WBR0505: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{WBRQuestion |QuestionAuthor=Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D. [mailto:gromero@wikidoc.org] |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 |MainCategory=Pathology |SubCategory=Neurolog...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Neurology, Reproductive | |SubCategory=Neurology, Reproductive | ||
|Prompt=A 57- year old patient comes to the ER after presenting with | |Prompt=A 57- year-old male patient comes to the ER after presenting with visual deficits. The symptoms have been gradually worsening over the last 6 months. His family history is insignificant. His wife denies any history of trauma or drug ingestion. The physician on call performs a thorough history and physical examination. His vitals are within normal limits. The physician encounters on neurological exam a right hemianopsia with macular sparing, and becomes concerned that the patient may have a stroke or a tumor. A CT scan is ordered and shows a mass in the posterior fossa. Following 48 hours of admission the patient develops a Grand-mal seizure and undergoes respiratory arrest. Despite aggressive resuscitation measures the patient dies. The team on call is concerned about malpraxis and orders an autopsy with the wife’s consent. Upon entering the skull, the pathologist notices a tumor arising from the membranes covering the brain. A specimen under the microscope shows the picture below. Which of the following ovarian tumors is also associated with the latter histologic findings of this tumor? | ||
[[File:WBR0505.jpg|center|pix200]] | |||
|Explanation=This patient is presenting with visual hallucinations and visual deficits which have been worsened over time and right hemianopsia with macular sparing, on CT scan a tumor rising from the occipital region of the meninges correlate with the clinical findings. The histo-pathologic findings of laminated, concentric, calcific spherules are also known as Psammoma bodies which are diagnostic for a meningioma compressing the occipital lobe. Psammoma bodies are also found in: | |||
Following 48 hours of admission the patient develops a Grand-mal seizure and undergoes respiratory arrest. Despite aggressive resuscitation measures the patient dies. The team on call is concerned about malpraxis and orders an autopsy with the wife’s consent. Upon entering the skull, the pathologist notices a tumor arising from the membranes covering the brain. | |||
|Explanation= | |||
# Papillary adenocarcinoma of thyroid | # Papillary adenocarcinoma of thyroid | ||
# Serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary | # Serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary | ||
Revision as of 19:37, 24 September 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology, SubCategory::Reproductive |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 57- year-old male patient comes to the ER after presenting with visual deficits. The symptoms have been gradually worsening over the last 6 months. His family history is insignificant. His wife denies any history of trauma or drug ingestion. The physician on call performs a thorough history and physical examination. His vitals are within normal limits. The physician encounters on neurological exam a right hemianopsia with macular sparing, and becomes concerned that the patient may have a stroke or a tumor. A CT scan is ordered and shows a mass in the posterior fossa. Following 48 hours of admission the patient develops a Grand-mal seizure and undergoes respiratory arrest. Despite aggressive resuscitation measures the patient dies. The team on call is concerned about malpraxis and orders an autopsy with the wife’s consent. Upon entering the skull, the pathologist notices a tumor arising from the membranes covering the brain. A specimen under the microscope shows the picture below. Which of the following ovarian tumors is also associated with the latter histologic findings of this tumor?
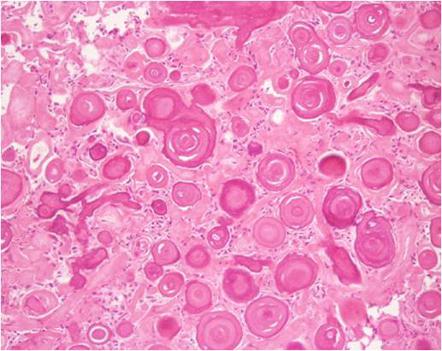 |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Granulosa cell tumor |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp:: |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Brenner tumor |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp:: |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp:: |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Serous cystadenoma |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp:: |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Kruckenberg tumor |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp:: |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::This patient is presenting with visual hallucinations and visual deficits which have been worsened over time and right hemianopsia with macular sparing, on CT scan a tumor rising from the occipital region of the meninges correlate with the clinical findings. The histo-pathologic findings of laminated, concentric, calcific spherules are also known as Psammoma bodies which are diagnostic for a meningioma compressing the occipital lobe. Psammoma bodies are also found in:
Educational Objective: |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Psammoma bodies |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |