WBR0971: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | |QuestionAuthor= {{Rim}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
Latest revision as of 02:14, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1] (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biochemistry |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::General Principles |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::In an experiment, liver mitochondrial subfractions are purified from sample of bovine livers, and mitochondrial enzymes involved in the urea cycle are isolated. Fatty acylation assays are then carried out on the samples in order to study the regulatory role of fatty acylation in the kinetic activity of these enzymes. Which of the following enzymes is most likely present in the purified mitochondrial sample?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Arginase |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Arginase is a cytoplasmic enzyme.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Argininosuccinate synthetase |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Argininosuccinate synthetase is a cytoplasmic enzyme.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Argininosuccinase |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Argininosuccinase is a cytoplasmic enzyme.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I |
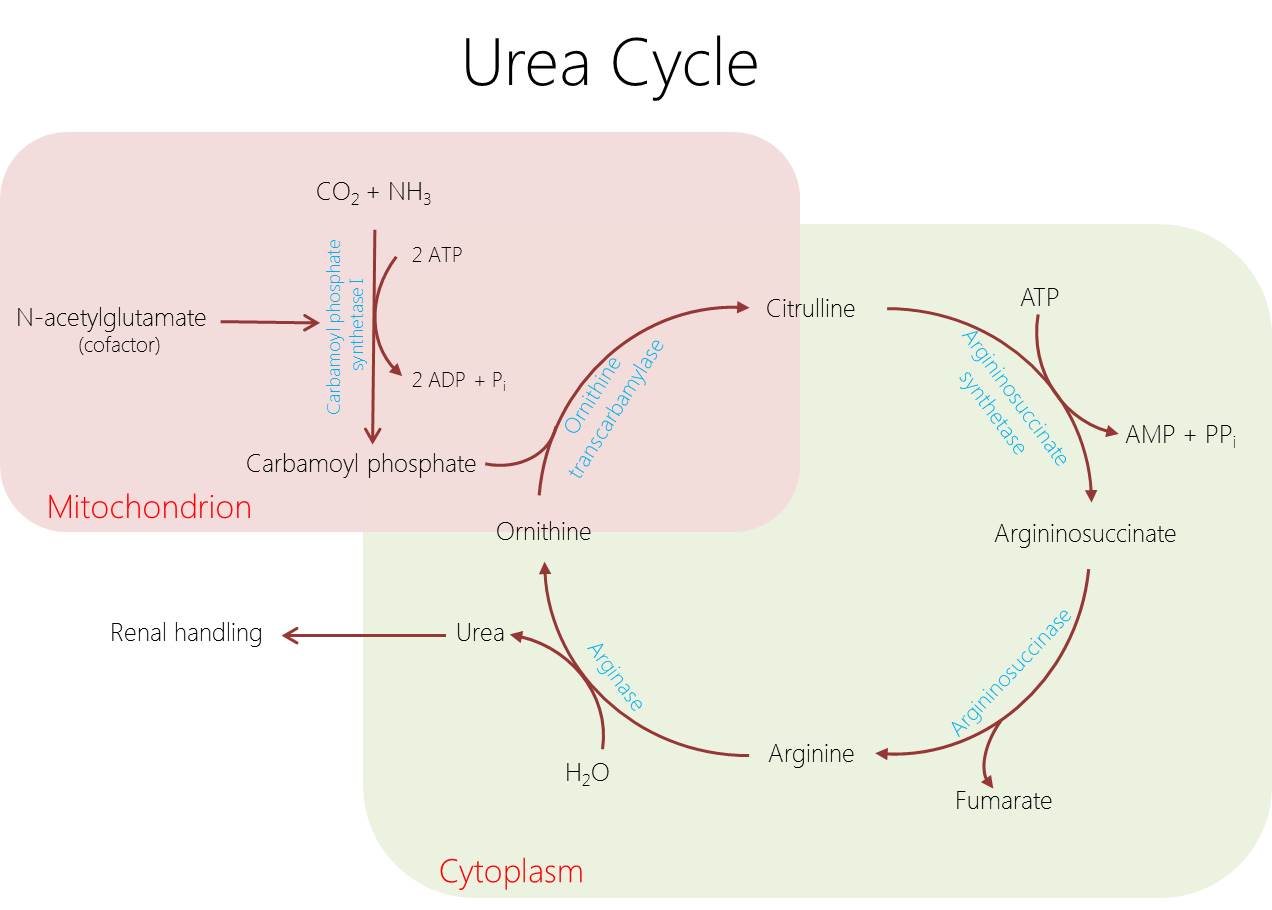
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the urea cycle. It utilizes ATP to catalyze the reaction that produces carbamoyl phosphate from carbon dioxide and ammonia.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the reaction that produces carbamoyl phosphate.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The urea cycle involves a set of 5 hepatic enzymes that collectively convert ammonia into urea. Two of the reactions involved in urea synthesis occur within the mitochondria, whereas the remaining reactions occur in the cytoplasm.
|
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Urea cycle, WBRKeyword::Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I, WBRKeyword::Mitochondrial enzyme, WBRKeyword::Enzyme, WBRKeyword::Mitochondria, WBRKeyword::Urea synthesis, WBRKeyword::Ammonia, WBRKeyword::Bovine liver, WBRKeyword::Experiment, WBRKeyword::Fatty acylation |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |