Pituitary apoplexy pathophysiology
|
Pituitary apoplexy Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pituitary apoplexy pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pituitary apoplexy pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pituitary apoplexy pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Akshun Kalia M.B.B.S.[2]
Overview
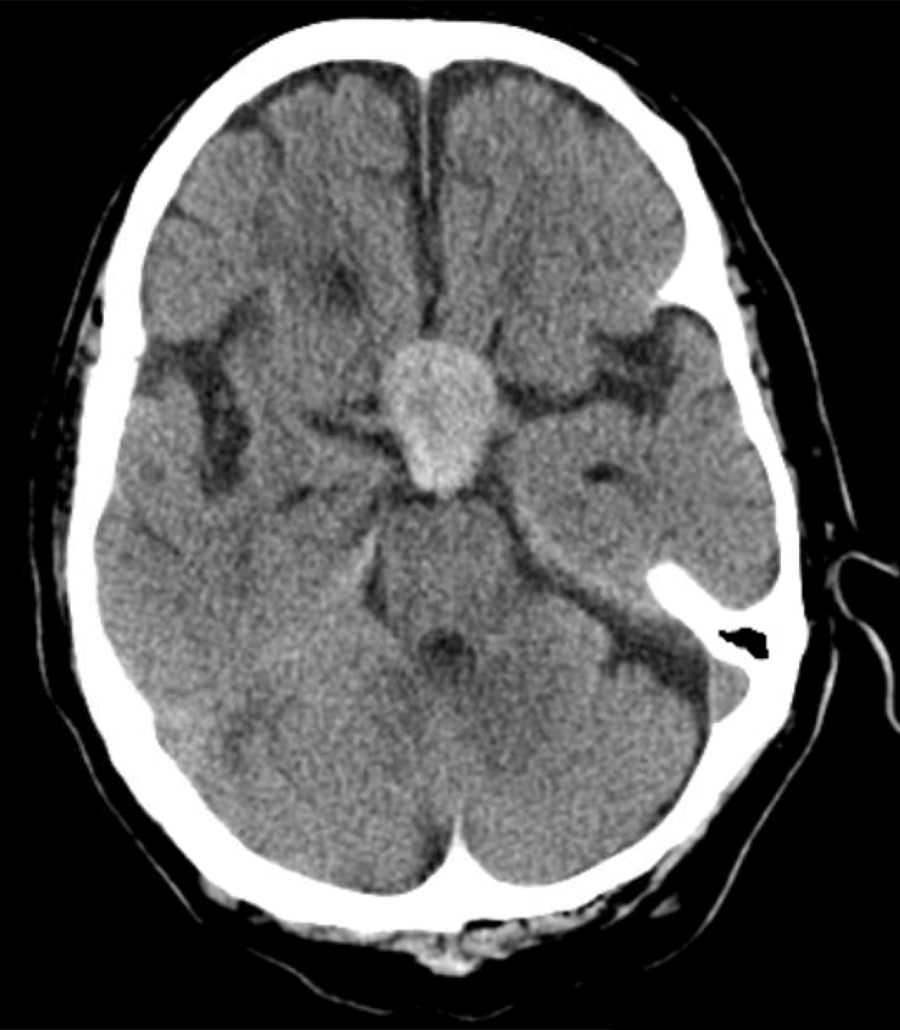
Pituitary apoplexy is an acute clinical syndrome caused by hemorrhage and necrosis in the pituitary gland. Most commonly it is associated with pituitary adenoma.
Pathophysiology
Pituitary apoplexy is caused by bleeding into pituitary gland.
- Most often, pituitary apoplexy is seen with a pituitary adenoma. Pituitary adenoma's have an increased risk of bleeding within the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary adenoma's have fenestrated endothelium surrounded by a variable number of smooth muscle cells, which are not found in normal pituitary gland.
- Enlarging pituitary adenoma may outgrow their blood supply making them susceptible to bleeding and infarction. The bleeding may lead to increase in intrasellar pressure. The increased intrasellar pressure may compress the adjoining structures and lead to clinical symptoms of pituitary apoplexy.[1]
- In addition, these pituitary adenoma have decreased blood supply and angiogenesis .[2][3][4] An enlarged pituitary tumor may become impacted at the diaphragmatic notch, leading to compression of hypophyseal stalk and its vascular supply. This may render the anterior pituitary gland and it's tumor with reduced blood supply causing ischemia and subsequent necrosis. Reperfusion after infarction may lead to hemorrhage within pituitary gland or adenoma.
Genetics
- Gene involved in the pathogenesis of pituitary apoplexy include mutation in AIP gene, which is located on chromosome 11q13.2
- The most common mutation site in AIP gene is p.R304 locus.
- Mutated AIP loses its activity as a tumor supressor gene and leads to increased proliferation.
- The penetration of AIP postive carriers is 12-30%.
Associated Conditions
Pituitary apoplexy is seen with 0.6 to 10% of pituitary adenomas.
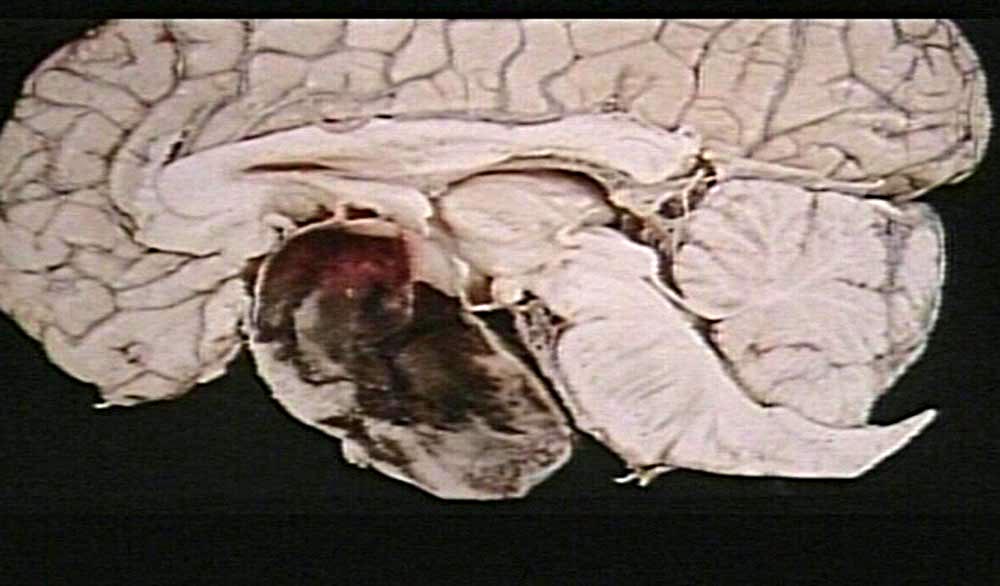
Gross Pathology
- The predominant finding is hemorrhage with or without necrosis.
- Pale, necrotic material was particularly found when there was a long interval between the acute clinical event and surgery.
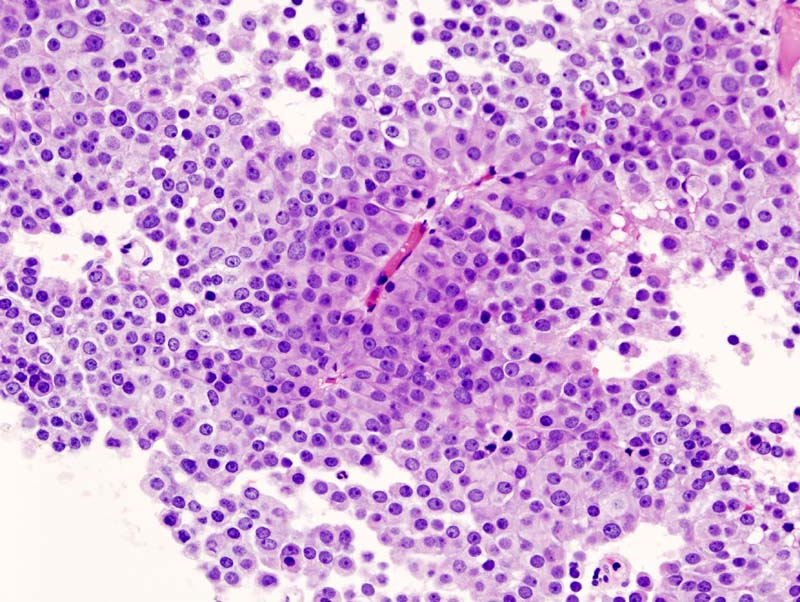
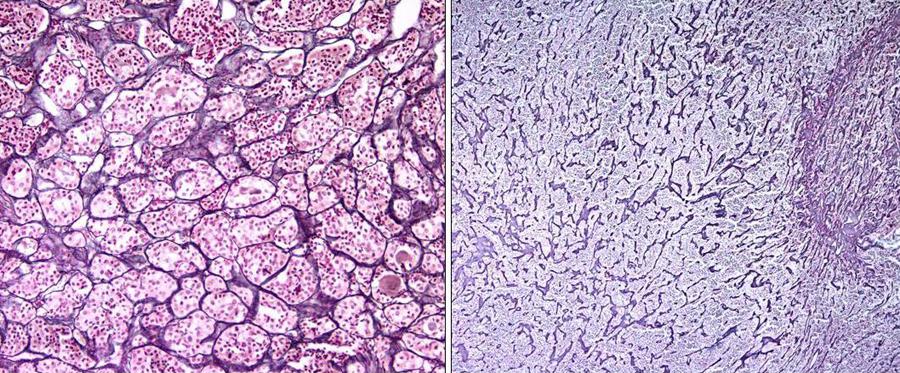
Microscopic Feautres
- Electron microscopic shows evidence of abnormal fenestration of tumor vessels (pituitary adenoma) with fragmented basal membranes that may predispose to hemorrhage.
References
- ↑ Zayour DH, Selman WR, Arafah BM (2004). "Extreme elevation of intrasellar pressure in patients with pituitary tumor apoplexy: relation to pituitary function". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89 (11): 5649–54. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0884. PMID 15531524.
- ↑ Oldfield EH, Merrill MJ (2015). "Apoplexy of pituitary adenomas: the perfect storm". J Neurosurg. 122 (6): 1444–9. doi:10.3171/2014.10.JNS141720. PMID 25859802.
- ↑ Schechter J (1972). "Ultrastructural changes in the capillary bed of human pituitary tumors". Am J Pathol. 67 (1): 109–26. PMC 2032586. PMID 5055626.
- ↑ Schechter J, Goldsmith P, Wilson C, Weiner R (1988). "Morphological evidence for the presence of arteries in human prolactinomas". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 67 (4): 713–9. doi:10.1210/jcem-67-4-713. PMID 3417848.