |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::Sorbitol concentration is measured in hepatocytes of normal rats and mutant rats with glucose intolerance. The aim of the experiment is to establish the association between the concentration of glucose in blood and the concentration of sorbitol in hepatocytes. Shown below is a figure that illustrates sorbitol metabolism. Which compounds correspond to the cofactors X and Y, respectively? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::X=NADPH and Y=NAD+ |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::X=NAD+ and Y=NADPH |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::While both NAD+ and NADPH are needed for sorbitol metabolism, X corresponds to NADPH and Y corresponds to NAD+, and the order by which the enzymes and their cofactors function in the sorbitol pathway is important. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::X=ATP and Y=NAD+ |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ATP is not a cofactor in either reaction. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::X=NADPH and Y=ADP |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ADP is not a cofactor in either reaction. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::X=NAD+ and Y=ATP |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors for aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase, respectively. Both enzymes and their cofactors are involved in sorbitol metabolism. ATP is not a cofactor in either reaction. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+ whereas NAD+ is the oxidized form of NADH. Both NADPH and NAD+ are cofactors are electron carriers and donors in the redox reactions of sorbitol metaolism. Glucose is converted to sorbitol by the action of aldose reductase (requires NADPH), and sorbitol is then converted to fructose by the action of sorbitol dehydrogenase (requires NAD+). While some cells are lacking sorbitol dehydrogenase (cells of the retina, Schwann cells, and kidney cells), other cells (e.g. hepatocytes and cells of the ovaries and seminal vesicles) have both enzymes to metabolize glucose into fructose. Shown below is a figure that illustrates sorbitol metabolism |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::NADPH, WBRKeyword::NAD+, WBRKeyword::Fructose, WBRKeyword::Cofactor, WBRKeyword::Sorbitol, WBRKeyword::Sorbitol metabolism, WBRKeyword::Sorbitol pathway, WBRKeyword::Diabetes, WBRKeyword::Rat. Experiment, WBRKeyword::Hepatocyte |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |