Sulfadiazine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Deepika Beereddy, MBBS [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Sulfadiazine is a anti-infective, anti-parasitic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of {{{indication}}}. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Acute otitis media, Due to Haemophilus influenzae, in combination with penicillin
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Chancroid
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Congenital toxoplasmosis; Adjunct
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Haemophilus influenzae meningitis, In combination with parenteral streptomycin; Adjunct
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sulfadiazine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sulfadiazine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Sulfadiazine in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sulfadiazine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sulfadiazine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Sulfadiazine is contraindicated in the following circumstances: Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides.
In infants less than 2 months of age (except as adjunctive therapy with pyrimethamine in the treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis).
In pregnancy at term and during the nursing period, because sulfonamides cross the placenta and are excreted in breast milk and may cause kernicterus.
Warnings
The sulfonamides should not be used for the treatment of group A betahemolytic streptococcal infections. In an established infection, they will not eradicate the streptococcus and, therefore, will not prevent sequelae such as rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis.
Deaths associated with the administration of sulfonamides have been reported from hypersensitivity reactions, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and other blood dyscrasias.
The presence of such clinical signs as sore throat, fever, pallor, purpura or jaundice may be early indications of serious blood disorders.
The frequency of renal complications is considerably lower in patients receiving the more soluble sulfonamides.
Precautions
General
Sulfonamides should be given with caution to patients with impaired renal or hepatic function and to those with severe allergy or bronchial asthma.
Hemolysis may occur in individuals deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This reaction is dose related.
Adequate fluid intake must be maintained in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation.
Laboratory Tests
Complete blood counts and urinalyses with careful microscopic examinations should be done frequently in patients receiving sulfonamides.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Blood Dyscrasias
Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, purpura, hypoprothrombinemia and methemoglobinemia.
Allergic Reactions
Erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), generalized skin eruptions, epidermal necrolysis, urticaria, serum sickness, pruritus, exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylactoid reactions, periorbital edema, conjunctival and scleral injection, photosensitization, arthralgia, allergic myocarditis, drug fever and chills.
Gastrointestinal Reactions
Nausea, emesis, abdominal pains, hepatitis, diarrhea, anorexia, pancreatitis and stomatitis.
C.N.S. Reactions
Headache, peripheral neuritis, mental depression, convulsions, ataxia, hallucinations, tinnitus, vertigo and insomnia.
Renal
Crystalluria, stone formation, toxic nephrosis with oliguria and anuria; periarteritis nodosa and lupus erythematosus phenomenon have been noted.
Miscellaneous Reactions
The sulfonamides bear certain chemical similarities to some goitrogens, diuretics (acetazolamide and the thiazides) and oral hypoglycemic agents. Goiter production, diuresis, and hypoglycemia have occurred rarely in patients receiving sulfonamides. Cross-sensitivity may exist with these agents.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
Administration of a sulfonamide may increase the effect of oral anticoagulants and methotrexate, probably by displacement of these drugs from binding sites on plasma albumin. Potentiation of the action of sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agents, thiazide diuretics and uricosuric agents may also be noted. This may also be due to displacement of the drugs from albumin or a pharmacodynamic mechanism may play a role. Conversely, agents such as indomethacin, probenecid and salicylates may displace sulfonamides from plasma albumin and increase the concentrations of free drug in plasma.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
The safe use of sulfonamides in pregnancy has not been established. The teratogenic potential of most sulfonamides has not been thoroughly investigated in either animals or humans. However, a significant increase in the incidence of cleft palate and other bony abnormalities in offspring has been observed when certain sulfonamides of the short, intermediate and long acting types were given to pregnant rats and mice in high oral doses (7 to 25 times the human therapeutic dose).
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Sulfadiazine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Sulfadiazine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Sulfadiazine is contraindicated for use in nursing mothers because the sulfonamides cross the placenta, are excreted in breast milk and may cause kernicterus.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from sulfadiazine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. See CONTRAINDICATIONS.
Pediatric Use
Sulfadiazine is contraindicated in infants less than 2 months of age (except as adjunctive therapy with pyrimethamine in the treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis). See CONTRAINDICATIONSand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sulfadiazine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Sulfadiazine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
SYSTEMIC SULFONAMIDES ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN INFANTS UNDER 2 MONTHS OF AGE except as adjunctive therapy with pyrimethamine in the treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis.
Usual Dosage for Infants over 2 Months of Age and Children
Initially, one-half the 24-hour dose. Maintenance, 150 mg/kg or 4 g/m2, divided into 4 to 6 doses, every 24 hours, with a maximum of 6 g every 24 hours. Rheumatic fever prophylaxis, under 30 kg (66 pounds), 500 mg every 24 hours; over 30 kg (66 pounds), 1 g every 24 hours.
Usual Adult Dosage
Initially, 2 g to 4 g. Maintenance, 2 g to 4 g, divided into 3 to 6 doses, every 24 hours.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
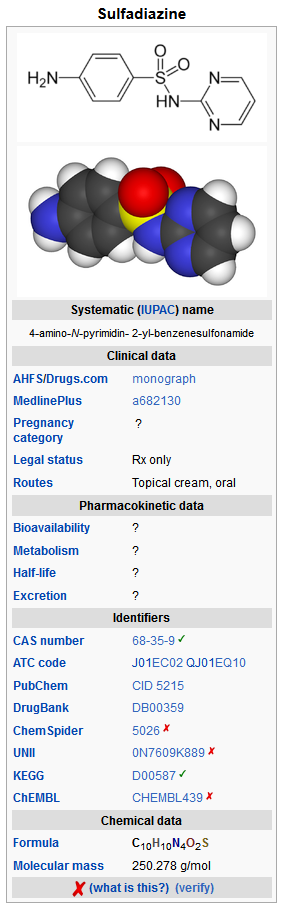
Mechanism of Action
The systemic sulfonamides are bacteriostatic agents having a similar spectrum of activity. Sulfonamides competitively inhibit bacterial synthesis of folic acid (pteroylglutamic acid) from aminobenzoic acid. Resistant strains are capable of utilizing folic acid precursors or preformed folic acid.
Structure
Sulfadiazine is an oral sulfonamide anti-bacterial agent.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 500 mg sulfadiazine. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, docusate sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, sodium benzoate, sodium starch glycolate and stearic acid.
Sulfadiazine occurs as a white or slightly yellow powder. It is odorless or nearly so and slowly darkens on exposure to light. It is practically insoluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The chemical name of sulfadiazine is N1-2-pyrimidinylsulfanilamide. The molecular formula is C10H10N4O2S. It has a molecular weight of 250.27. The structural formula is shown below:
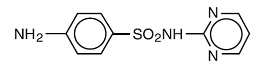
Most sulfonamides slowly darken on exposure to light.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfonamides exist in the blood in 3 forms - free, conjugated (acetylated and possibly others) and protein bound. The free form is considered to be the therapeutically active one.
Sulfadiazine given orally is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After a single 2 g oral dose, a peak of 6.04 mg/100 mL is reached in 4 hours; of this, 4.65 mg/100 mL is free drug.
When a dose of 100 mg/kg of body weight is given initially and followed by 50 mg/kg every 6 hours, blood levels of free sulfadiazine are about 7 mg/100mL. Protein binding is 38% to 48%. Sulfadiazine diffuses into the cerebrospinal fluid; free drug reaches 32% to 65% of blood levels and total drug 40% to 60%.
Sulfadiazine is excreted largely in the urine, where concentrations are 10 to 25 times greater than serum levels. Approximately 10% of a single oral dose is excreted in the first 6 hours, 50% within 24 hours and 60% to 85% in 48 to 72 hours. Of the amount excreted in the urine, 15% to 40% is in the acetyl form.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The sulfonamides bear certain chemical similarities to some goitrogens. Rats appear to be especially susceptible to the goitrogenic effects of sulfonamides and long-term administration has produced thyroid malignancies in rats.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Sulfadiazine in the drug label.
How Supplied
- SulfADIAZine Tablets USP for oral administration are available as:
500 mg: white, unscored, capsule-shaped tablets, debossed “E 757” on one face and supplied as:
NDC 0185-0757-30 bottles of 30
NDC 0185-0757-01 bottles of 100
NDC 0185-0757-10 bottles of 1000
Storage
Storage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP with a child-resistant closure, as required.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sandoz Inc. at 1-800-525-8747 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Sulfadiazine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

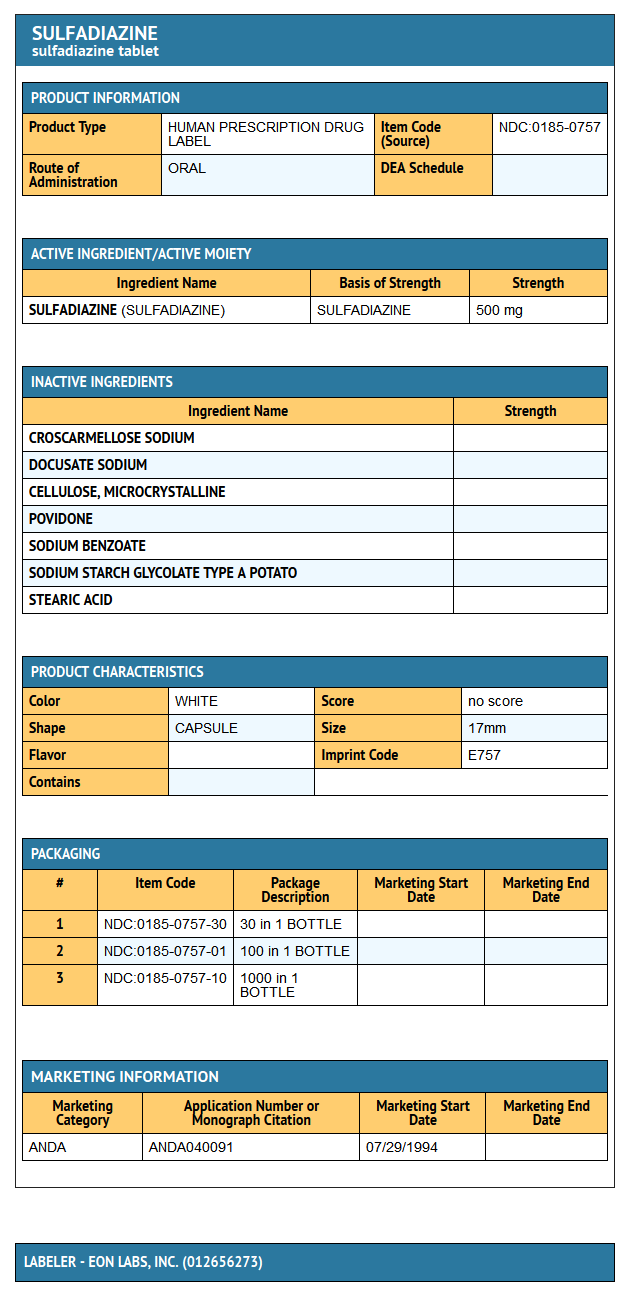
{{#ask: Label Page::Sulfadiazine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Information for Patients
Patients should be instructed to drink an eight ounce glass of water with each dose of medication and at frequent intervals throughout the day. Caution patients to report promptly the onset of sore throat, fever, pallor, purpura or jaundice when taking this drug, since these may be early indications of serious blood disorders.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Sulfadiazine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Sulfadiazine
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sulfadiazine |Label Name=Sulfadiazine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sulfadiazine |Label Name=Sulfadiazine11.png
}}