WBR0765: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{ | |QuestionAuthor= {{YD}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology | |SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology | |SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology | ||
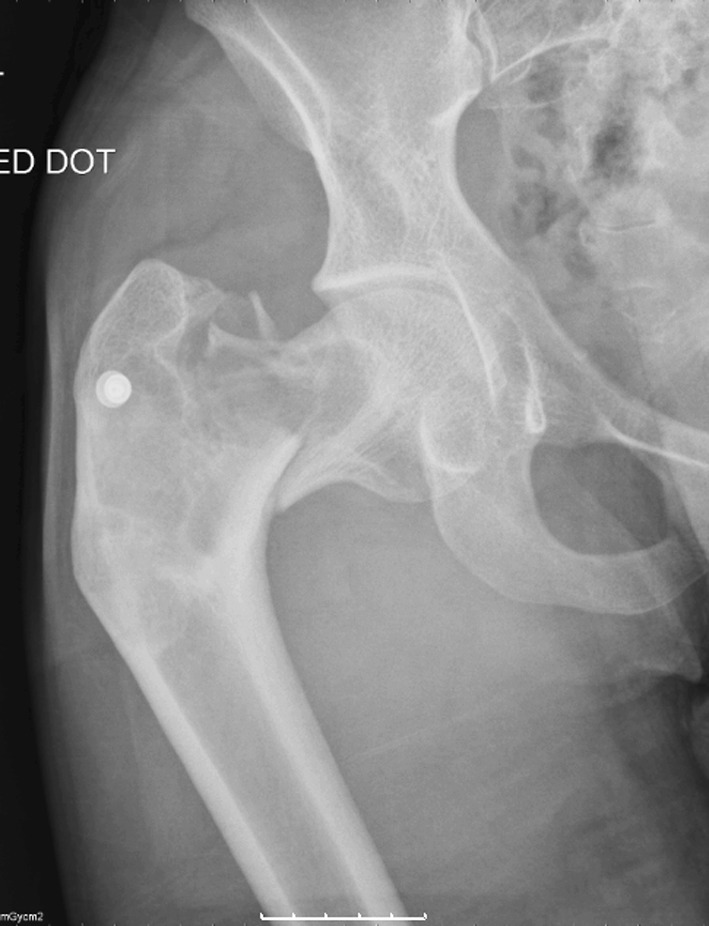
|Prompt=A 14 year old girl is brought by her mother to the physician's office for facial asymmetry and a limp on the right side. Her past medical history is significant for McCune-Albright syndrome. Physical examination is remarkable for facial asymmetry, breast enlargement, and multiple cafe-au- | |Prompt=A 14-year-old girl is brought by her mother to the physician's office for facial asymmetry and a limp on the right side. Her past medical history is significant for McCune-Albright syndrome. Physical examination is remarkable for facial asymmetry, breast enlargement, and multiple cafe-au-lait spots on her skin. X-ray of the right proximal femur demonstrates a "ground glass" appearance and findings consistent with a "shepherd's crook" deformity. The physician explains that the patient's condition is caused by a disease of the bone marrow stromal cells with abnormal production of fibro-osseous masses of tissue. Biopsy of the bone lesions will most likely show which of the following findings? | ||
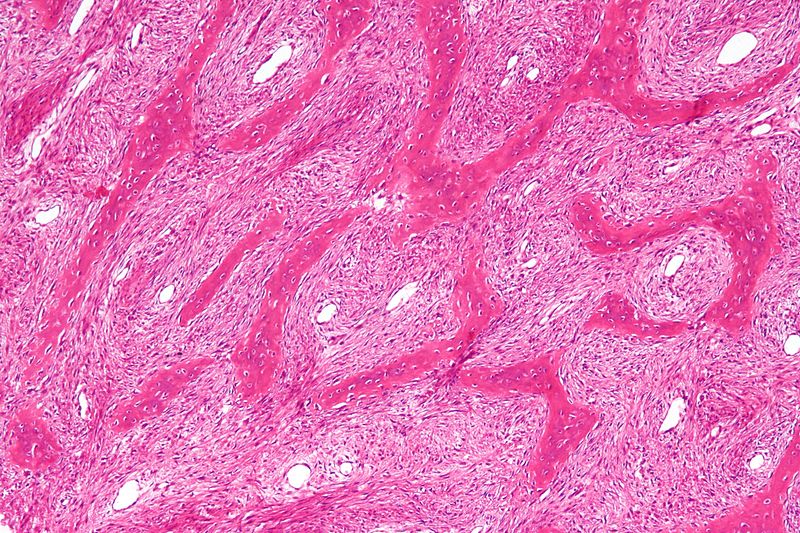
|Explanation=Fibrous dysplasia (FD) of the bone is a rare congenital disease caused by mutations in cAMP regulating protein Gs-alpha. | |Explanation=Fibrous dysplasia (FD) of the bone is a rare congenital disease caused by mutations in cAMP regulating protein Gs-alpha. In patients with fibrodysplasia, bone marrow stromal cells causes abnormal production of fibro-osseous masses of tissue instead of bone. Bone is replaced by fibroblasts, collagen, and irregular bony trabeculae. The most common form of FD is mono-ostotic (involving only one bone). In many cases, the bone findings are incidental during work-up, whereas in other cases patients present with a limp due to involvement of the proximal femur or a bulging mass from the ribs. The lesion in FD may be painless or painful. Less commonly, patient have poly-ostotic disease (involving multiple bones), which is associated with McCune-Albright (endocrinopathy that manifests with precocious puberty and cafe-au-lait spots among young girls). Craniofacial involvement in FD is common and typically involves the skull base. The disease might be extensive and may result in extensive damage that includes visual defects, auditory disturbances, or facial asymmetry. On X-ray, ground glass appearance of bone is characteristic. When the proximal femur is involved, the lesion demonstrates a characteristic "Shepherd's crook" deformity (shown below). On histopathology, FD appears as "Chinese characters" (curvilinear trabeculae) that involve bone trabeculae (shown below).<br> | ||
The most common form of FD is | |||
Craniofacial involvement in FD is common | |||
On | |||
Shown below is a bone biopsy (H&E stain) of a patient with fibrous dysplasia, showing characteristic "Chinese characters" with absence of osteoblastic rimming<br> | |||
[[Image:WBR0765 Fibrous Dysplasia .jpg|500px]]<br><br> | |||
Shown below is an AP x-ray of the right hip that demonstrates a shepherd's crook deformity with intracapsular femoral neck fracture<br> | |||
[[Image:Shepherd's crook deformity.jpg|500px]]<br> | |||
|AnswerA=Spindle-shaped cells with multi-nucleated giant cells | |AnswerA=Spindle-shaped cells with multi-nucleated giant cells | ||
|AnswerAExp=Giant cell tumor (osteoclastoma) is characterized | |AnswerAExp=Giant cell tumor (osteoclastoma) is characterized by spindle-shaped cells with multi-nucleated giant cells. | ||
|AnswerB="Chinese characters" made of bone | |AnswerB="Chinese characters" made of bone trabeculae | ||
|AnswerBExp=Fibrous dysplasia of bone is characterized | |AnswerBExp=Fibrous dysplasia of bone is characterized by "Chinese characters", which are curvilinear trabeculae made of bone trabeculae. | ||
|AnswerC=Small blue anaplastic cells | |AnswerC=Small blue anaplastic cells | ||
|AnswerCExp=Ewing's sarcoma is characterized | |AnswerCExp=Ewing's sarcoma is characterized by small blue anaplastic cells. | ||
|AnswerD=High grade spindle cells that produce osteoid matrix with no cartilage connections | |AnswerD=High-grade spindle cells that produce osteoid matrix with no cartilage connections | ||
|AnswerDExp=Osteoid sarcoma is characteriezd | |AnswerDExp=Osteoid sarcoma is characteriezd by high-grade spindle cells that produce osteoid matrix with no cartilage connections. | ||
|AnswerE=Small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone | |AnswerE=Small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone | ||
|AnswerEExp=Osteoid osteoma is characterized by small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone. | |AnswerEExp=Osteoid osteoma is characterized by small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Fibrous dysplasia manifests with bone lesions that appear as "Chinese characters" in bone trabeculae. | |||
|References=Leet AI, Collins MT. Current approach to fibrous dysplasia of bone and McCune-Albright syndrome. J Child Orthop. 2007;1(1):3-17.<br> | |||
Biopsy Image Attribution: Fibrous dysplasia - intermed mag.jpg by user:Nephron at "http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Fibrous_dysplasia_-_intermed_mag.jpg" under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License v1.2 licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.<br> | |||
X-ray Image Attribution: Al-Mouazzen L, Rajakilendran K, Ahad N. Fibrous dysplasia, shepherd’s crook deformity and an intra-capsular femoral neck fracture. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013;8(3):187-191.<br> | |||
|RightAnswer=B | |RightAnswer=B | ||
|WBRKeyword= | |WBRKeyword=Fibrous dysplasia, Chinese characters, Facial asymmetry, Limp, Bone biopsy, Cafe-au-lait spots, Bone lesions, McCune-Albright syndrome, Endocrinopathy, Shepherd's crook, | ||
|Approved= | |Approved=Yes | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:38, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 14-year-old girl is brought by her mother to the physician's office for facial asymmetry and a limp on the right side. Her past medical history is significant for McCune-Albright syndrome. Physical examination is remarkable for facial asymmetry, breast enlargement, and multiple cafe-au-lait spots on her skin. X-ray of the right proximal femur demonstrates a "ground glass" appearance and findings consistent with a "shepherd's crook" deformity. The physician explains that the patient's condition is caused by a disease of the bone marrow stromal cells with abnormal production of fibro-osseous masses of tissue. Biopsy of the bone lesions will most likely show which of the following findings?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Spindle-shaped cells with multi-nucleated giant cells |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Giant cell tumor (osteoclastoma) is characterized by spindle-shaped cells with multi-nucleated giant cells. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::"Chinese characters" made of bone trabeculae |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Fibrous dysplasia of bone is characterized by "Chinese characters", which are curvilinear trabeculae made of bone trabeculae. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Small blue anaplastic cells |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Ewing's sarcoma is characterized by small blue anaplastic cells. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::High-grade spindle cells that produce osteoid matrix with no cartilage connections |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Osteoid sarcoma is characteriezd by high-grade spindle cells that produce osteoid matrix with no cartilage connections. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Osteoid osteoma is characterized by small circumscribed irregular trabeculae and sclerotic nidus of woven bone. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::B |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Fibrous dysplasia (FD) of the bone is a rare congenital disease caused by mutations in cAMP regulating protein Gs-alpha. In patients with fibrodysplasia, bone marrow stromal cells causes abnormal production of fibro-osseous masses of tissue instead of bone. Bone is replaced by fibroblasts, collagen, and irregular bony trabeculae. The most common form of FD is mono-ostotic (involving only one bone). In many cases, the bone findings are incidental during work-up, whereas in other cases patients present with a limp due to involvement of the proximal femur or a bulging mass from the ribs. The lesion in FD may be painless or painful. Less commonly, patient have poly-ostotic disease (involving multiple bones), which is associated with McCune-Albright (endocrinopathy that manifests with precocious puberty and cafe-au-lait spots among young girls). Craniofacial involvement in FD is common and typically involves the skull base. The disease might be extensive and may result in extensive damage that includes visual defects, auditory disturbances, or facial asymmetry. On X-ray, ground glass appearance of bone is characteristic. When the proximal femur is involved, the lesion demonstrates a characteristic "Shepherd's crook" deformity (shown below). On histopathology, FD appears as "Chinese characters" (curvilinear trabeculae) that involve bone trabeculae (shown below). Shown below is a bone biopsy (H&E stain) of a patient with fibrous dysplasia, showing characteristic "Chinese characters" with absence of osteoblastic rimming |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Fibrous dysplasia, WBRKeyword::Chinese characters, WBRKeyword::Facial asymmetry, WBRKeyword::Limp, WBRKeyword::Bone biopsy, WBRKeyword::Cafe-au-lait spots, WBRKeyword::Bone lesions, WBRKeyword::McCune-Albright syndrome, WBRKeyword::Endocrinopathy, WBRKeyword::Shepherd's crook |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |