WBR0934: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | |QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
Latest revision as of 02:06, 28 October 2020
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Anatomy |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, SubCategory::Vascular |
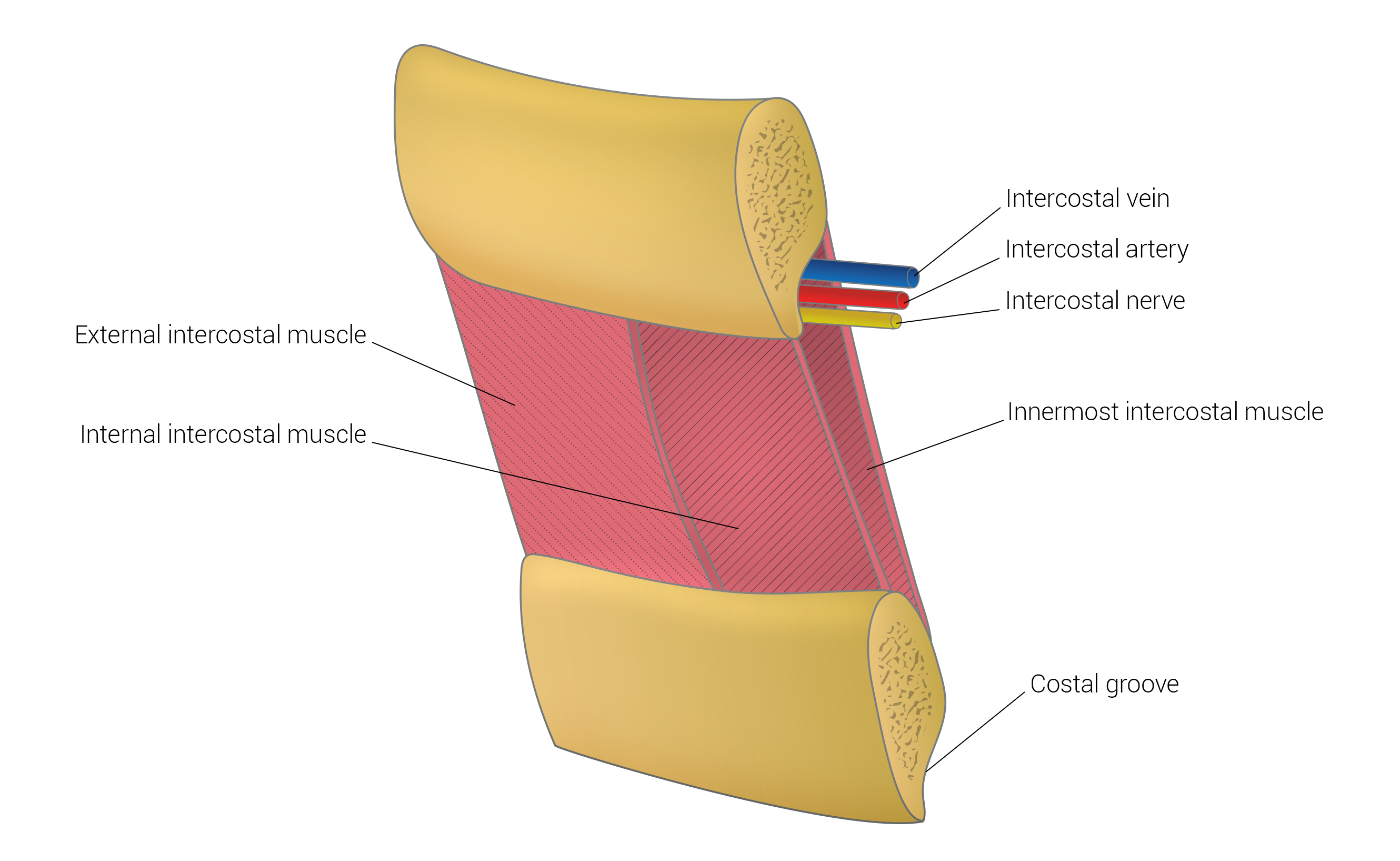
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 55-year-old smoker presents to his primary care physician for dyspnea. Physical examination reveals a right sided pleural effusion and chest-CT is concerning for malignancy. The physician is set to perform a thoracentesis, but must recall the positioning of the neurovascular bundle in the intercostal space. Which of the following represents the order of structures in the intercostal space from inferior to superior?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Artery, Nerve, Vein |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::The intercostal space contains the intercostal Vein, Artery, and Nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Vein, Nerve, Artery |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::The intercostal space contains the intercostal Vein, Artery, and Nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Nerve, Artery, Vein |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::The intercostal space contains the intercostal Vein, Artery, and Nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. Note that the question asks for the order from inferior to superior. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Nerve, Vein, Artery |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::The intercostal space contains the intercostal Vein, Artery, and Nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Vein, Artery, Nerve |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::The intercostal space contains the intercostal Vein, Artery, and Nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Lung tumors are a common cause of pleural effusions. Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the intercostal space to aspirate excess fluid or air from the lung. The neurovascular bundle runs high in the intercostal space in the intercostal groove and is composed of the vein, artery and nerve (VAN) in that order from superior to inferior. When performing thoracentesis, the physician must insert the needle immediately superior to the bottom rib of the intercostal space to avoid injuring structures in the neurovascular bundle. This space is not free of neurovascular structures, but the existing ones are collaterals that are not as essential as the main intercostal artery and vein.
|
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Vasculature, WBRKeyword::Nerve, WBRKeyword::Artery, WBRKeyword::Vein, WBRKeyword::Intercostal, WBRKeyword::Thoracic, WBRKeyword::Thoracic anatomy, WBRKeyword::Thorax, WBRKeyword::Rib, WBRKeyword::Ribs, WBRKeyword::Lungs, WBRKeyword::Lung, WBRKeyword::Pleural effusion, WBRKeyword::Pleurocentesis, WBRKeyword::Anatomy |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |