Ranula: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
'''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' Berna Zorkun DMD [mailto:bernazorkun@gmail.com] | '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' Berna Zorkun DMD [mailto:bernazorkun@gmail.com] | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
A '''ranula''' is a type of [[mucocele]] found on the floor of the [[mouth]]. Ranulas present as a [[Swelling (medical)|swelling]] of [[connective tissue]] consisting of collected [[mucin]] from a ruptured [[salivary gland]] [[duct]], which is usually caused by local trauma. | A '''ranula''' is a type of [[mucocele]] found on the floor of the [[mouth]]. Ranulas present as a [[Swelling (medical)|swelling]] of [[connective tissue]] consisting of collected [[mucin]] from a ruptured [[salivary gland]] [[duct]], which is usually caused by local trauma. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 31: | ||
==Appearance== | ==Appearance== | ||
An oral ranula is a fluctuant swelling with a bluish translucent color that somewhat resembles the underbelly of a frog | An oral ranula is a fluctuant swelling with a bluish translucent color that somewhat resembles the underbelly of a frog "Rana". If it is deeper it does not have this bluish appearance. If it is large ( 2 or more cm.), it may hide the salivary gland and affect the location of the tongue. Most frequently it stems from the sublingual [[salivary gland]], but also from the [[submandibular gland]]. | ||
Though normally above the [[mylohyoid muscle]], if a ranula is found deeper in the floor of the mouth, it can appear to have a normal color. A ranula below the mylohyoid muscle is referred to as a "plunging or cervical ranula", and produces swelling of the neck with or without swelling in the floor of the mouth. | Though normally above the [[mylohyoid muscle]], if a ranula is found deeper in the floor of the mouth, it can appear to have a normal color. A ranula below the [[mylohyoid muscle]] is referred to as a "plunging or cervical ranula", and produces swelling of the neck with or without swelling in the floor of the mouth. | ||
Ranulas measure several centimeters in diameter and are usually larger than [[ | Ranulas measure several centimeters in diameter and are usually larger than [[mucocele]]s. As a result, when ranulas are present the tongue may be elevated. As with [[mucocele]]s, ranulas may be subject to recurrent swelling with occasional rupturing of its contents. When pressed, they may not blanch. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Ranulas are usually asymptomatic, although they may change gradually in size, shrinking and swelling. The overlying skin is usually intact. The mass is not fixed and is also not tender. The mass is not connected to the thyroid gland or lymph nodes. The mass may not be well defined. If it gets large enough it may interfere with swallowing, and cervical ranulas may even interfere with breathing. Some pain may be connected with very larrge ranulas. | Ranulas are usually asymptomatic, although they may change gradually in size, shrinking and swelling. The overlying skin is usually intact. The mass is not fixed and is also not tender. The mass is not connected to the thyroid gland or lymph nodes. The mass may not be well defined. If it gets large enough it may interfere with swallowing, and cervical ranulas may even interfere with breathing. Some pain may be connected with very larrge ranulas. | ||
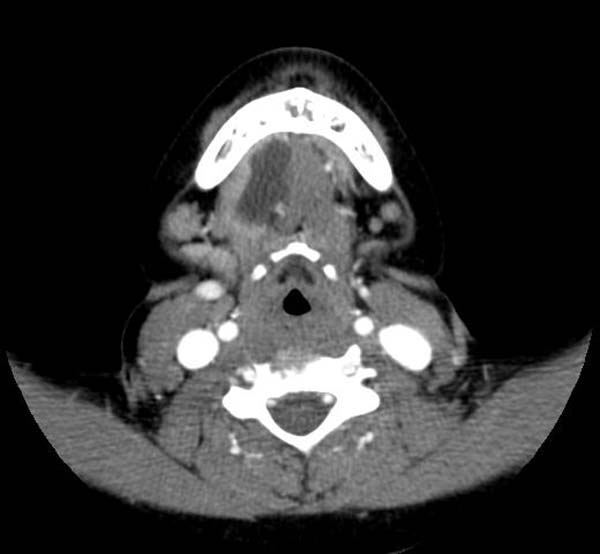
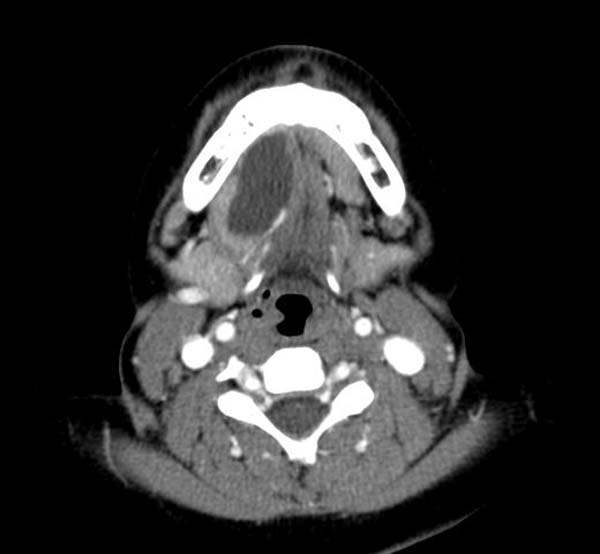
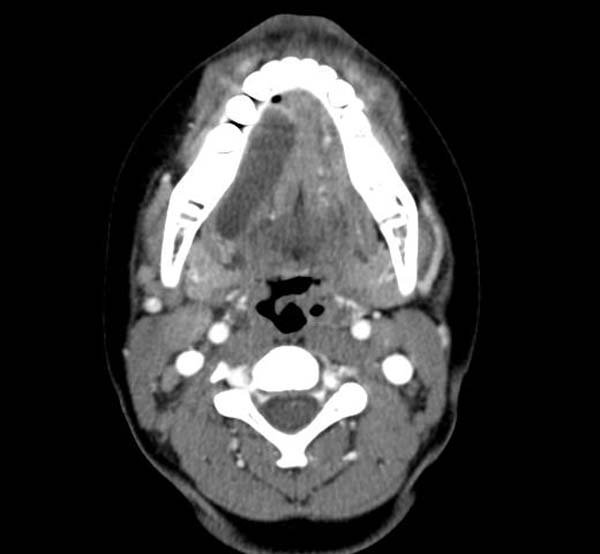
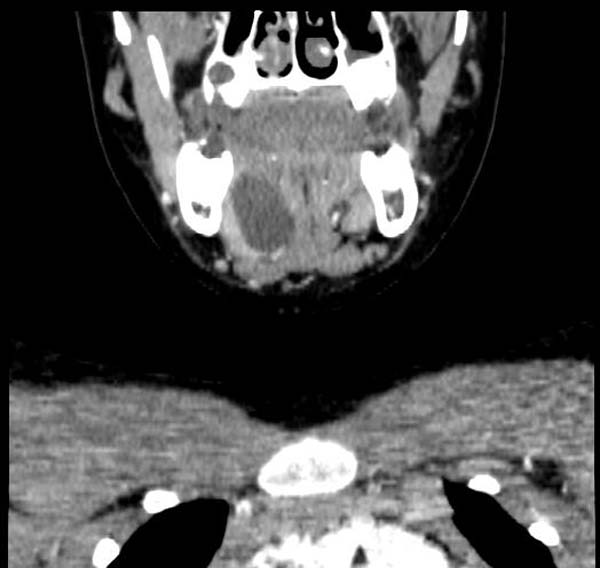
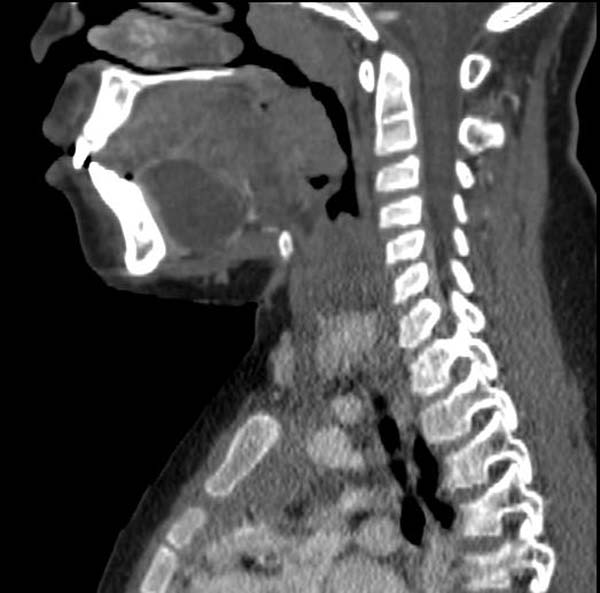
==CT== | |||
Cystic mass in the sublingual area. | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:Ranula-001.jpg|CT demonstrates a Ranula <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Ranula-002.jpg|CT demonstrates a Ranula <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Ranula-003.jpg|CT demonstrates a Ranula <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Ranula-004.jpg|CT demonstrates a Ranula <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Ranula-005.jpg|CT demonstrates a Ranula <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 71: | ||
* http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic648.htm Ranula Catherine M Flaitz, DDS, MS | * http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic648.htm Ranula Catherine M Flaitz, DDS, MS | ||
{{Oral pathology}} | {{Oral pathology}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 20 August 2012
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
WikiDoc Resources for Ranula |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Ranula at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Ranula at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Ranula
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Ranula Risk calculators and risk factors for Ranula
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Berna Zorkun DMD [2]
Overview
A ranula is a type of mucocele found on the floor of the mouth. Ranulas present as a swelling of connective tissue consisting of collected mucin from a ruptured salivary gland duct, which is usually caused by local trauma.
Etymology
The latin rana means frog, and a ranula is so named because its appearance is sometimes compared to a frog's underbelly.
Locations
The gland that most likely causes a ranula is the sublingual gland. Nonetheless, the submandibular gland and minor salivary glands may be involved.
Appearance
An oral ranula is a fluctuant swelling with a bluish translucent color that somewhat resembles the underbelly of a frog "Rana". If it is deeper it does not have this bluish appearance. If it is large ( 2 or more cm.), it may hide the salivary gland and affect the location of the tongue. Most frequently it stems from the sublingual salivary gland, but also from the submandibular gland.
Though normally above the mylohyoid muscle, if a ranula is found deeper in the floor of the mouth, it can appear to have a normal color. A ranula below the mylohyoid muscle is referred to as a "plunging or cervical ranula", and produces swelling of the neck with or without swelling in the floor of the mouth.
Ranulas measure several centimeters in diameter and are usually larger than mucoceles. As a result, when ranulas are present the tongue may be elevated. As with mucoceles, ranulas may be subject to recurrent swelling with occasional rupturing of its contents. When pressed, they may not blanch.
Symptoms
Ranulas are usually asymptomatic, although they may change gradually in size, shrinking and swelling. The overlying skin is usually intact. The mass is not fixed and is also not tender. The mass is not connected to the thyroid gland or lymph nodes. The mass may not be well defined. If it gets large enough it may interfere with swallowing, and cervical ranulas may even interfere with breathing. Some pain may be connected with very larrge ranulas.
CT
Cystic mass in the sublingual area.
-
CT demonstrates a Ranula Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrates a Ranula Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrates a Ranula Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrates a Ranula Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrates a Ranula Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
Histology
Microscopically, ranulas are cystic saliva filled distensions of salivary gland ducts on the floor of the mouth along side the tongue, and are lined by epithelium. A salivary mucocele, in contrast is not lined by epithelium.
Treatment
Treatment of ranulas involves excision of the top of the lesion in a procedure known as "marsupialization". Ranulas may reoccur if the sublingual gland or other gland causing them is not removed. There is little morbidity or mortality connected with treatment.
References
- Kahn, Michael A. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Volume 1. 2001.
External links
- Template:DermAtlas
- http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic648.htm Ranula Catherine M Flaitz, DDS, MS