WBR0849: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{WBRQuestion |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 |MainCategory=Biochemistry |SubCategory=General Principles |MainCategory=Biochemistry |SubCategory=General Princip...") |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
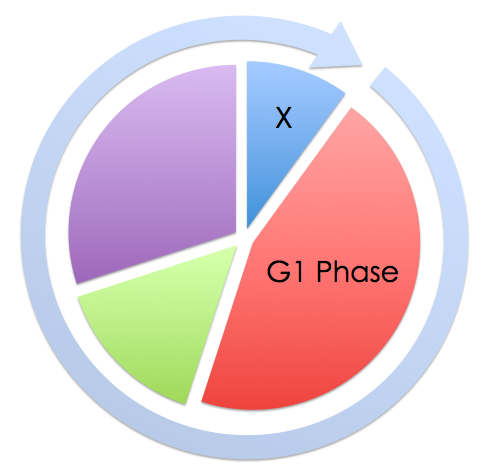
|Prompt=A researcher is studying the cell cycle in different tissue samples. Using rats, he obtains tissue samples from different sites and prepares the tissues for histopathological analysis. Based on the illustration below, which of the tissue sites will most abundantly contain cells in phase X? | |Prompt=A researcher is studying the cell cycle in different tissue samples. Using rats, he obtains tissue samples from different sites and prepares the tissues for histopathological analysis. Based on the illustration below, which of the tissue sites will most abundantly contain cells in phase X? | ||
[[Image:WBR0849.png| | [[Image:WBR0849.png|350px]] | ||
|Explanation=[[Image:Cell_Cycle.png| | |Explanation=[[Image:Cell_Cycle.png|350px]] | ||
Phase X depicts mitosis or M phase of the cell cycle, which is the shortest, but the most active, phase of the life cycle. It is characterized by several stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and finally telophase.Following mitosis, 2 cells are produced. Not all cells have the same pattern of cell cycle or the same rate of cell division. While labile cells, like the bone marrow cells, gut epithelial cells of the skin and the gut, hair follicular cells, and germ cells are highly active cells that continuously undergo division, other cells are stable unless stimulated, such as hepatocytes and lymphocytes, or even permanent remaining in G0 phase even if stimulated, like red blood cells, neurons, and cardiac cells. | Phase X depicts mitosis or M phase of the cell cycle, which is the shortest, but the most active, phase of the life cycle. It is characterized by several stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and finally telophase.Following mitosis, 2 cells are produced. Not all cells have the same pattern of cell cycle or the same rate of cell division. While labile cells, like the bone marrow cells, gut epithelial cells of the skin and the gut, hair follicular cells, and germ cells are highly active cells that continuously undergo division, other cells are stable unless stimulated, such as hepatocytes and lymphocytes, or even permanent remaining in G0 phase even if stimulated, like red blood cells, neurons, and cardiac cells. | ||
Revision as of 01:31, 19 November 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biochemistry |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::General Principles |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A researcher is studying the cell cycle in different tissue samples. Using rats, he obtains tissue samples from different sites and prepares the tissues for histopathological analysis. Based on the illustration below, which of the tissue sites will most abundantly contain cells in phase X? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Hepatocytes |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Hepatocytes are stable (quiescent) cells that undergo division only when stimulated. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Lymphocytes |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Lymphocytes are stable (quiescent) cells that only undergo division only when stimulated. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Cardiac cells |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Cardiac cells are permanent cells that do not undergo division. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Red blood cells |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Red blood cells (RBCs) are permanent cells that lack nuclei and lack cell division. RBCs have a life span of 120 days and are normally cleared by the spleen. Several hematological diseases decrease the life span of RBCs. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Duodenal epithelial cells |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Cells of the gut and skin epithelium are labile cells that are continuously dividing. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::E |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::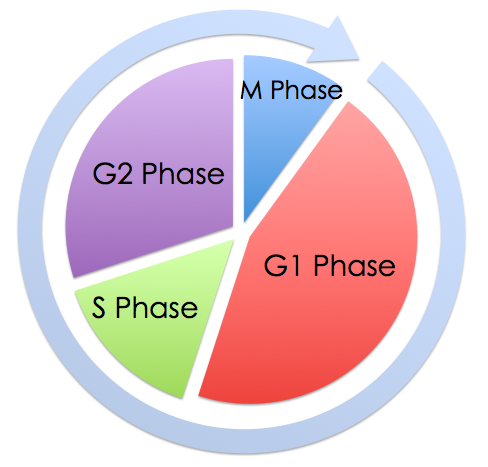
Phase X depicts mitosis or M phase of the cell cycle, which is the shortest, but the most active, phase of the life cycle. It is characterized by several stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and finally telophase.Following mitosis, 2 cells are produced. Not all cells have the same pattern of cell cycle or the same rate of cell division. While labile cells, like the bone marrow cells, gut epithelial cells of the skin and the gut, hair follicular cells, and germ cells are highly active cells that continuously undergo division, other cells are stable unless stimulated, such as hepatocytes and lymphocytes, or even permanent remaining in G0 phase even if stimulated, like red blood cells, neurons, and cardiac cells. Under histopathological analysis, labile cells that are continuously dividing are most likely to have cells undergoing mitosis at any given time. Educational Objective: Gut epithelial cells are labile cells that are most likely to be undergoing division at any given time. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::cell, WBRKeyword::cycle, WBRKeyword::prophase, WBRKeyword::metaphase, WBRKeyword::anaphase, WBRKeyword::telophase, WBRKeyword::labile, WBRKeyword::permanent, WBRKeyword::stable, WBRKeyword::quiescent, WBRKeyword::cells, WBRKeyword::gut, WBRKeyword::epithelial, WBRKeyword::epithelium, WBRKeyword::skin, WBRKeyword::continuous, WBRKeyword::division |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |