WBR0845: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{WBRQuestion |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 |Prompt=A researcher is studying the life cycle of Clostridium difficile. He allows the growth of C. difficile in ...") |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
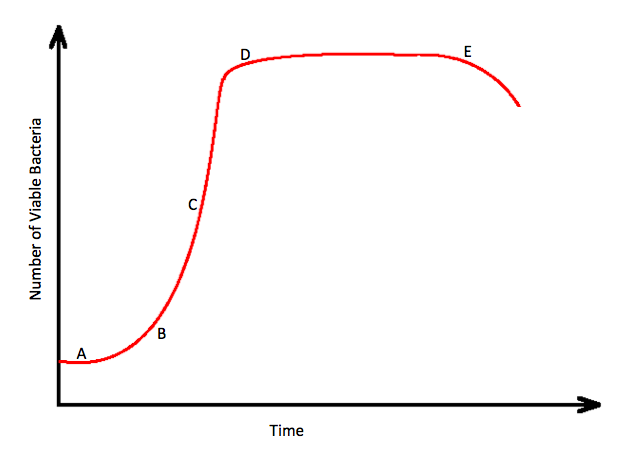
Based on the bacterial growth curve explained below, spore formation is typically seen at the end of the stationary phase of the life cycle, where nutrients become limited and survival conditions for the bacteria become harsher. | Based on the bacterial growth curve explained below, spore formation is typically seen at the end of the stationary phase of the life cycle, where nutrients become limited and survival conditions for the bacteria become harsher. | ||
[[ | [[Bacterial Growth Curve.png|500px]] | ||
Educational Objective: Spores contain dipicolinic acid in their core. They are typically formed at the end of the bacterial growth curve. | Educational Objective: Spores contain dipicolinic acid in their core. They are typically formed at the end of the bacterial growth curve. | ||
Revision as of 04:01, 13 November 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | |
| Sub Category | |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A researcher is studying the life cycle of Clostridium difficile. He allows the growth of C. difficile in appropriate culture media for several days and notes his observations during the experiment. The researcher reveals that at a specific stage during the life cycle, levels of dipicolinic acid rise significantly. Based on the diagram below, these changes most likely correspond to which phase of the C. difficile growth curve? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::A |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::A corresponds to the lag phase of the bacterial growth curve |
| Answer B | AnswerB::B |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::B corresponds to the beginning of the exponential phase of the bacterial growth curve. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::C |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::C corresponds to the exponential phase of the bacterial growth curve. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::D |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::D corresponds to the beginning of the stationary phase of the bacterial growth curve. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::E |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::E corresponds to the end of the stationary phase and the beginning of the death phase due to limited resources for the bacteria to survive. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::E |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::C. difficile are gram-positive, endospore forming, anaerobic bacilli. Spores are defined as a one-celled reproductive unit that may resist heart and chemicals and have almost no metabolic activity. Spores contain dipicolinic acid in their core. In addition to Clostridium difficile, other Clostridia species, such as C. botulinum, C. perfringens, and C. tetani and other organisms like Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Coxiella burnetii are all capable of forming spores.
Based on the bacterial growth curve explained below, spore formation is typically seen at the end of the stationary phase of the life cycle, where nutrients become limited and survival conditions for the bacteria become harsher. Educational Objective: Spores contain dipicolinic acid in their core. They are typically formed at the end of the bacterial growth curve. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::bacteria, WBRKeyword::bacterial, WBRKeyword::growth, WBRKeyword::curve, WBRKeyword::stationary, WBRKeyword::lag, WBRKeyword::phase, WBRKeyword::exponential, WBRKeyword::death, WBRKeyword::stationary, WBRKeyword::spore, WBRKeyword::endospore, WBRKeyword::forming, WBRKeyword::formation, WBRKeyword::clostridium, WBRKeyword::clostridial, WBRKeyword::difficile, WBRKeyword::C. difficile, WBRKeyword::resistance, WBRKeyword::resistant, WBRKeyword::heat, WBRKeyword::chemicals |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |