Failure to thrive CT scan
|
Failure to thrive Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Failure to thrive CT scan On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Failure to thrive CT scan |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Failure to thrive CT scan |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Akash Daswaney, M.B.B.S[2]
Overview
CTs are useful in diagnosing organic causes of failure to thrive.
CT scan
- CTs are useful in diagnosing organic causes of failure to thrive.
- Listing down each organic cause is beyond the scope of this microchapter.
- Some examples are
- Unilateral renal ectopia
- CT pelvis of a boy who presented failure to thrive, fatigue, intermittent fevers, weight loss, night sweats, and vague discomfort in his abdomen and extremities.
- CT shows the right kidney ectopically positioned in the right lower quadrant.

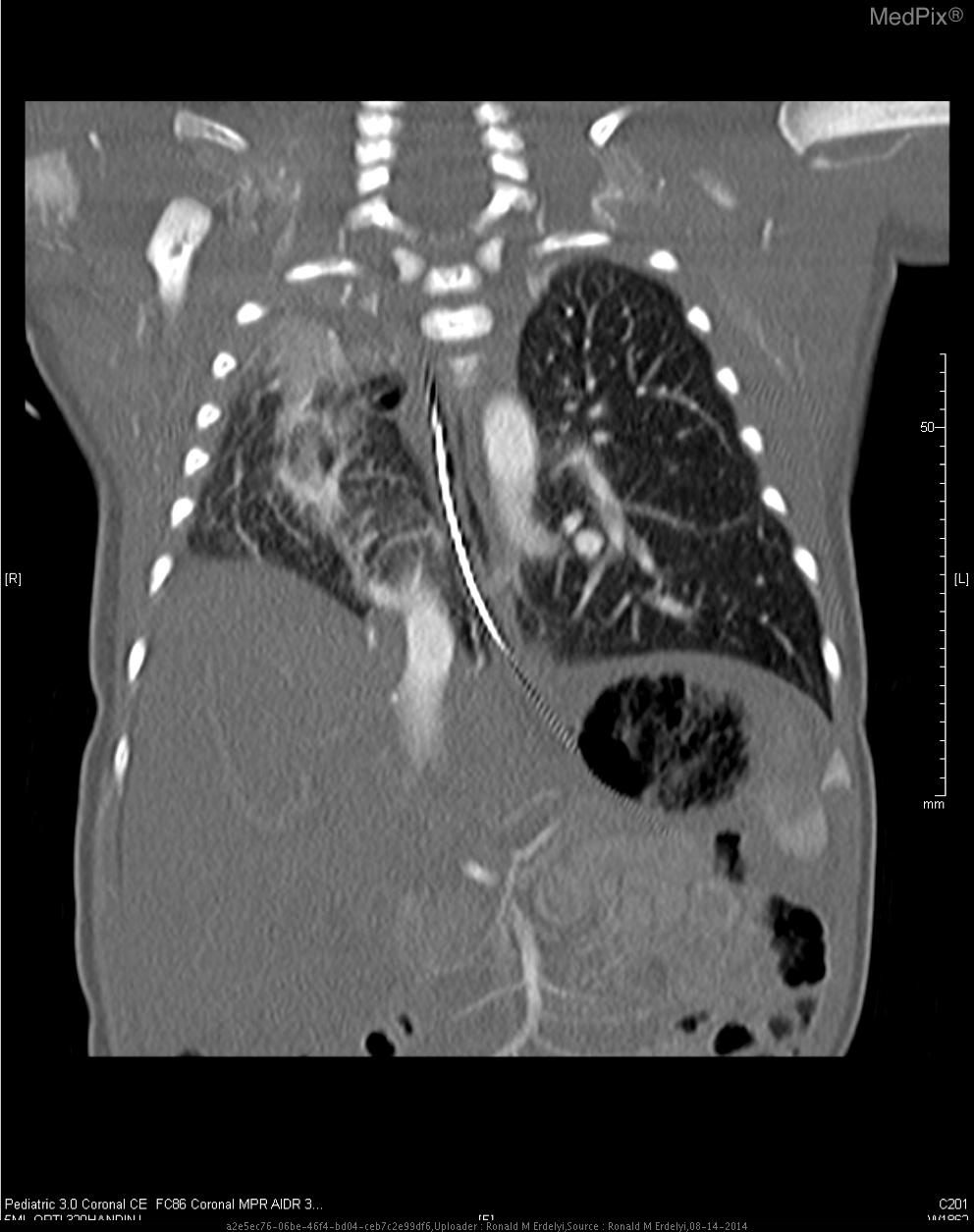
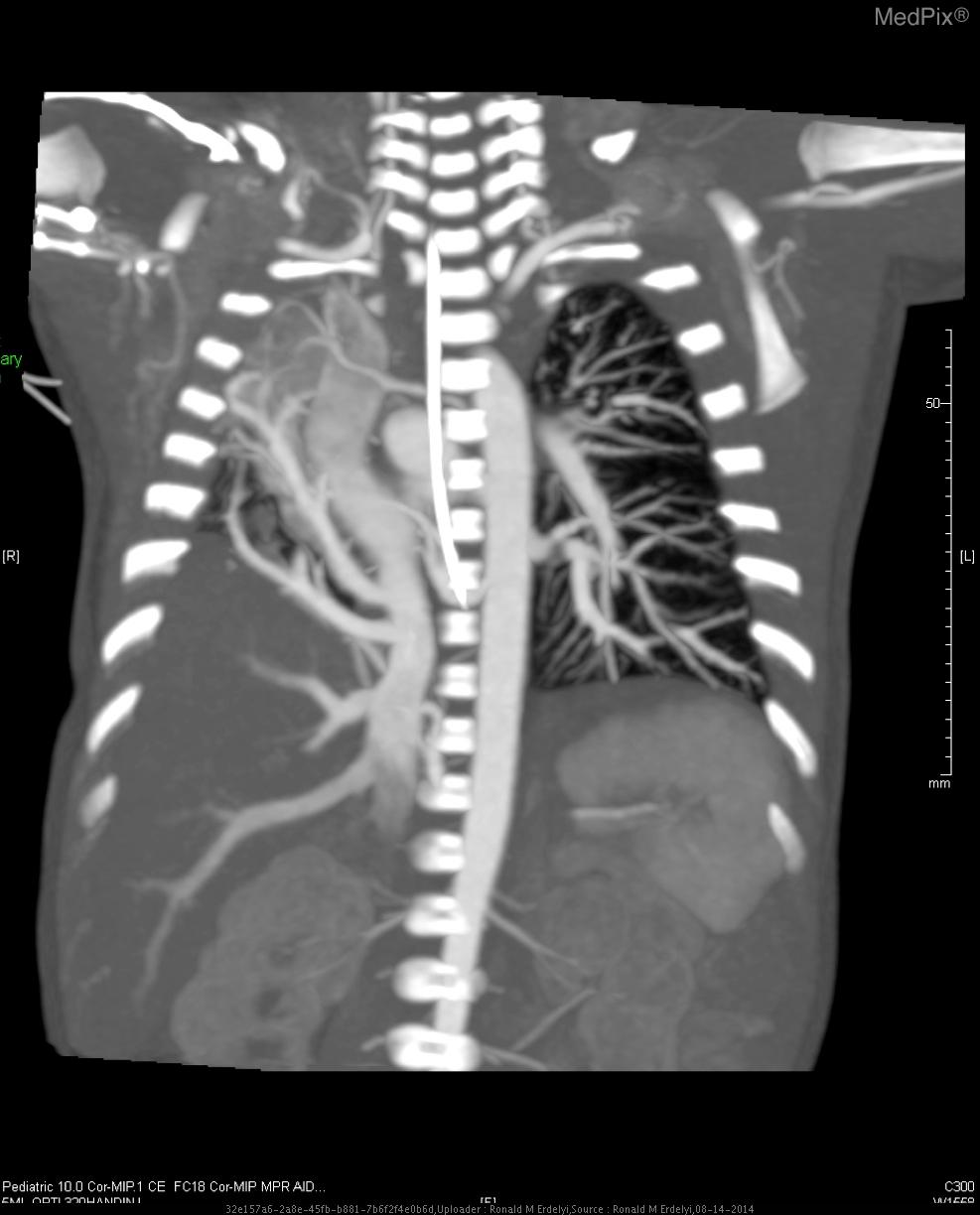
- Scimitar syndrome
- CT with IV contrast shows a hypoplastic right lung with arterial blood supply coming off of the descending aorta, as well as venous drainage directly into inferior vena cava.