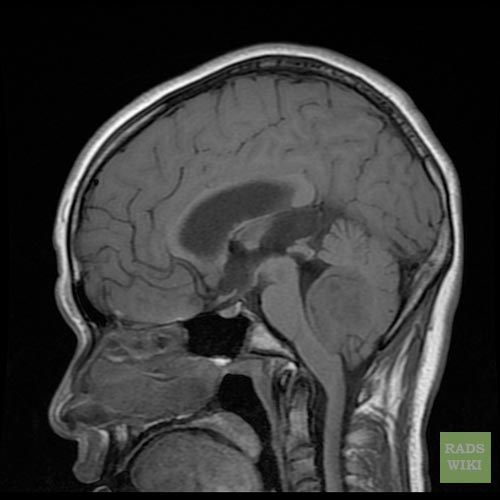
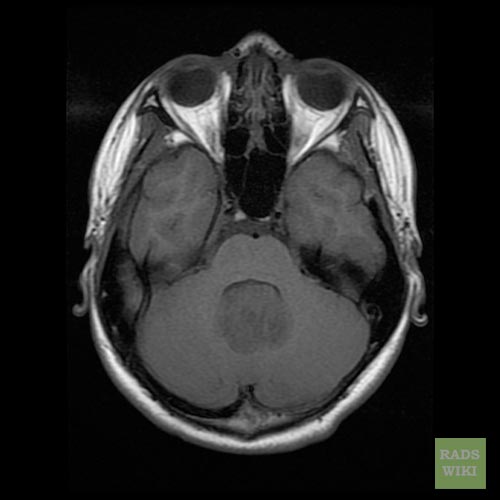
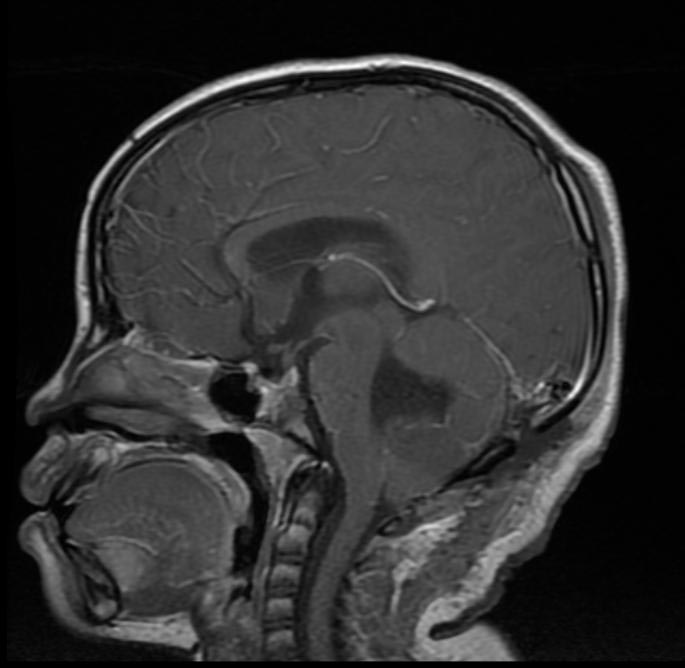
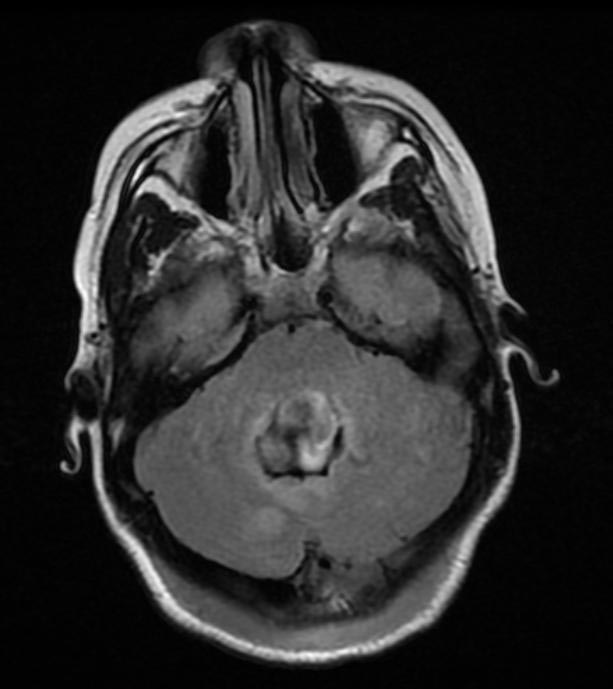
Medulloblastoma MRI
|
Medulloblastoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Medulloblastoma MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Medulloblastoma MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Haytham Allaham, M.D. [2]
Overview
MRI
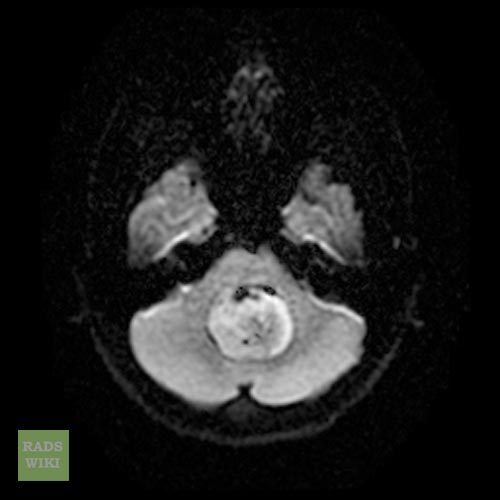
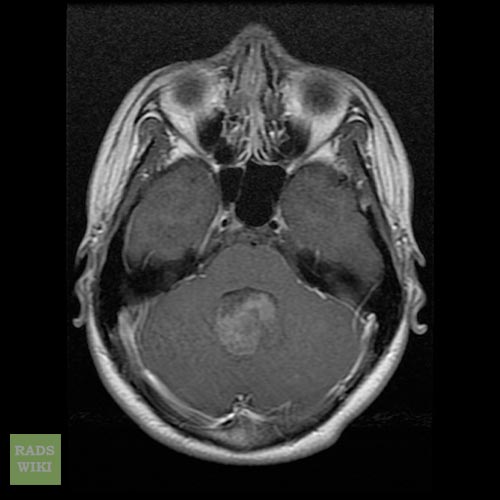
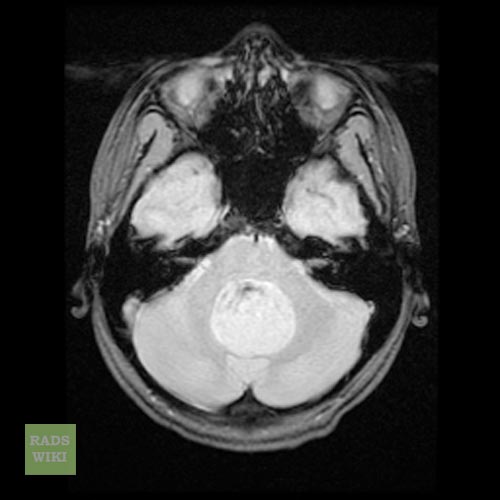
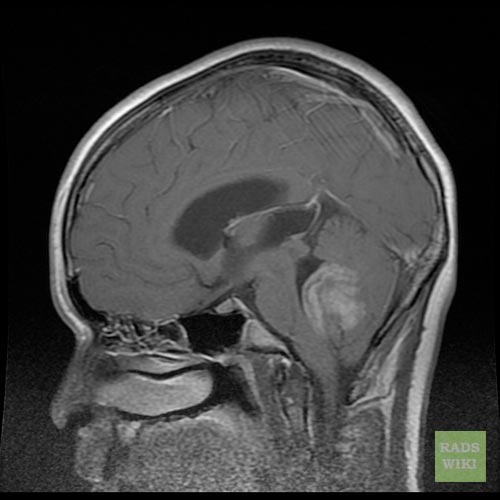
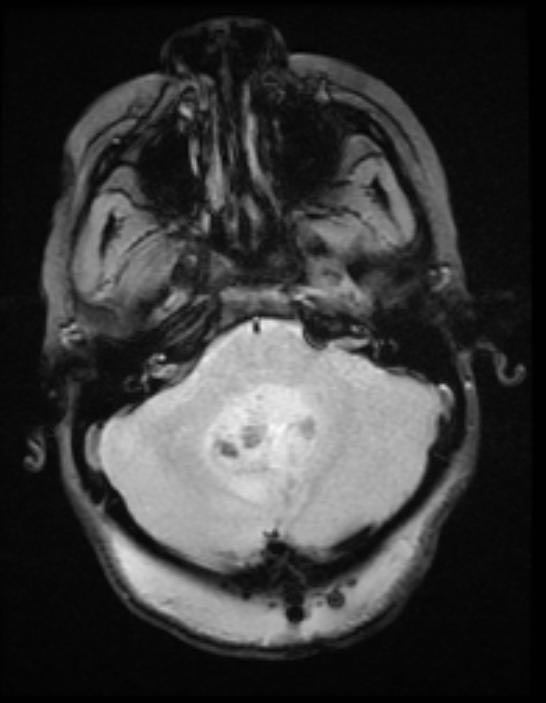
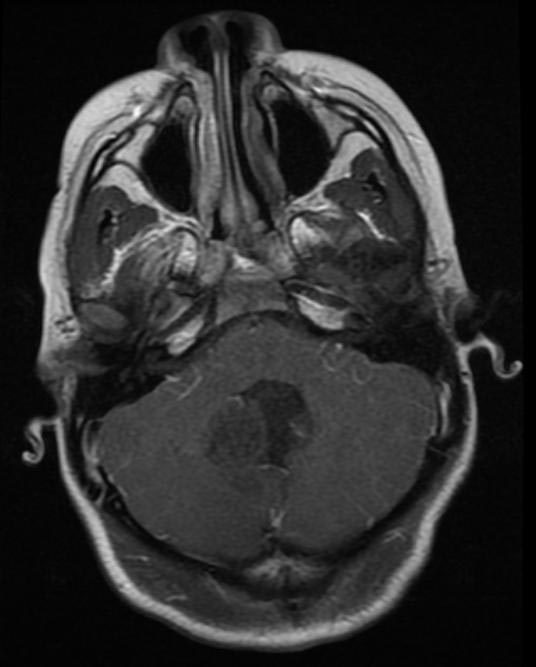
- Brain MRI with gadolinium is the investigation of choice for the diagnosis of medulloblastoma.
- On brain MRI, medulloblastoma is characterized a mass located at the posterior fossa
- Go
- MRI image characteristics observed among meningioma patients include:
- T1 weighted image illustrates a hypointense mass
- T1 C+ (Gd) image illustrates a heterogeneous enhancement in 90% of the cases
- T2 weighted image illustrates a heterogeneous heperintense enhancement
due to calcification, necrosis, and cyst formation
- FLAIR MRI image may illustrates a:[1]
- Localized areas of isointensity or hypointensity
- Radiating star-shaped enhancement
- Multi-nodular enhancing pattern
DWI: shows restricted diffusion MR spectroscopy: elevated choline, NAA decreased, may show a taurine peak 5
MRI is able to delineate the fourth ventricle and subarachnoid space to a much greater degree than CT. Although medulloblastomas project into the fourth ventricle, unlike ependymomas they do not usually extend into the basal cisterns 7.
As CSF seeding is common at presentation, imaging with godalinium contrast of the whole neuraxis is recommended to identify drop metastases and leptomeningeal spread. Although rare, extraneural spread is reported.
Gallery
Patient#1
-
Medulloblastoma
-
Medulloblastoma
-
Medulloblastoma
-
Medulloblastoma
-
Medulloblastoma
-
Medulloblastoma
Patient#2
References
- ↑ Liu HQ, Yin X, Li Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tchoyoson Lim CC; et al. (2012). "MRI features in children with desmoplastic medulloblastoma". J Clin Neurosci. 19 (2): 281–5. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2011.04.029. PMID 22209398.