WBR0510: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor=[[User:Gonzalo Romero|Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D.]] [mailto:gromero@wikidoc.org] | |QuestionAuthor=[[User:Gonzalo Romero|Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D.]] [mailto:gromero@wikidoc.org] (Reviewed by Will Gibson) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | ||
|SubCategory=Endocrine, Reproductive | |SubCategory=Endocrine, Reproductive | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology, Physiology | ||
|SubCategory=Endocrine, Reproductive | |SubCategory=Endocrine, Reproductive | ||
|Prompt=A pharmacist is planning a study with mice in order to determine the effects of a novel drug called | |Prompt=A pharmacist is planning a study with mice in order to determine the effects of a novel drug called “Compound A572”. He knows that the drug is supposed to work in the hypothalamus, to regulate the release of different pituitary hormones. He measures serum concentration of hypothalamic hormones and determines that the drug causes different changes in FSH and LH if dosed continuously or in a pulsatile fashion. Which of the following drugs has a similar mechanism of action as “Compound A572”? | ||
|Explanation=[[Leuprolide]] is a [[GnRH ]] | |Explanation=[[File:Pituitary Phys.png|center|600px]] | ||
[[Leuprolide]] is a [[GnRH ]] analogue. GnRH is normally secreted in a pulsatile fashion to stimulate the HPA axis. GnRH secretion is negatively regulated by prolactin secreted in the pituitary. GnRH is thought to be positively regulated by kisspeptin, but the precise circuitry underlying the GnRH pulse generator is still unclear. Leuprolide acts similarly to endogenous GnRH; when used in pulsatile fashion, it acts as an agonist, while if used continuously, it acts as an antagonist. Continuous dosing of the drug causes the pituitary to downregulate GnRH receptors due to negative feedback. The anterior pituitary thereby decreases the production of Follice Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Leutenizing Hormone (LH). Recall that FSH and LH are responsible for stimulating the release of sex hormones in both men and women. Leuprolide therefore causes hypogonadism and has important therapeutic roles in diseases associated with the activity of sex hormones. | |||
Leuprolide is often used continuously with flutamide to treat prostatic cancer or uterine fibroids. [[Leuprolide]] is administered in pulsatile dosing in cases of infertility. | |||
|AnswerA=Flutamide | |AnswerA=Flutamide | ||
|AnswerAExp=[[Flutamide]] is a nonsteroidal competitive inhibitor of androgens at the | |AnswerAExp=[[Flutamide]] is a nonsteroidal competitive inhibitor of androgens at the androgen receptor. It is used to treat [[prostate cancer]] and hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovarian syndrome. | ||
|AnswerB=Finasteride | |AnswerB=Finasteride | ||
|AnswerBExp=[[Finasteride]] is a 5 | |AnswerBExp=[[Finasteride]] is a 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia and male-pattern baldness. | ||
|AnswerC=Mifepristone | |AnswerC=Mifepristone | ||
|AnswerCExp= | |AnswerCExp=[[Mifepristone]] is a competitive inhibitor of progestins at the [[progesterone]] receptors. It is used to terminate [[pregnancy]] in combination with [[misoprostol]] (PGE1 analogue). | ||
|AnswerD= | |AnswerD=Ketoconazole | ||
|AnswerDExp= [[ | |AnswerDExp=[[Ketoconazole]] is a steroid synthesis inhibitor that inhibits desmolase, the enzyme responsible for transforming [[cholesterol]] into [[pregnenolone]]. | ||
|AnswerE=Leuprolide | |AnswerE=Leuprolide | ||
|AnswerEExp= | |AnswerEExp=Leuprolide is a GnRH analogue. When dosed continuously, it inhibits the production of FSH and LH, thereby leading to hypogonadism. When dosed in a pulsatile manner, it increases the production of FSH and LH. In turn, FSH and LH stimulate the production of sex hormones. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Leuprolide is a GnRH analogue, which acts on the pituitary. If used continously it decreases FSH and LH. If used in a pulsatile fashion it increases FSH and LH levels. | |||
|References=Okamura H, Tsukamura H, Ohkura S, Uenoyama Y, Wakabayashi Y, Maeda K. Kisspeptin and GnRH pulse generation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;784:297-323. | |||
<br>Friedman, A. J., Barbieri, R. L., Doubilet, P. M., Fine, C. A. L. L. I. O. P. E., & Schiff, I. S. A. A. C. (1988). A randomized, double-blind trial of a gonadotropin releasing-hormone agonist (leuprolide) with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of leiomyomata uteri. Fertility and sterility, 49(3), 404-409. | |||
<br>Crawford, E. D., Eisenberger, M. A., McLeod, D. G., Spaulding, J. T., Benson, R., Dorr, F. A., ... & Goodman, P. J. (1989). A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 321(7), 419-424. | |||
<br>First Aid 2014 page 590 | |||
|RightAnswer=E | |RightAnswer=E | ||
|WBRKeyword=Pituitary hormones | |WBRKeyword=Pituitary hormones, Pituitary, Hypothalamus, GnRH, Gonadotropins, Gonadotropin releasing hormone, Gonadotropin, Leuprolide, Hormone | ||
|Approved= | |Approved=Yes | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:48, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D. [1] (Reviewed by Will Gibson)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pharmacology, MainCategory::Physiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Endocrine, SubCategory::Reproductive |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A pharmacist is planning a study with mice in order to determine the effects of a novel drug called “Compound A572”. He knows that the drug is supposed to work in the hypothalamus, to regulate the release of different pituitary hormones. He measures serum concentration of hypothalamic hormones and determines that the drug causes different changes in FSH and LH if dosed continuously or in a pulsatile fashion. Which of the following drugs has a similar mechanism of action as “Compound A572”?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Flutamide |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Flutamide is a nonsteroidal competitive inhibitor of androgens at the androgen receptor. It is used to treat prostate cancer and hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovarian syndrome.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Finasteride |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Finasteride is a 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia and male-pattern baldness.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Mifepristone |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Mifepristone is a competitive inhibitor of progestins at the progesterone receptors. It is used to terminate pregnancy in combination with misoprostol (PGE1 analogue).]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Ketoconazole |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Ketoconazole is a steroid synthesis inhibitor that inhibits desmolase, the enzyme responsible for transforming cholesterol into pregnenolone.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Leuprolide |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Leuprolide is a GnRH analogue. When dosed continuously, it inhibits the production of FSH and LH, thereby leading to hypogonadism. When dosed in a pulsatile manner, it increases the production of FSH and LH. In turn, FSH and LH stimulate the production of sex hormones.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::E |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::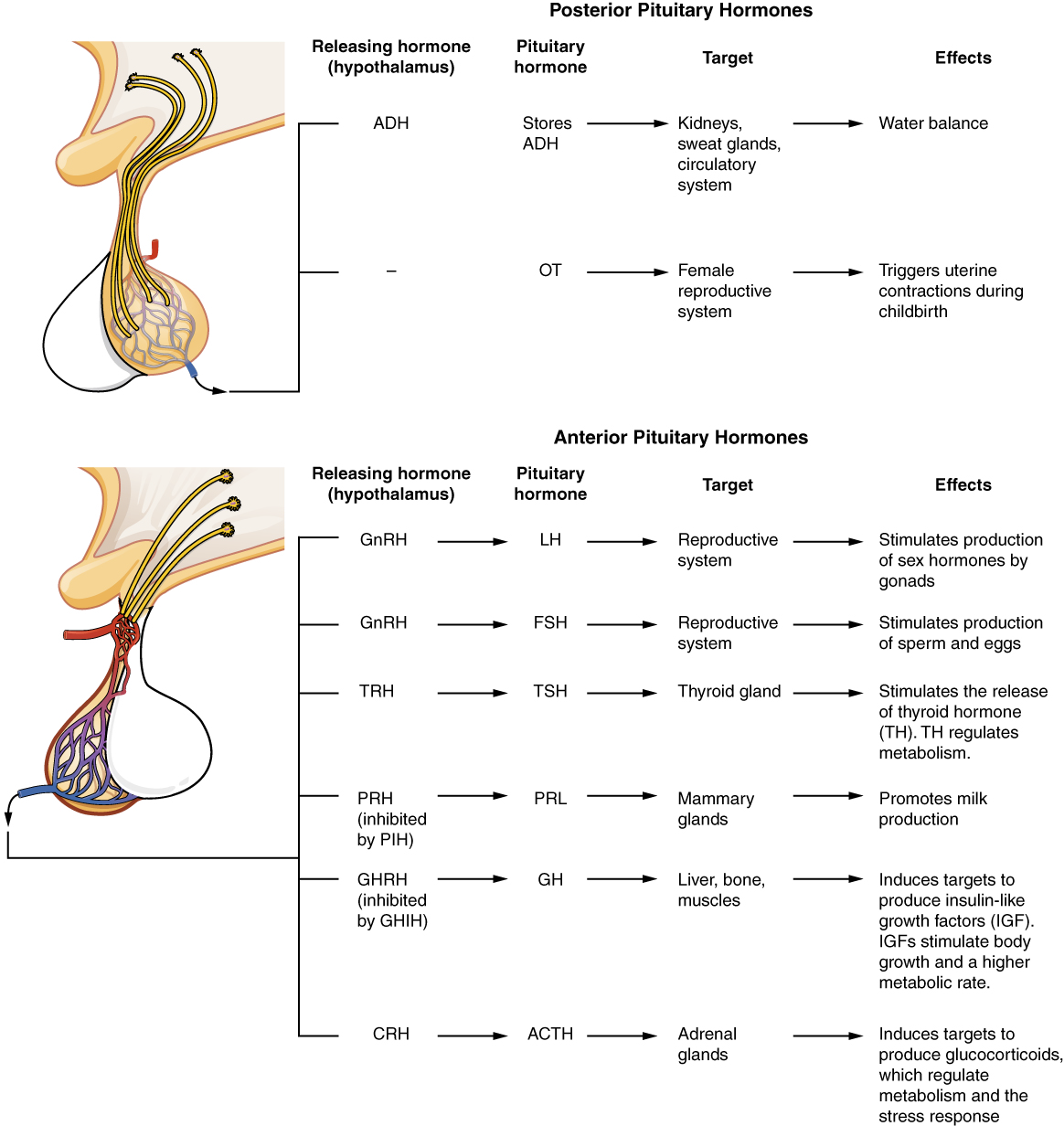 Leuprolide is a GnRH analogue. GnRH is normally secreted in a pulsatile fashion to stimulate the HPA axis. GnRH secretion is negatively regulated by prolactin secreted in the pituitary. GnRH is thought to be positively regulated by kisspeptin, but the precise circuitry underlying the GnRH pulse generator is still unclear. Leuprolide acts similarly to endogenous GnRH; when used in pulsatile fashion, it acts as an agonist, while if used continuously, it acts as an antagonist. Continuous dosing of the drug causes the pituitary to downregulate GnRH receptors due to negative feedback. The anterior pituitary thereby decreases the production of Follice Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Leutenizing Hormone (LH). Recall that FSH and LH are responsible for stimulating the release of sex hormones in both men and women. Leuprolide therefore causes hypogonadism and has important therapeutic roles in diseases associated with the activity of sex hormones. Leuprolide is often used continuously with flutamide to treat prostatic cancer or uterine fibroids. Leuprolide is administered in pulsatile dosing in cases of infertility. |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Pituitary hormones, WBRKeyword::Pituitary, WBRKeyword::Hypothalamus, WBRKeyword::GnRH, WBRKeyword::Gonadotropins, WBRKeyword::Gonadotropin releasing hormone, WBRKeyword::Gonadotropin, WBRKeyword::Leuprolide, WBRKeyword::Hormone |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |