Isoproterenol (aerosol)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Adeel Jamil, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Isoproterenol (aerosol) is a beta-adrenergic agonist and bronchodilator that is FDA approved for the treatment of reversible obstructive airways disease. Common adverse reactions include nausea, headache, palpitation, tachycardia, flushing of the skin, tremor, vertigo, central excitation and insomnia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- MEDIHALER-ISO is indicated for the treatment of reversible obstructive airways disease.
Dosing Information
- The usual dose for the relief of dyspnea in the acute episode is one or two inhalations. Start with a single inhalation. If no relief is evident after two to five minutes, a second inhalation may be taken. For daily maintenance, use one or two inhalations four to six times daily or as directed by the physician. The physician should be careful to instruct the patient in the proper technique of administration so that the number of inhalations per treatment and the frequency of retreatment may be titrated to the patient's response.
- No more than two inhalations should be taken at any one time, nor more than six inhalations in any one hour during a 24-hour period, unless advised by the physician. Lower doses in elderly patients may be required due to increased sympathomimetic sensitivity.
- Each depression of the valve delivers through the oral adapter 0.08 mg isoproterenol sulfate.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- The use of isoproterenol in patients with pre-existing cardiac arrhythmias associated with tachycardia is contraindicated because the cardiac stimulant effects of the drug may aggravate such disorders. MEDIHALER-ISO must not be used by patients with known hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines.
Warnings
- Excessive use of an adrenergic aerosol should be discouraged, as it may lose effectiveness. Occasional patients have been reported to develop severe paradoxical airway resistance with repeated, excessive use of isoproterenol inhalation preparations (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). The cause of this is unknown. It is advisable that in such instances the use of this preparation be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted, since in the reported cases the patients did not respond to other forms of therapy until the drug was withdrawn. Deaths have been reported following excessive use of isoproterenol inhalation preparations, and the exact cause is unknown. Cardiac arrest was noted in several instances.
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions:
- Isoproterenol and epinephrine may be used interchangeably if the patient becomes unresponsive to one or the other, but should not be used concurrently. If desired, these drugs may be alternated, provided an interval of at least four hours has elapsed. As with all sympathomimetic drugs, isoproterenol should be used with great caution in the presence of coronary insufficiency, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes.
Information for Patients: Patients who are being treated with MEDIHALER-ISO should be informed adequately of the dangers of overusage, tolerance, and rebound bronchospasm (see WARNINGS; ADVERSE REACTIONS). They should be instructed to take no more than two inhalations at any one time, nor more than six in any one hour during a 24-hour period, unless advised by the physician (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION; PATIENT INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE).
Isoproterenol may cause the patient's saliva to turn pinkish to red in color. Proper use of MEDIHALER-ISO oral inhaler should be demonstrated and discussed. Patient Instructions for Use are available with the package insert and should be provided when the medication is dispensed.
As with any drug, patients should be advised against the ingestion of alcohol during treatment.
Drug Interactions: Corticosteroids may be used to restore responsiveness to isoproterenol if necessary. This may come about by increasing the sensitivity of the beta-adrenergic receptors to isoproterenol. No adverse cardiovascular effects were observed in normal volunteers given isoproterenol by inhalation along with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor or a tricyclic anti-depressant.
Concomitant administration of ergot alkaloids and isoproterenol may result in additive peripheral vasoconstriction.
Arrhythmias may result from the administration of isoproterenol to patients who are receiving digitalis, epinephrine, cyclopropane, or halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetics. Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs such as propranolol antagonize the cardiac, bronchodilating, and vasodilating effects of isoproterenol.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following adverse effects, listed by organ system in decreasing frequency have been associated with the use of MEDIHALER-ISO and are similar to those produced by other sympathomimetic agents:
Cardiovascular:
- Palpitation, tachycardia, coronary insufficiency, flushing of the skin, blood pressure changes, cardiac arrhythmias, anginal pain, cardiac arrest.
Pulmonary:
- Paradoxical airway resistance (see WARNINGS), rebound bronchospasm.
Central Nervous System:
- Headache, tremor, vertigo, central excitation, insomnia.
Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions:
- Isoproterenol causes false elevations of bilirubin as measured in vitro by a sequential multiple analyzer. An effect on serum bilirubin determinations in patients receiving the drug has not been determined. Isoproterenol inhalation may result in enough absorption of the drug to produce elevated values for urinary epinephrine. This effect is probably small with standard inhalation doses, but is likely to increase with larger doses.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at aerosol doses (30 minutes per day for 12 days) up to 15 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to isoproterenol. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether isoproterenol is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when MEDIHALER-ISO is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safe and effective use of MEDIHALER-ISO in children below the age of 12 has not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Lower doses in elderly patients may be required due to increased sympathomimetic sensitivity
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Isoproterenol (aerosol) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Isoproterenol (aerosol) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- The oral LD50 values for isoproterenol are as follows: mouse, 1260 mg/kg: rabbit, 3070 mg/kg; male rat, 2230 mg/kg; female rat, 2840 mg/kg; and dog, 600 mg/kg. The intravenous LD50 values are as follows: mouse, 126 mg/kg; rabbit, 27 mg/kg; male rat, 96 mg/kg; female rat, 112 mg/kg; and dog, 50 mg/kg.
- Overdosage effects may occur at doses equal to the therapeutic dose.
Symptoms:
- Manifestations of acute overdosage include chest pain, dizziness, headache, irregular heartbeat, fast or pounding heartbeat, nausea or vomiting, restlessness, weakness, flushing, or decreased diastolic pressure.
Treatment:
- Discontinued dosing allows rapid reversal of adverse effects. Blood pressure and ECG may be monitored and the following treatment used, as appropriate: tachycardia in asthmatic patients may be treated with cardio-selective beta-blockers (metoprolol or atenolol, but used cautiously since cardio-selectivity may not be absolute) and in nonasthmatics with propranolol; blood pressure may be regulated with rapid-acting vasodilators (nitrites, sodium nitroprusside) or alpha-blocking agents (quinidine, phentolamine).
- It is not known if isoproterenol is dialyzable; however, its rapid elimination should preclude the need for dialysis.
Pharmacology

| |
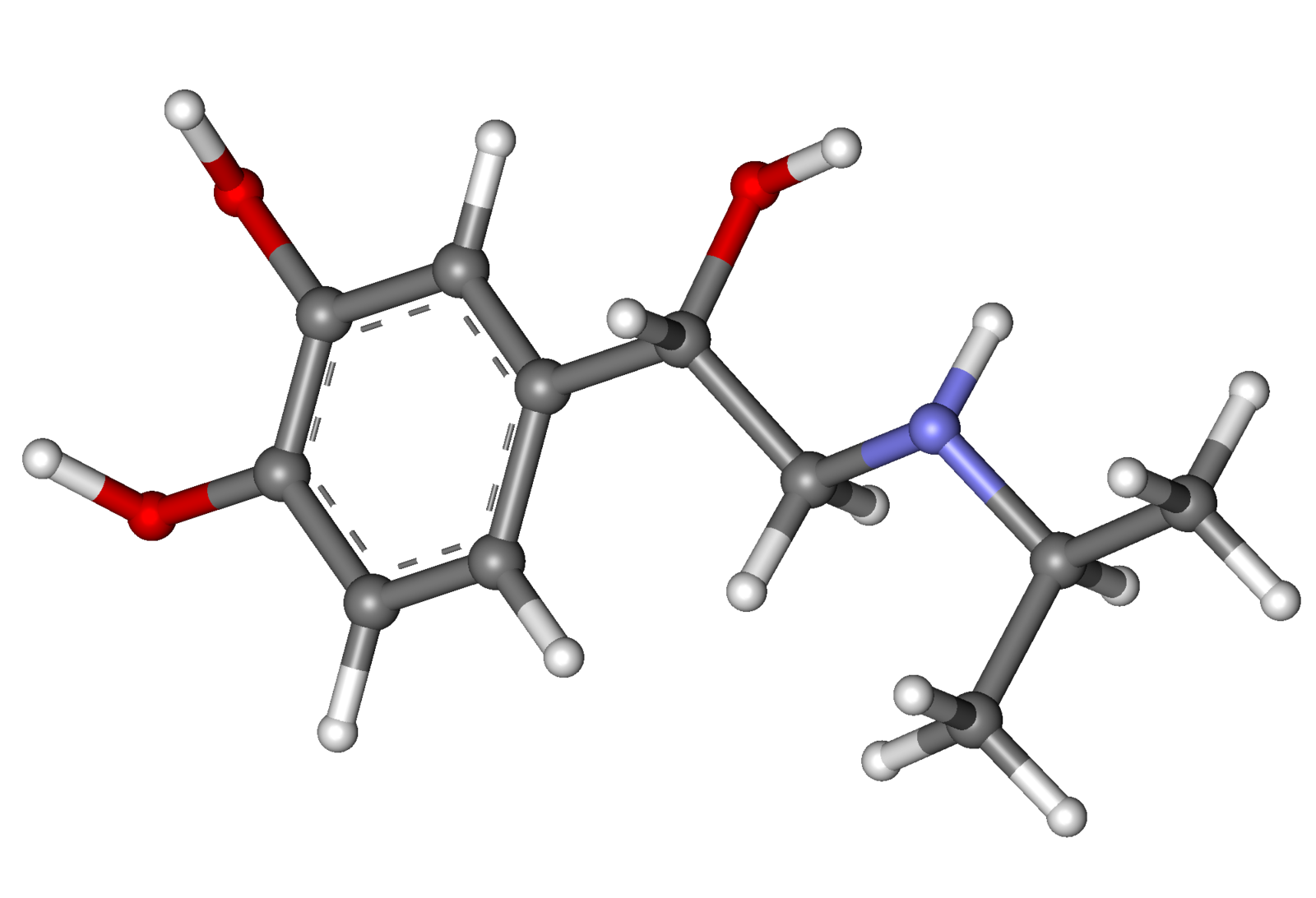
| |
Isoproterenol (aerosol)
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (RS)-4-[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C01 R03AB02 (WHO) R03CB01 (WHO) |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 211.258 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C |
| Legal status |
Template:Unicode Prescription only |
| Routes | inhaled 80-120μg |
Mechanism of Action
- MEDIHALER-ISO (isoproterenol sulfate) is a short-acting sympathomimetic administered by oral inhalation for the treatment of bronchoconstriction. Each metered dose of the aerosol delivers through the oral adapter 0.08 mg isoproterenol sulfate of appropriate particle size (the majority less than 5μ). This drug product also contains dichlorodifluoromethane, dichlorotetrafluoroethane, sorbitan trioleate, and trichloromonofluoromethane. Chemically, isoproterenol sulfate is 4-1-hyroxy-2-(1-methylethyl)amino ethyl-1,2-benzenediol sulfate.
- Structural formula:
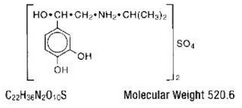
Structure
- This drug product also contains dichlorodifluoromethane, dichlorotetrafluoroethane, sorbitan trioleate, and trichloromonofluoromethane. Chemically, isoproterenol sulfate is 4-[1-hyroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-1,2-benzenediol sulfate.
Structural formula:
Pharmacodynamics
- Isoproterenol acts directly on beta-adrenergic receptors of tissues supplied by sympathetic nerves. The beta-adrenergic effects stem from the release of cyclic AMP following the activation of the enzyme adenyl cyclase. Therapeutic doses of isoproterenol result in relaxation of the smooth muscle of the bronchial tree and decrease in peripheral vascular resistance; increased cardiac output and stroke volume may occur due to its positive inotropic and chronotropic action. The coronary arteries may be dilated, increasing the blood flow. Isoproterenol also inhibits uterine motility and causes decreased tone and motility of intestinal musculature even when epinephrine causes contraction.
- In patients with bronchial constriction, isoproterenol relieves bronchospasm, increases pulmonary function, decreases residual air, and facilitates lung clearance by increasing ciliary motility and mucous transport. Bronchodilatation occurs quickly after oral inhalation and lasts up to one hour. It is one of the most potent bronchodilators known and can be used in patients who do not respond to the bronchodilating action of epinephrine. The drug will prevent or overcome histamine-induced asthma in both experimental animals and man, and is effective when used prophylactically.
- Isoproterenol has a cardio-accelerating effect, but its vasoconstricting action is less pronounced than that of epinephrine. Therapeutic doses may produce a slight increase in systolic blood pressure but a slight decrease in diastolic. Larger doses may cause peripheral vasodilation in the renal, mesenteric, and femoral beds; some patients respond with a decrease in diastolic but no change in systolic pressure. Such effects are usually of very short duration.
Pharmacokinetics
- The average plasma half-life for isoproterenol given intravenously in seven healthy volunteers was four minutes while the average half-life of the drug administered by aerosol to five patients was five minutes. In children, the decline in plasma concentration was biphasic, with a half-life during the first phase of two to five minutes and of three to seven hours during the second phase. A plasma concentration of 0.03 ng/ml was found within minutes, following an aerosol inhalation dose of 500 mcg.
- Excretion following inhalation administration is primarily renal and the major metabolite is the sulfate conjugate of isoproterenol. When the drug is administered directly into the bronchial tree, it is inactivated by the enzyme catechol-o-methyl transferase, and the predominant metabolite is 3-o-methylisoproterenol sulfate. The explanation for this difference is supported by the observation that most (90%) of an aerosol dose is deposited in the mouth and pharynx and is swallowed. The swallowed isoproterenol is converted to its sulfate conjugate in the gut wall, and to a lesser extent in the liver. The remaining isoproterenol is excreted as follows: 1% to 2% unchanged, 1% to 2% free methylated metabolite, and small amounts of metabolites in the bile.
- Recent studies in laboratory animals (minipigs, rodents, and dogs) recorded the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death (with histologic evidence of myocardial necrosis) when beta agonists and methylxanthines were concomitantly administered. The significance of these findings when applied to human usage is currently unknown.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Isoproterenol (aerosol) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Isoproterenol (aerosol) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Patient Instructions for Use
Medihaler-Iso™
(isoproterenol sulfate)
FOR ORAL INHALATION THERAPY ONLY
- For speed of relief and convenience, the MEDIHALER-ISO oral inhaler comes ready to use. It consists of a metal vial, containing the medication, with a single dose valve which fits into an oral adapter (plastic mouthpiece), and a dust cap. The vial can be used only with the MEDIHALER-ISO oral adapter.
- Before each use, remove dust cap and inspect mouthpiece for foreign objects. Shake MEDIHALER-ISO well.
- To get the medication deep into the lungs, follow these three simple steps which can be completed within five seconds:
- Breathe out fully and place mouthpiece well into the mouth aimed at the back of the throat.
- As you begin to breathe in deeply, press the vial firmly down into the adapter with the index finger. This releases one dose.
- Release pressure on vial and remove unit from mouth. Hold your breath as long as possible, then breathe out slowly.
- Replace dust cap after each use.
- Start with a single inhalation. If no relief is evident after two to five minutes, a second inhalation may be taken. No more than two inhalations should be taken at any one time, nor more than six inhalations in any one hour during a 24-hour period, unless advised by the physician. IF DIFFICULTY IN BREATHING PERSISTS, CONTACT YOUR PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY.
- Proper cleaning of the oral adapter (plastic mouthpiece) is critical to the accurate delivery of each dose. At the end of each day's use, simply remove metal vial and wash oral adapter with soap and hot water and rinse thoroughly. Dry adapter thoroughly and replace the vial.
- Note: The indented statement below is required by the Federal government's Clean Air Act for all products containing or manufactured with chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's).
- This product contains trichloromonofluoromethane, dichlorodifluoromethane, and dichlorotetrafluoroethane, substances which harm the environment by destroying ozone in the upper atmosphere.
- Your physician has determined that this product is likely to help your personal health. USE THIS PRODUCT AS DIRECTED, UNLESS INSTRUCTED TO DO OTHERWISE BY YOUR PHYSICIAN. If you have any questions about alternatives, consult with your physician.
- CAUTION: CONTENTS UNDER PRESSURE. Do not puncture or incinerate container. Store at controlled room temperature between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
3M Pharmaceuticals
3M
Northridge, CA 91324
December 1995
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Isoproterenol (aerosol) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Isoproterenol (aerosol) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.