Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol is a hormone that is FDA approved for the prophylaxis of indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use oral contraceptives as a method of contraception.. Common adverse reactions include thrombophlebitis and thrombosis, arterial thromboembolism, Pulmonary embolism, Myocardial infarction and coronary thrombosis, Cerebral hemorrhage, Cerebral thrombosishypertension, gallbladder disease, benign and malignant liver tumors, and other hepatic lesions.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Zovia 1/35E and Zovia 1/50E are indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use oral contraceptives as a method of contraception. Oral contraceptive products such as Zovia 1/50E, which contain 50 mcg of estrogen, should not be used unless medically indicated.
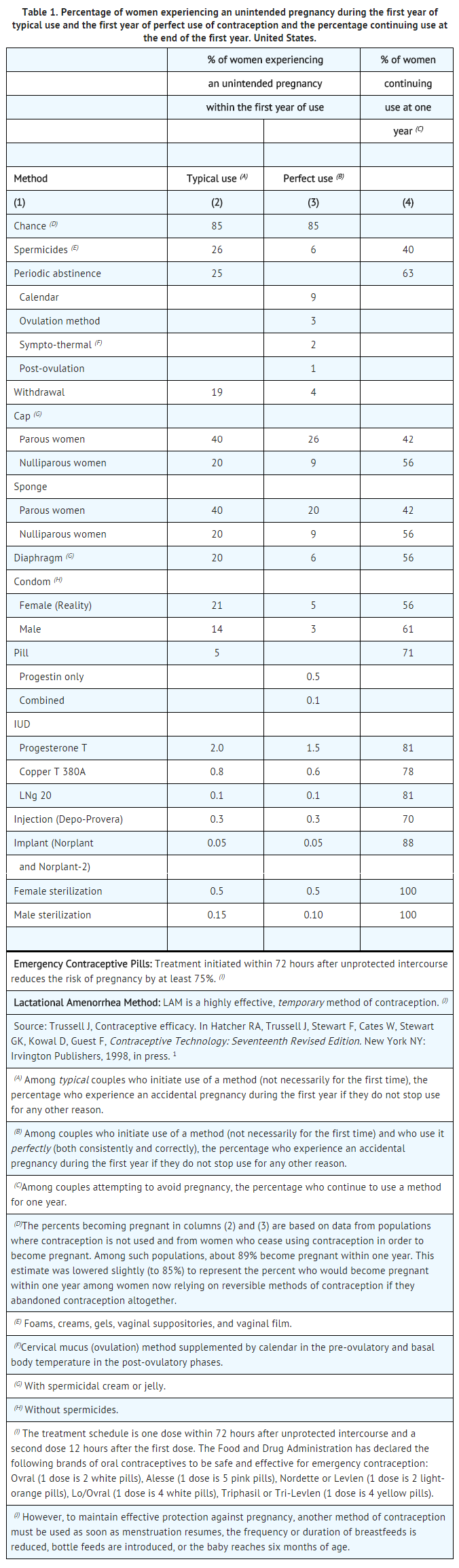
- Oral contraceptives are highly effective.
- The efficacy of these contraceptive methods, except sterilization and progestogen implants and injections, depends upon the reliability with which they are used. Correct and consistent use of methods can result in lower failure rates.
- DOsage
- To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, oral contraceptives must be taken exactly as directed and at intervals of 24 hours.
- If the Sunday start schedule is selected, the patient should be instructed to use an additional method of protection until after the first week of administration in the initial cycle.
- The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of use should be considered.
Zovia 1/35E-28 Zovia 1/50E-28 Dosage Schedules
- The Zovia 1/35E-28 and Zovia 1/50E-28 tablet dispensers contain 21 colored active tablets arranged in three numbered rows of 7 tablets each, followed by a fourth row of 7 white placebo tablets.
- Days of the week are printed above the tablets, starting with Sunday on the left.
- 28-Day Schedule: For a DAY 1 START, count the first day of menstrual flow as Day 1 and the first tablet (light pink or pink) is then taken on Day 1. For a SUNDAY START when menstrual flow begins on or before Sunday, the first tablet (light pink or pink) is taken on that day. With either a DAY 1 START or SUNDAY START, 1 tablet (light pink or pink) is taken each day at the same time for 21 days. Then the white tablets are taken for 7 days, whether bleeding has stopped or not. After all 28 tablets have been taken, whether bleeding has stopped or not, the same dosage schedule is repeated beginning on the following day.
- Special notes
- Spotting, breakthrough bleeding, or nausea. If spotting (bleeding insufficient to require a pad), breakthrough bleeding (heavier bleeding similar to a menstrual flow), or nausea occurs the patient should continue taking her tablets as directed. The incidence of spotting, breakthrough bleeding or nausea is minimal, most frequently occurring in the first cycle. Ordinarily spotting or breakthrough bleeding will stop within a week. Usually the patient will begin to cycle regularly within two or three courses of tablet-taking. In the event of spotting or breakthrough bleeding organic causes should be borne in mind.
- Missed menstrual periods
- Withdrawal flow will normally occur 2 or 3 days after the last active tablet is taken. Failure of withdrawal bleeding ordinarily does not mean that the patient is pregnant, providing the dosage schedule has been correctly followed.
- If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosage regimen, the possibility of pregnancy should be considered after the first missed period, and oral contraceptives should be withheld until pregnancy has been ruled out.
- If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out before continuing the contraceptive regimen.
- The first intermenstrual interval after discontinuing the tablets is usually prolonged; consequently, a patient for whom a 28-day cycle is usual might not begin to menstruate for 35 days or longer. Ovulation in such prolonged cycles will occur correspondingly later in the cycle.
- Post-treatment cycles after the first one, however, are usually typical for the individual woman prior to taking tablets.
- Missed tablets. If a woman misses taking one active tablet, the missed tablet should be taken as soon as it is remembered. In addition, the next tablet should be taken at the usual time. If two consecutive active tablets are missed in week 1 or week 2 of the dispenser, the dosage should be doubled for the next 2 days.
- The regular schedule should then be resumed, but an additional method of protection must be used as backup for the next 7 days if she has sex during that time or she may become pregnant.
- If two consecutive active tablets are missed in week 3 of the dispenser or three consecutive active tablets are missed during any of the first 3 weeks of the dispenser, direct the patient to do one of the following: Day 1 Starters should discard the rest of the dispenser and begin a new dispenser that same day; Sunday Starters should continue to take 1 tablet daily until Sunday, discard the rest of the dispenser and begin a new dispenser that same day. The patient may not have a period this month; however, if she has missed two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out. An additional method of protection must be used as a backup for the next 7 days after the tablets are missed if she has sex during that time or she may become pregnant.
- While there is little likelihood of ovulation if only one active tablet is missed, the possibility of spotting or breakthrough bleeding is increased and should be expected if two or more successive active tablets are missed. However, the possibility of ovulation increases with each successive day that scheduled active tablets are missed.
- If one or more placebo tablets of Zovia 1/35E-28 or Zovia 1/50E-28 are missed, the Zovia 1/35E-28 or Zovia 1/50E-28 schedule should be resumed on the eighth day after the last colored tablet was taken. Omission of placebo tablets in the 28-tablet courses does not increase the possibility of conception provided that this schedule is followed.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Oral contraceptives should not be used in women who have the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A past history of deep vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebral vascular disease, myocardial infarction, or coronary artery disease, or a past history of these conditions
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast, or a history of this condition
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the female reproductive organs or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia, or a history of these conditions
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- History of cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior oral contraceptive use
- Past or present, benign or malignant liver tumors
- Known or suspected pregnancy
Warnings

The use of oral contraceptives is associated with increased risk of several serious conditions including venous and arterial thromboembolism, thrombotic and hemorrhagic stroke, myocardial infarction, liver tumors or other liver lesions, and gallbladder disease. The risk of morbidity and mortality increases significantly in the presence of other risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, and diabetes mellitus.
Practitioners prescribing oral contraceptives should be familiar with the following information relating to these and other risks.
The information contained herein is principally based on studies carried out in patients who used oral contraceptives with formulations containing higher amounts of estrogens and progestogens than those in common use today. The effect of long-term use of the oral contraceptives with lesser amounts of both estrogens and progestogens remains to be determined.
Throughout this labeling, epidemiological studies reported are of two types: retrospective casecontrol studies and prospective cohort studies. Case-control studies provide an estimate of the relative risk of a disease, which is defined as the ratio of the incidence of a disease among oral contraceptive users to that among nonusers. The relative risk (or odds ratio) does not provide information about the actual clinical occurrence of a disease. Cohort studies provide a measure of both the relative risk and the attributable risk. The latter is the difference in the incidence of disease between oral contraceptive users and nonusers. The attributable risk does provide information about the actual occurrence or incidence of a disease in the subject population. For further information, the reader is referred to a text on epidemiological methods.
1. Thromboembolic disorders and other vascular problems. a. Myocardial infarction.
An increased risk of myocardial infarction has been associated with oral contraceptive use.2-21 This increased risk is primarily in smokers or in women with other underlying risk factors for coronary artery disease such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia. The relative risk for myocardial infarction in current oral contraceptive users has been estimated to be 2 to 6. The risk is very low under the age of 30. However, there is the possibility of a risk of cardiovascular disease even in very young women who take oral contraceptives.
Smoking in combination with oral contraceptive use has been reported to contribute substantially to the risk of myocardial infarction in women in their mid-thirties or older, with smoking accounting for the majority of excess cases.22 Mortality rates associated with circulatory disease have been shown to increase substantially in smokers, especially in those 35 years of age and older among women who use oral contraceptives (see Figure 1, Table 2).
Figure 1. Circulatory disease mortality rates per 100,000 woman-years by age, smoking status, and oral contraceptive use.14
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol
|Pill Name=
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol |Label Name=Zovia01.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol |Label Name=Zovia02.jpg
}}