Stomach cancer other imaging findings: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*Lesion on nondependent or anterior wall; etched in white by a thin layer of barium trapped between edge of mass & adjacent mucosa | *Lesion on nondependent or anterior wall; etched in white by a thin layer of barium trapped between edge of mass & adjacent mucosa | ||
*Ulcerated carcinoma (penetrating cancer): 70% of all gastric cancers<ref>http://radiopaedia.org/articles/gastric-carcinoma</ref> | *Ulcerated carcinoma (penetrating cancer): 70% of all gastric cancers<ref>http://radiopaedia.org/articles/gastric-carcinoma</ref> | ||
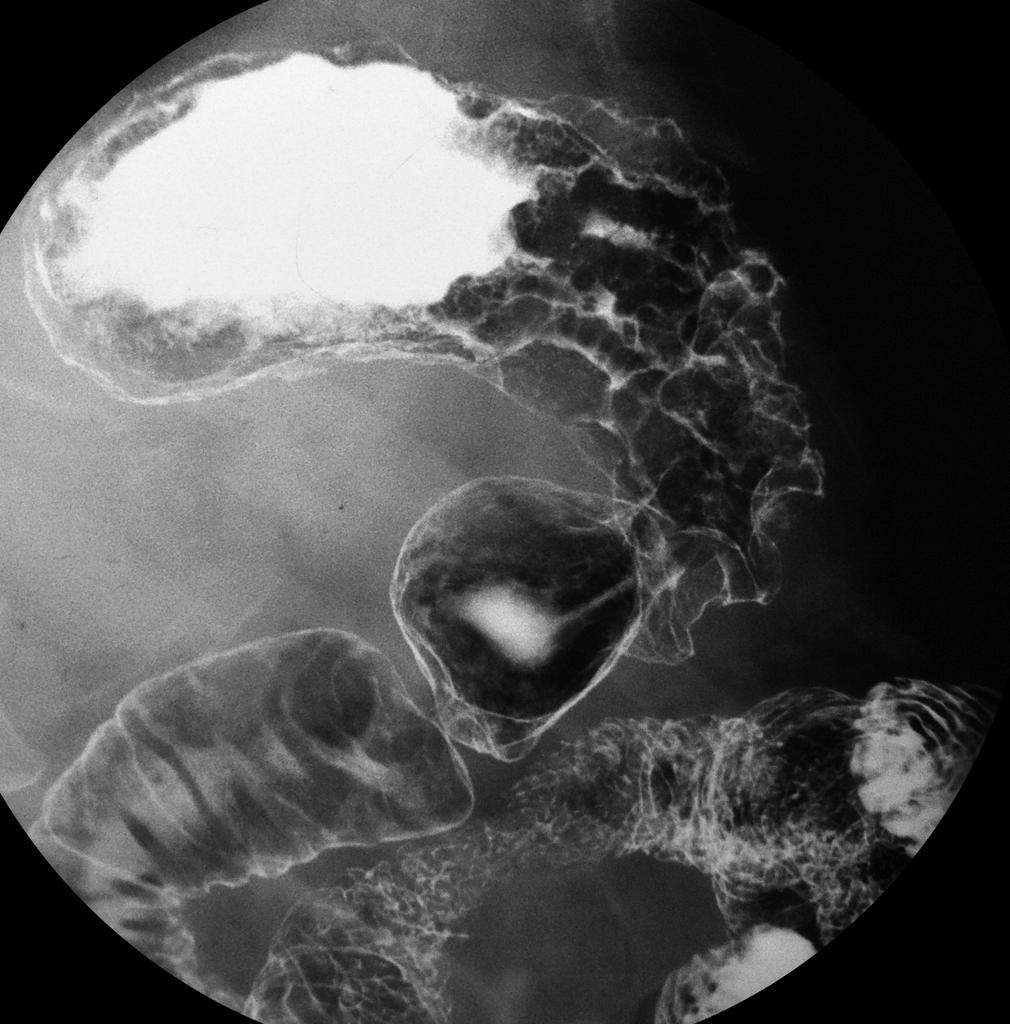
[[File:Gastric-carcinoma.jpg|300px|center|thumb|Double contrast images from a barium meal study showing an advanced gastric malignancy involving the body of stomach, source: Case courtesy of Dr Ian Bickle, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 21214]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 19:32, 16 November 2017
|
Stomach cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Stomach cancer other imaging findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Stomach cancer other imaging findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Stomach cancer other imaging findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Parminder Dhingra, M.D. [2]
Overview
Fluoroscopy may be diagnostic of stomach cancer.
Barium studies
Barium studies can identify both malignant gastric ulcers and infiltrating lesions
false-negative barium studies can occur in as many as 50 percent of cases [17].
early gastric cancer where the sensitivity of barium meals may be as low as 14 percent [18].
Early gastric cancer (elevated, superficial, shallow):
- Type I: elevated lesion, protrudes >5 mm into lumen (polypoid)
- Type II: superficial lesion (plaque-like, mucosal nodularity, ulceration)
- Type III: shallow, irregular ulcer crater with adjacent nodular mucosa and clubbing/fusion/amputation of radiation folds
Advanced gastric cancer:
- Polypoid cancer can be lobulated or fungating
- Lesion on dependent or posterior wall; filling defect in barium pool
- Lesion on nondependent or anterior wall; etched in white by a thin layer of barium trapped between edge of mass & adjacent mucosa
- Ulcerated carcinoma (penetrating cancer): 70% of all gastric cancers[1]