Metastasis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===Pulmonary metastases=== | ===Pulmonary metastases=== | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 14 September 2012
| Metastasis | |
 | |
|---|---|
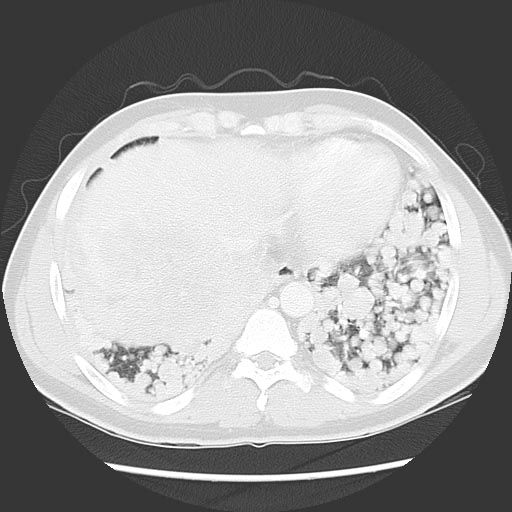
| CT scan with metastatic tumour in lung (upper left lobe, seen on the right side of picture) | |
| DiseasesDB | 28954 |
| MedlinePlus | 002260 |
|
Metastasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Metastasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Metastasis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Metastatic neoplasm; secondary tumor; disseminated cancer; metastases
Overview
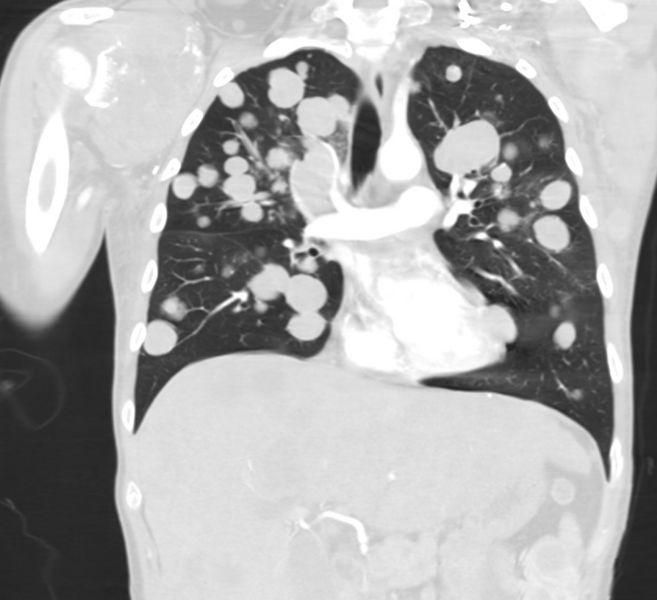
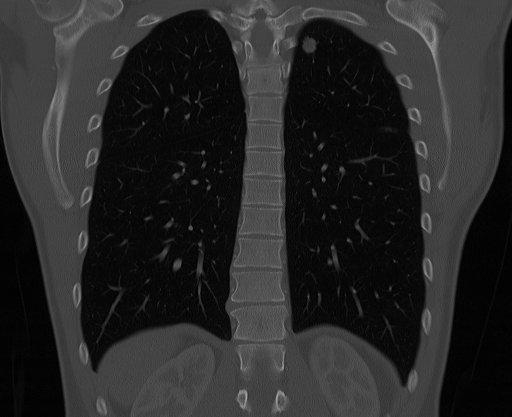
Pulmonary metastases
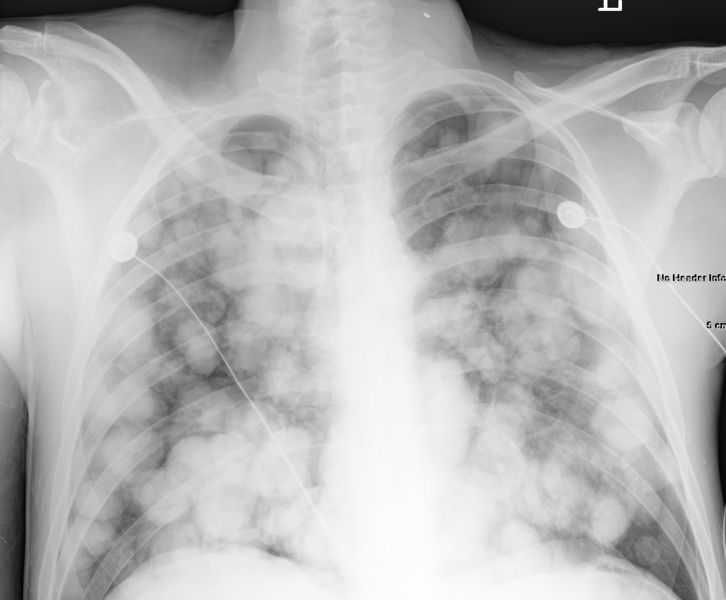
Patient#1
Patient#2
Treatments for metastatic cancer
Whether or not a cancer is local or has spread to other locations affects treatment and survival. If the cancer spreads to other tissues and organs, it may decrease a patient's likelihood of survival. However, there are some cancers (i.e., leukemia, brain) that can kill without spreading at all.
When cancer has metastasized, it may be treated with radiosurgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biological therapy, hormone therapy, surgery or a combination of these. The choice of treatment generally depends on the type of primary cancer, the size and location of the metastasis, the patient's age and general health, and the types of treatments used previously. In patients diagnosed with CUP, it is still possible to treat the disease even when the primary tumor cannot be located.
The treatment options currently available are rarely able to cure metastatic cancer, though some tumors, such as testicular cancer, are usually still curable.
Related chapters
Resources
Medical information about metastatic cancer
- Q&A: Metastatic Cancer – from the National Cancer Institute
- Invasion and Metastases – from Cancer Medicine e.5
- How Cancer Grows and Spreads – an interactive Flash presentation that explores the progression of a carcinoma from a single cell to metastasis; from the research department of Children's Hospital Boston
- Metastasis photo at the Atlas of Pathology website
Charities and advocacy groups dealing with metastatic cancer
- The MetaCancer Foundation – resources and support for metastatic cancer survivors and their caregivers
- Metastatic Breast Cancer Network
- Children's Cancer Research Charity for Metastatic Cancer in Kids
Not specifically about metastatic cancer
- Understanding Cancer Types and Staging – a patients' guide at the CancerGuide website
- Cancer Forums – physicians answering questions about cancer
References
ar:نقيلة bg:Метастаза ca:Metàstasi cs:Metastáza da:Metastase de:Metastase eu:Metastasi fa:متاستاز hr:Metastaze id:Metastasis it:Metastasi he:גרורה la:Metastasis lt:Metastazė hu:Áttét ms:Metastasis nl:Uitzaaiing simple:Metastasis sk:Metastáza fi:Etäpesäke sv:Metastas