Pericarditis (patient information)
For the WikiDoc page for this topic, click here Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Jinhui Wu, MD Associate Editor-In-Chief: Ujjwal Rastogi, MBBS [2]
Overview
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic disease that causes inflammation of the joints between the spinal bones, and the joints between the spine and pelvis. Researches demonstrate HLA-B27, ARTS1 and IL23R gene,may be associated with this disease. Usual symptoms include chronic pain in the lower back and hips, stiffness in the lower back or hip area, joint pain, joint swelling. With disease progresses, patinets may show damages outside joints and spine, such as eye inflammation or uveitis, fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss. Test on HLA-B27 gene and images of spine and joints may help diagnose ankylosing spondylitis. Treatments include medications, surgery and physical therapy. Many patients with ankylosing spondylitis go well after treatment.
What are the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis?
Early signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis may limit in your back and hip. When the disease developes, other organs may be involved.
- Chronic pain in your lower back and hips, stiffness in your lower back or hip area, especially in the morning and after periods of inactivity. With disease progresses, your symptoms get worse and you may feel pain and stiffness over time.
- Joint pain
- Joint swelling
- Stiff, inflexible spine
- Eye inflammation or uveitis
- Restricted expansion of your chest
- Low fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
Diseases with similar symptoms are :
- Strain of lumbosacral joint
- Osteoarthritis
- Forestier's disease
- Tuberculous spondylitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Bone cancer
Who is at risk for ankylosing spondylitis?
The cause of ankylosing spondylitis is not clear. Researches demonstrate the following factors may be associated with this disease.
- Heredity: Almost 90% of patients with ankylosing spondylitis are born with the HLA-B27 gene. Recent data demonstrate gene ARTS1 and IL23R are associated with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Gender: Male
- Age: 10~40 years old.
When to seek urgent medical care?
Call your health care provider if symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis develop.
Treatment options
- HLA-B27 gene examinaton: Absence of gene HLA-B27 may suggest that you have less probobility to have ankylosing spondylitis.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): As an autoimmune disease, ESR my elevate in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): CRP is a protein that your liver produces when the immune is damaged. CRP my elevate in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Complete blood count (CBC): Patients may demonstrate anemia, a complication that can result from the chronic inflammation of ankylosing spondylitis.
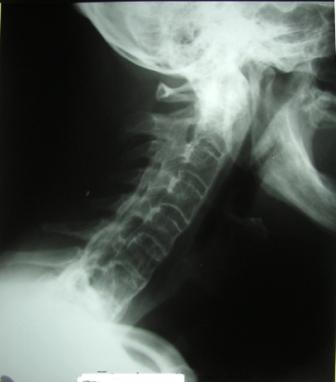
- X-rays, CT or MRI in spine and joints: These images allow the doctor to trace the changes in your spine, joints and bones, then modify your treatments.
- Meidcations
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs may be used to control inflammation and pain in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Usual drugs include ibuprofen, naproxen and indomethacin. Usual side effects are pain, bleeding and ulcers in upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are generally prescribed for patients who cannot take NSAIDs. These drugs can be used by oral or by injection into the joint to control inflammation and pain. Side effects of corticosteroids may include a decreased ability against infection, worse healing in the wound and osteoporosis.
- TNF-alpha inhibitors: TNF-alpha inhibitors, such as etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab, can also help relieve symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis. Side effects include injection site irritation, congestive heart failure, lymphoma and increased risk of infection.
- Cytotoxic drugs: These kind of drugs are used to treat patients without good respond to corticosteroids and always used in active peroid of ankylosing spondylitis. They may interfere with growth of normal and neoplastic cells by cross-linking of DNA or RNA or proteins. Usual drugs include cyclophosphamide and azathioprine. Side effects include marrow suppression, liver damage, nausea and vomiting.
- Surgery: Most patients with ankylosing spondylitis do not need surgery. Surgery is only recommended for those who suffers severe pain or joint damage.
- Physical therapy: The purpose of physical therapy is to relieve pain and improved physical strength and flexibility. The therapist can treat you by hands or by assistive devices. Common therapies for patients with ankylosing spondylitis include:
- Keep a proper posture
- Range-of-motion and stretching exercises
- Specific breathing exercises
- Abdominal and back exercises
Where to find medical care for ankylosing spondylitis?
Directions to Hospitals Treating ankylosing spondylitis
What to expect (Outlook/Prognosis)?
Prognosis of ankylosing spondylitis varies from person to person. Most patients can maintain a good function. Wwhile other patients may lose daily functions. Prognosis depends on:
- Onset age: The early onset age, the worse prognosis will be.
- Whether organs outside joints are affected.
- Whether the patient is treated in time.
- Whether the patient is got physical therapy.