WBR0936: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | |QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
Latest revision as of 02:07, 28 October 2020
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biochemistry |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Endocrine, SubCategory::Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A scientist is studying the mechanism of exercise-induced insulin sensitivity in diabetic patients. A biopsy of the vastus lateralis muscle is obtained from a patient's left leg at rest. Three to six weeks later, the subjects performs 60 minutes of cycling at 70% VO2 max, and immediately thereafter another biopsy is obtained from the right vastus lateralis muscle. The investigator performs immunohistochemistry for both obtained tissues. Which of the following will demonstrate increased localization to the plasma membrane?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::GLUT1 |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::GLUT1 is expressed in erythrocytes and the brain. It does not translocate to the cell membrane with exercise. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::GLUT2 |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::GLUT2 is a bidirectional glucose transporter that is expressed in pancreatic islet cells, the liver and the kidney. It does not translocate to the cell membrane with exercise. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::GLUT3 |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::GLUT3 is primarily expressed in neurons and does not translocate to the cell membrane with exercise. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::GLUT4 |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::GLUT4 is an insulin-responsive glucose transporter found in adipose tissue and muscle that translocates to the cell membrane upon exercise. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::GLUT5 |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::GLUT5 is a fructose transporter expressed on the apical border of enterocytes in the small intestine. It does not translocate to the cell membrane with exercise. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
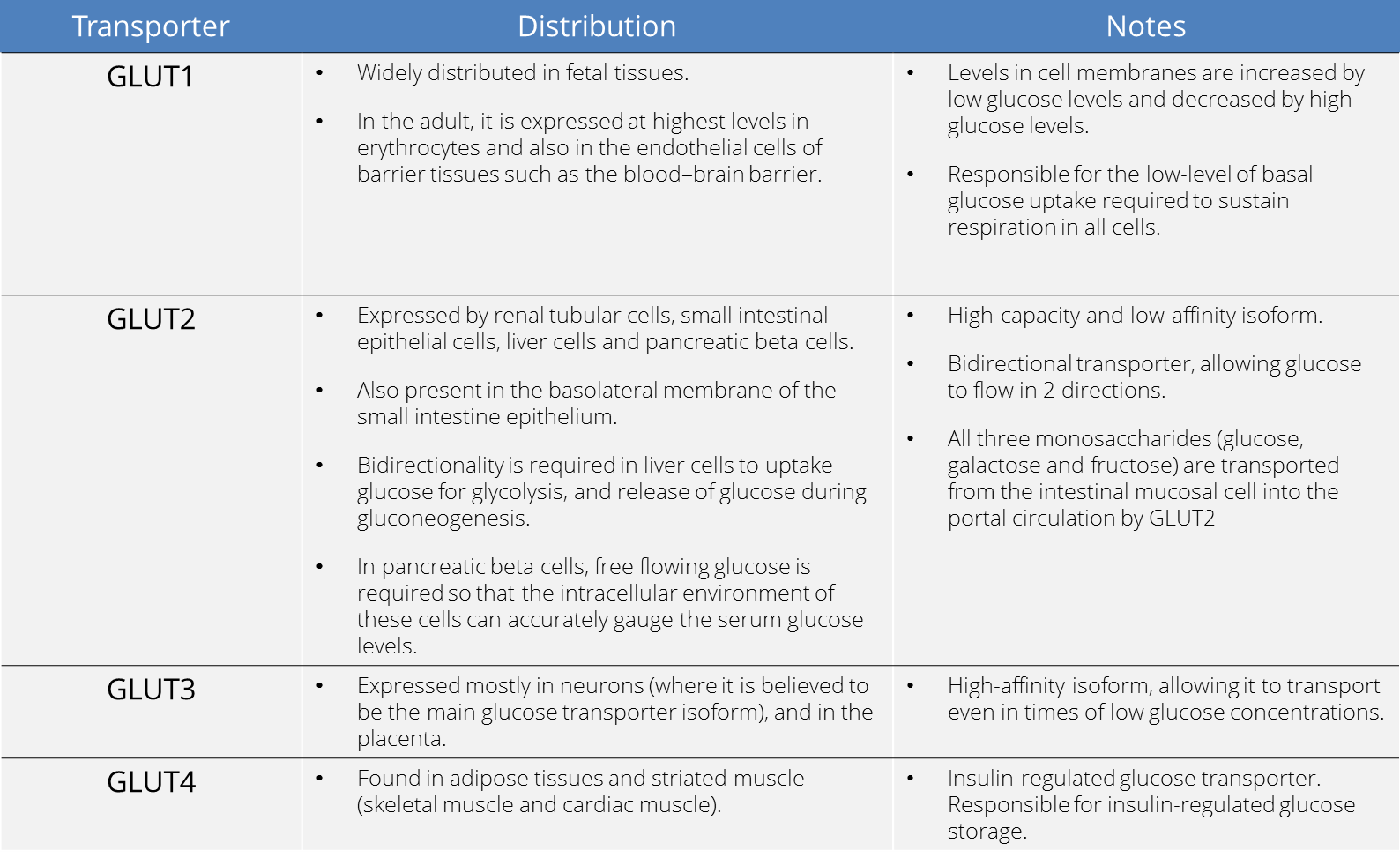
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Glucose is a charged molecule that requires transporters to enter cells. The glucose transporters found in various cell types in the body are deferentially expressed and regulate glucose uptake differently. GLUT4 is the insulin responsive glucose transporter. It is expressed in muscle and adipose tissue, and its cell-surface expression can be increased by exercise.
The following table summarizes the glucose transporters. |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Muscle, WBRKeyword::Insulin, WBRKeyword::Glucose, WBRKeyword::Receptor, WBRKeyword::Exercise, WBRKeyword::Transporter |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |