WBR0944: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | |QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
Latest revision as of 02:08, 28 October 2020
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Dermatology, SubCategory::Oncology |
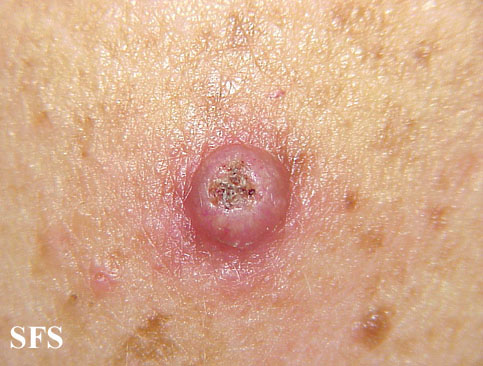
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 54-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a wart-like lesion on her cheek. She reports that the lesion first appeared as a red, inflamed spot 2 weeks ago and has rapidly grown to its present size (shown below). The physician schedules the patient for surgical removal of the lesion in one month. When the patient returns for the appointment, the physician notices that the lesion has largely regressed. What is the most likely diagnosis? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Keratoacanthoma |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Keratoacanthomas are benign skin growths characterized by a dimpled, keratin filled center. They grow rapidly before spontaneously regressing. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::HPV |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::HPV infections are responsible for many cutaneous lesions in humans, including skin warts and genital warts. HPV infected lesions do not display the explosive growth and regression of this case and do not share the same gross appearance. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Squamous cell carcinoma |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Squamous cell carcinoma is often characterized macroscopically by a slow growing, erythematous, ulcerating lesion on a sun-exposed area. The rapidly growing mass in this vignette and its spontaneous regression is inconsistent with squamous cell carcinoma.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Actinic keratosis |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Actinic keratosis is a premalignant condition that occurs commonly in older individuals on sun-exposed areas. These lesions are characterized by a scaly appearance and should be monitored because they may progress to squamous cell carcinoma. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Basal cell carcinoma |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer. It occurs in sun-exposed areas and is often invasive but rarely metastasizes. It often presents as a pearly nodule, and can later appear as a chronically non-healing ulcer. The explosive growth and regression of the mass in this patient is inconsistent with basal cell carcinoma.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Keratoacanthoma (KA), a common low-grade skin tumour that is believed to originate from the neck of the hair follicle. The defining characteristic of KA is that it is dome-shaped, symmetrical, surrounded by a smooth wall of inflamed skin, and capped with keratin scales and debris. It always grows rapidly, reaching a large size within days or weeks, and if untreated will starve itself of nourishment, necrose (die), slough, and heal with scarring. Approximately 6% of KA progress to squamous cell carcinoma when left untreated. Educational Objective: Keratoacanthoma is a low-grade skin tumor characterized by a dome-shaped growth with a keratin-filled central dimple. It grows rapidly over several weeks, then spontaneously regresses. |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Skin, WBRKeyword::Skin cancer, WBRKeyword::Cancer, WBRKeyword::Dermatology, WBRKeyword::Skin lesion |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |