Hiatus hernia (patient information): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
http://www.healthscout.com/ency/68/57/main.html | http://www.healthscout.com/ency/68/57/main.html | ||
[[Category:Patient information]] | |||
[[Category:Mature chapter]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology patient information]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery patient information]] | |||
{{SIB}} | |||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 23:15, 31 July 2011
For the WikiDoc page for this topic, click here
| Hiatus hernia | |
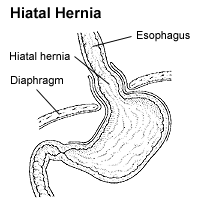 | |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 | K44, Q40.1 |
| ICD-9 | 553.3, 750.6 |
| OMIM | 142400 |
| DiseasesDB | 29116 |
| eMedicine | med/1012 radio/337 |
| MeSH | D006551 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Jinhui Wu, M.D.
Overview
A hiatal hernia is an anatomical abnormality in which part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm and up into the chest. The cause of hiatus hernia may be old age, obesity, pregnacy, persistent and intense coughing and vomiting, chronic constipation, or ascites. Most patients with hiatus hernias cause no symptoms. Usual symptoms include heartburn and regurgitation, anemia, difficulty swallowing, even chronic cough, wheezing, and pneumonia. Upper gastrointestinal x-ray and endoscopy may help diagnose. Treatment options of hiatus hernia include changes in lifestyle, medications such as H-2-receptor blockers and proton pump inhibitors (PPI), and surgery. Most patients with hiatus hernias can be treated well.
How do I know if I have hiatus hernia and what are the symptoms of hiatus hernia?
In most patients, hiatus hernias cause no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they usually experience the symptoms like those of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or its complications.
- Heartburn and regurgitation, when stomach acid refluxes back into the esophagus. Chronic reflux of acid into the esophagus may cause injury and bleeding.
- Anemia
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic cough, wheezing, and even pneumonia: These symptoms in respiratory system are caused because stomach secretions can seep up the esophagus and into the lungs while sleeping.
Other health problems may also cause these symptoms. Only a doctor can tell for sure. A person with any of these symptoms should tell the doctor so that the problems can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Who is at risk for hiatus hernia?
- Old people: Muscle weakening and loss of elasticity as people age.
- Pregnacy: Intra-abdominal forces exerted in pregnancy.
- Persistent and intense pressure on the surrounding muscles, such as when coughing, vomiting, or straining during a bowel movement or while lifting heavy objects
- Chronic constipation
- Western, fiber-depleted diet
- Obesity
- Chronic esophagitis
- Abdominal ascites
How to know you have hiatus hernia?
- Upper gastrointestinal x-ray: During a barium X-ray, you are asked to drink a chalky liquid containing barium that coats your upper digestive tract. This provides a clear silhouette of the esophagus, stomach and the upper part of the duodenum on an X-ray. During swallows, the hiatal hernia appears as a separate "sac" is delineated by the lower esophageal sphincter above and the diaphragm below, lying between the esophagus and the stomach.
- Endoscopy: During this procedure, after you are sedated, an endoscope which is a thin, flexible, lighted tube was passed down your throat to check for inflammation. Endoscopy is always used to diagnose complications such as erosive esophagitis, ulcers in the hiatal hernia, Barrett esophagus, or tumor.
When to seek urgent medical care?
Call your health care provider if symptoms of hiatus hernia develop. If you experience either of the following symptoms, seeking urgent medical care as soon as possible:
- Bleeding in your upper digestive tract
- Severe abdominal pain or chest pain
Treatment options
Since sliding hiatal hernias rarely cause problems themselves but rather contribute to acid reflux, the treatment for patients with hiatal hernias is usually the same as for the associated GERD. And large para-esophageal hernias causing symptoms requires surgery.
- Maintain a good lifestyle: Control your weight, avoidance of obesity. Eat a healthy diet, avoidance of constiption. Avoid foods and substances that increase reflux of acid into the esophagus, such as caffeine, chocolate, fatty foods, peppermint, alcohol or spearmint.
- Medications
- Antacids, such as Maalox, Mylanta, Gelusil, Rolaids and Tums, can be used to neutralize stomach acid. Over-the-counter antacids.
- H-2-receptor blockers, such as cimetidine, famotidine, nizatidine or ranitidine.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI), such as lansoprazole and omeprazole.
- Surgery: Surgery is generally reserved for emergency situations and for people who aren't helped by medications to relieve heartburn and acid reflux.
Diseases with similar symptoms
Where to find medical care for hiatus hernia?
Directions to Hospitals Treating hiatus hernia
Prevention of hiatus hernia
- Treatment of symptoms such as ascites, coughing, vomiting and constipation.
- Eat a healthy diet, avoidance of a western, fiber-depleted diet
- Control weight
What to expect (Outlook/Prognosis)?
Most patients with hiatus hernias can be treated well. The prognosis of hiatus hernia depends on the complications.
Copyleft Sources
http://www.gicare.com/Diseases/hiatus-hernia.aspx
http://www.medicinenet.com/hiatal_hernia/article.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/178393-overview
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiatal-hernia/DS00099/DSECTION=symptoms