Rifampin (oral)
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=Kiran Singh, M.D. [1] |aOrAn=a |adverseReactions= |blackBoxWarningTitle=ConditionName: |blackBoxWarningBody=ConditionName:
- Content
|fdaLIADAdult===Indications==
- In the treatment of both tuberculosis and the meningococcal carrier state, the small number of resistant cells present within large populations of susceptible cells can rapidly become the predominant type. Bacteriologic cultures should be obtained before the start of therapy to confirm the susceptibility of the organism to rifampin and they should be repeated throughout therapy to monitor the response to treatment. Since resistance can emerge rapidly, susceptibility tests should be performed in the event of persistent positive cultures during the course of treatment. If test results show resistance to rifampin and the patient is not responding to therapy, the drug regimen should be modified.
Tuberculosis Rifampin is indicated in the treatment of all forms of tuberculosis.
A three-drug regimen consisting of rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide [e.g., RIFATER®]5 is recommended in the initial phase of short-course therapy which is usually continued for 2 months. The Advisory Council for the Elimination of Tuberculosis, the American Thoracic Society, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that either streptomycin or ethambutol be added as a fourth drug in a regimen containing isoniazid (INH), rifampin, and pyrazinamide for initial treatment of tuberculosis unless the likelihood of INH resistance is very low. The need for a fourth drug should be reassessed when the results of susceptibility testing are known. If community rates of INH resistance are currently less than 4%, an initial treatment regimen with less than four drugs may be considered.
Following the initial phase, treatment should be continued with rifampin and isoniazid [e.g., RIFAMATE®]6 for at least 4 months. Treatment should be continued for longer if the patient is still sputum or culture positive, if resistant organisms are present, or if the patient is HIV positive.
Meningococcal Carriers Rifampin is indicated for the treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis to eliminate meningococci from the nasopharynx. Rifampin is not indicated for the treatment of meningococcal infection because of the possibility of the rapid emergence of resistant organisms. (See WARNINGS).
Rifampin should not be used indiscriminately, and therefore, diagnostic laboratory procedures, including serotyping and susceptibility testing, should be performed for establishment of the carrier state and the correct treatment. So that the usefulness of rifampin in the treatment of asymptomatic meningococcal carriers is preserved, the drug should be used only when the risk of meningococcal disease is high.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of rifampin and other antibacterial drugs, rifampin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy |offLabelAdultGuideSupport======Condition1=====
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in adult patients.
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport======Condition1=====
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in adult patients.
|fdaLIADPed======Condition1=====
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
|offLabelPedGuideSupport======Condition1=====
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport======Condition1=====
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Rifampin (oral) in pediatric patients.
|contraindications=* Rifampin is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to rifampin or any of the components, or to any of the rifamycins.
- Rifampin is contraindicated in patients who are also receiving ritonavir-boosted saquinavir due to an increased risk of severe hepatocellular toxicity.
- Rifampin is contraindicated in patients who are also receiving atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, saquinavir, or tipranavir due to the potential of rifampin to substantially decrease plasma concentrations of these antiviral drugs, which may result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
|clinicalTrials=There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
|postmarketing=There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
|drugInteractions=* Drug
- Description
|useInPregnancyFDA=* Pregnancy Category |useInPregnancyAUS=* Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Rifampin (oral) in women who are pregnant. |useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of Rifampin (oral) during labor and delivery. |useInNursing=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to nursing mothers. |useInPed=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to pediatric patients. |useInGeri=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to geriatric patients. |useInGender=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to specific gender populations. |useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) with respect to specific racial populations. |useInRenalImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients with renal impairment. |useInHepaticImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients with hepatic impairment. |useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Rifampin (oral) in women of reproductive potentials and males. |useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Rifampin (oral) in patients who are immunocompromised.
|administration=* Oral
- Intravenous
|monitoring=There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
- Description
|IVCompat=There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|overdose====Acute Overdose===
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|drugBox=
|mechAction=* Rifampin inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms. Specifically, it interacts with bacterial RNA polymerase but does not inhibit the mammalian enzyme.
|structure=* Rifampin capsules, USP for oral administration contain 150 mg or 300 mg rifampin per capsule. The 150 mg and 300 mg capsules also contain, as inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Red No. 40, gelatin, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
- The printing ink contains ammonium hydroxide, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, pharmaceutical glaze, propylene glycol, simethicone, and titanium dioxide
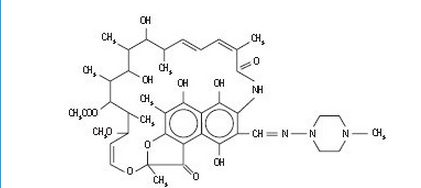
- Rifampin is a semisynthetic antibiotic derivative of rifamycin SV. Rifampin is a red-brown crystalline powder very slightly soluble in water at neutral pH, freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in ethyl acetate and in methanol. Its molecular weight is 822.95 and its chemical formula is C43H58N4O12.
- The chemical name for rifampin is either:
3-[[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl]rifamycin
or 5,6,9,17,19,21-hexahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,20,22-heptamethyl-8-[N-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)formimidoyl]-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-1,11(2H)-dione 21-acetate.
- Its structural formula is:
|PD=There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|PK=There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|nonClinToxic=There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|clinicalStudies=There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|howSupplied=* |packLabel= |fdaPatientInfo=There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Rifampin (oral) in the drug label.
|alcohol=* Alcohol-Rifampin (oral) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
|brandNames=* ®[1]
|lookAlike=* A® — B®[2]
|drugShortage= }} {{#subobject:
|Page Name=Rifampin (oral)
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Rifampin (oral) |Label Name=Rifampin (oral)11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Rifampin (oral) |Label Name=Rifampin (oral)11.png
}}
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)