WBR0723
{{WBRQuestion
|QuestionAuthor=Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|MainCategory=Pathology
|MainCategory=Pathology
|SubCategory=Vascular
|Prompt=A 38-year-old female patient presents to the physician's office complaining of pain and swelling in her left leg. Upon further questioning, she informs the physician that she recently returned to the United States from a vacation in Europe. Upon physical examination, you observe that the patient experiences tenderness of her left calf with erythema and non-pitting edema, while the right leg appears normal. Following appropriate work-up and imaging, the patient is diagnosed with May-Thurner syndrome. Which of the following anatomic findings best characterizes May-Thurner syndrome?
|Explanation=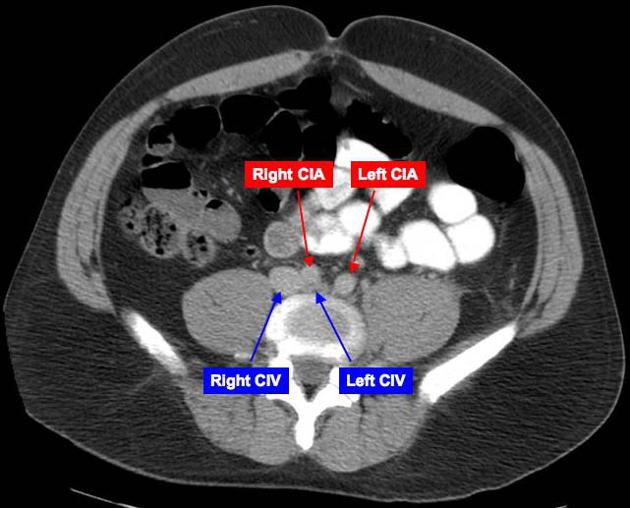 Courtery of radiopaedia.org
Courtery of radiopaedia.org
CIA: Common iliac artery, CIV: Common iliac vein
May-Thurner syndrome (MTS) is also called iliocaval compression syndrome because it is characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac artery. Patients with [[MTS are typically young female patients who present with symptoms consistent with deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
The DVT in MTS is more common on the left side than the right side because of the anatomic etiology of the disease that compresses the left venous side with impaired venous return on that side. However, mechanical compression may not be the only cause of DVTs in patients with MTS; it seems that chronic arterial pulsations from the right common iliac artery cause trauma to the venous wall leading to "spur formation" that contributes to the formation of DVT in these patients.
|EducationalObjectives= MTS is characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac artery.
Reference: Oguzkurt L, Ozkan U, Tercan F, Koc Z. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of iliac vein compression (May-Thurner) syndrome. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2007; 13(3):152-5
Baron HC, Sharms J Wayne M. Iliac vein compression syndrome: A new method of treatment. Am Surg. 2000; 66:653-655. |AnswerA=Compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac artery |AnswerAExp=May-Thurner syndrome (MTS) is characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac artery. |AnswerB=Compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding left iliac artery |AnswerBExp=MTS is not characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding left iliac artery. |AnswerC=Compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac vein |AnswerCExp=MTS is not characterized by the compression of the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding right iliac vein |AnswerD=Compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding left iliac vein |AnswerDExp=MTS is not characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by an overriding left iliac vein. |AnswerE=Compression of the left iliac vein by the iliac crest |AnswerEExp=MTS is not characterized by the compression of the left iliac vein by the iliac crest. |RightAnswer=A |WBRKeyword=may, thurner, syndrome, may-thurner, May-Thurner, May, Thurner, DVT, deep vein thrombosis, edema, erythema, pain, anatomical, iliac, vein, thrombosis, deep, vein |Approved=No }}