Struma ovarii echocardiography/ultrasound: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
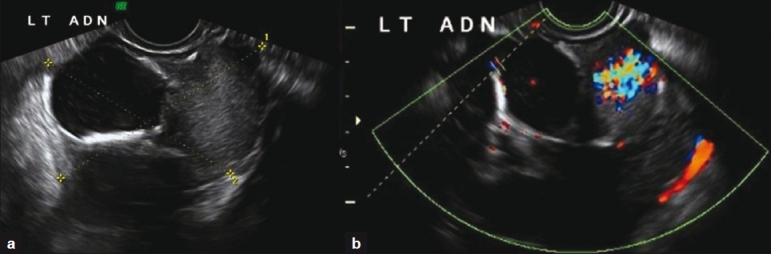
[[File:Struma_ovarii_Transabdomen_grayscale_US.jpg|thumb|none|450px| Transabdomen grayscale US image shows a heterogeneous lesion demonstrating solid and cystic portions arising from the left ovary. <ref name="pmid22315711">{{cite journal |vauthors=Alvarez DM, Lee V, Bhatt S, Dogra VS |title=Struma ovarii with papillary thyroid carcinoma |journal=J Clin Imaging Sci |volume=1 |issue= |pages=44 |year=2011 |pmid=22315711 |pmc=3272908 |doi=10.4103/2156-7514.84322 |url=}}</ref> ]] | [[File:Struma_ovarii_Transabdomen_grayscale_US.jpg|thumb|none|450px| Transabdomen grayscale US image shows a heterogeneous lesion demonstrating solid and cystic portions arising from the left ovary. <ref name="pmid22315711">{{cite journal |vauthors=Alvarez DM, Lee V, Bhatt S, Dogra VS |title=Struma ovarii with papillary thyroid carcinoma |journal=J Clin Imaging Sci |volume=1 |issue= |pages=44 |year=2011 |pmid=22315711 |pmc=3272908 |doi=10.4103/2156-7514.84322 |url=}}</ref> ]] | ||
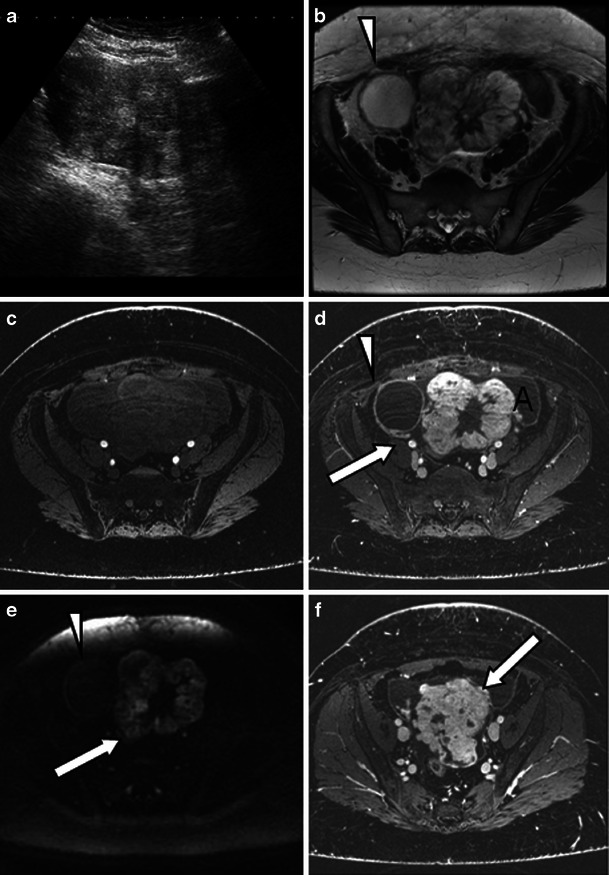
[[File:Struma_ovarii_-_ultrasound_2.jpg |thumb|none|450px| (a) Ultrasound shows a mixed solid cystic mass with predominantly solid features. On the 3-T T2-weighted high-resolution (b), unenhanced (c) and enhanced (d, f) T1 fat-saturated LAVA and diffusion-weighted images b = 1,200 mm/s2 (e), imaging features resemble a mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. d, e The lacy pattern caused by the enhancing solid elements (representing thyroid tissue) can be seen on T1 post-contrast imaging (d) and diffusion imaging (e) might be the only feature to suggest a struma. d, f Ascites is present (A) as well as extracapsular extension which is seen as tumour nodules on the capsular surface (arrow). d, e Some contrast medium uptake is shown in the tissues between the ovary and pelvic sidewall on the right (arrow). b, d, e A simple cyst arising from the right ovary does not present with restricted diffusion (arrowheads) <ref name="pmid24357453">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dujardin MI, Sekhri P, Turnbull LW |title=Struma ovarii: role of imaging? |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=5 |issue=1 |pages=41–51 |year=2014 |pmid=24357453 |pmc=3948908 |doi=10.1007/s13244-013-0303-3 |url=}}</ref> ]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 01:30, 11 August 2017
|
Struma ovarii Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Struma ovarii echocardiography/ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Struma ovarii echocardiography/ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Struma ovarii echocardiography/ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
- There are no echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with [disease name].
OR
- Echocardiography/ultrasound may be helpful in the diagnosis of [disease name]. Findings on an echocardiography/ultrasound suggestive of/diagnostic of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
- There are no echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with [disease name]. However, an echocardiography/ultrasound may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include [complication 1], [complication 2], and [complication 3].
Ultrasound
- Ultrasound may be helpful in the diagnosis of Struma ovarii. Findings on an echocardiography/ultrasound suggestive of Struma ovarii occurred more frequently (68.8%) in the right adnexa and was seen with a normal CA-125 level. [1]
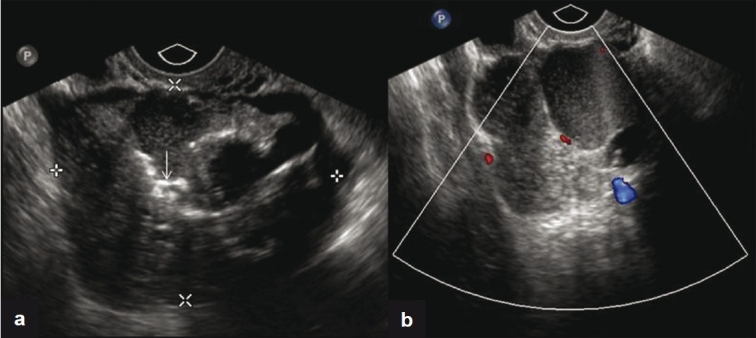
- Doppler flow study may help in the preoperative diagnosis of struma ovarii. In struma ovarii the blood flow signals may be more commonly detected from the center of the echoic lesion and areas of low resistance to flow. [1]
Findings on an ultrasound suggestive of Struma ovarii include:
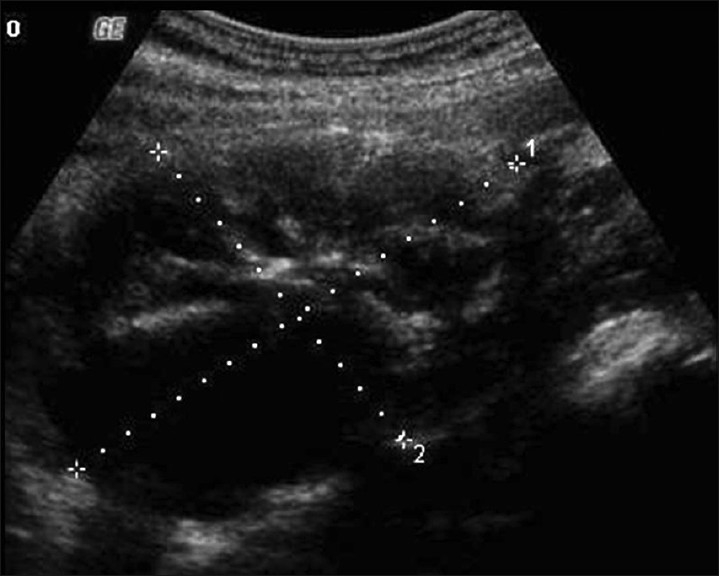
- Transvaginal ultrasound shows solid and cystic components of the ovary and also calcifications. [2]
- Transabdomen grayscale ultrasound image helps demonstrate solid and cystic portions arising from the ovary. [2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zalel Y, Seidman DS, Oren M, Achiron R, Gotlieb W, Mashiach S, Goldenberg M (2000). "Sonographic and clinical characteristics of struma ovarii". J Ultrasound Med. 19 (12): 857–61. PMID 11127011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Alvarez DM, Lee V, Bhatt S, Dogra VS (2011). "Struma ovarii with papillary thyroid carcinoma". J Clin Imaging Sci. 1: 44. doi:10.4103/2156-7514.84322. PMC 3272908. PMID 22315711.
- ↑ Dujardin MI, Sekhri P, Turnbull LW (2014). "Struma ovarii: role of imaging?". Insights Imaging. 5 (1): 41–51. doi:10.1007/s13244-013-0303-3. PMC 3948908. PMID 24357453.