Histoplasmosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Image = Histoplasmosis capsulatum.jpg | | Image = Histoplasmosis capsulatum.jpg | | ||
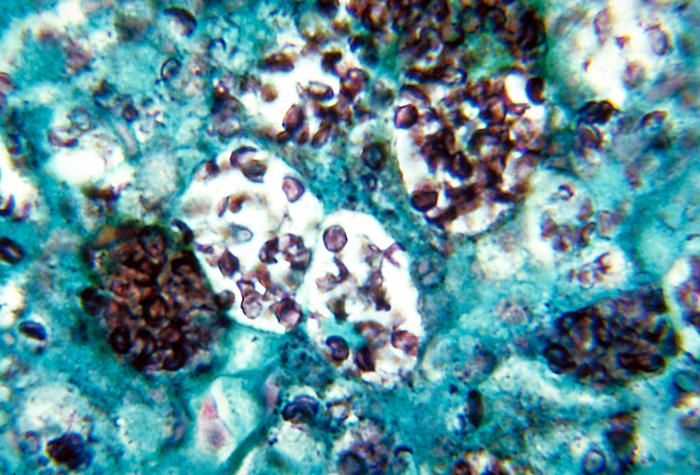
Caption = ''[[Histoplasma capsulatum]]''. Methenamine [[silver stain]] showing histopathologic changes in histoplasmosis. | | Caption = ''[[Histoplasma capsulatum]]''. Methenamine [[silver stain]] showing histopathologic changes in histoplasmosis. | | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Histoplasmosis}} | {{Histoplasmosis}} | ||
{{About1|Histoplasma capsulatum}} | |||
'''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{SSK}}, {{VB}}, {{PTD}}, {{AKI}} | ||
{{SK}} Ajellomyces capsulatus; Darling disease; | {{SK}} Ajellomyces capsulatus; Darling's disease; Cave's disease; Ohio valley disease; Spelunker's lung. | ||
==Overview== | ==[[Histoplasmosis overview|Overview]]== | ||
== | ==[[Histoplasmosis historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
== | ==[[Histoplasmosis pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
==[[Histoplasma capsulatum|Causes]]== | |||
[[ | ==[[Histoplasmosis differential diagnosis|Differentiating Histoplasmosis from other Diseases]]== | ||
== | ==[[Histoplasmosis epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ||
[[ | |||
==[[Histoplasmosis risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
== | ==[[Histoplasmosis natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ||
== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
[[Histoplasmosis history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Histoplasmosis physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Histoplasmosis laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Histoplasmosis chest x ray|Chest X Ray]] | [[Histoplasmosis CT|CT]] | [[Histoplasmosis other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Histoplasmosis other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
==Treatment== | |||
[[Histoplasmosis medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Histoplasmosis surgery|Surgery]] | [[Histoplasmosis primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Histoplasmosis secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | |||
{{Mycoses}} | {{Mycoses}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
[[Category:Fungal diseases]] | [[Category:Fungal diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Rat carried diseases]] | [[Category:Rat carried diseases]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Emergency mdicine]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | |||
[[ | [[Category:Pulmonology]] | ||
[[ | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[ | |||
[[ | |||
[[ | |||
Latest revision as of 22:11, 29 July 2020
| Histoplasmosis | |
 | |
|---|---|
| Histoplasma capsulatum. Methenamine silver stain showing histopathologic changes in histoplasmosis. |
|
Histoplasmosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Histoplasmosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Histoplasmosis |
This page is about clinical aspects of the disease. For microbiologic aspects of the causative organism(s), see Histoplasma capsulatum.
For patient information click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Serge Korjian M.D., Vidit Bhargava, M.B.B.S [2], Prince Tano Djan, BSc, MBChB [3], Aravind Kuchkuntla, M.B.B.S[4]
Synonyms and keywords: Ajellomyces capsulatus; Darling's disease; Cave's disease; Ohio valley disease; Spelunker's lung.
Overview
Historical Perspective
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Histoplasmosis from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Chest X Ray | CT | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention