Epoetin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|indication= | |indication= | ||
anemia due to chronic kidney disease, anemia due to zidovudine in hiv-infected patients, anemia due to chemotherapy in patients with cancer, reduction of allogeneic red blood cell transfusions in patients undergoing elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery. | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |blackBoxWarningTitle= | ||
ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |blackBoxWarningBody= | ||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | <i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | ||
* | *Chronic Kidney Disease: | ||
:*In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL. | |||
:*No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, ESA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks. | |||
:*Use the lowest Epogen dose sufficient to reduce the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusions. | |||
*Cancer: | |||
:*ESAs shortened overall survival and/or increased the risk of tumor progression or recurrence in clinical studies of patients with breast, non-small cell lung, head and neck, lymphoid, and cervical cancers. | |||
:*Prescribers and hospitals must enroll in and comply with the ESA APPRISE Oncology Program to prescribe and/or dispense Epogen to patients with cancer. | |||
:*Use the lowest dose to avoid RBC transfusions. | |||
:*Use ESAs only for anemia from myelosuppressive chemotherapy. | |||
:*ESAs are not indicated for patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy when the anticipated outcome is cure. | |||
:*Discontinue following the completion of a chemotherapy course. | |||
*Perisurgery: | |||
:*Due to increased risk of deep venous thrombosis (DVT), DVT prophylaxis is recommended. | |||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | <!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 60: | ||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |fdaLIADAdult= | ||
*Evaluate the iron status in all patients before and during treatment and maintain iron repletion. Correct or exclude other causes of anemia (e.g., vitamin deficiency, metabolic or chronic inflammatory conditions, bleeding, etc.) before initiating Epogen | |||
=====Chronic Kidney Disease===== | |||
:* | *Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease (CKD), including patients on dialysis and not on dialysis to decrease the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusion. | ||
*In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL. No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, ESA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks. Individualize dosing and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Physicians and patients should weigh the possible benefits of decreasing transfusions against the increased risks of death and other serious cardiovascular adverse events [see Boxed Warning and Clinical Studies (14)]. | |||
=====For all patients with CKD===== | |||
*When initiating or adjusting therapy, monitor hemoglobin levels at least weekly until stable, then monitor at least monthly. When adjusting therapy consider hemoglobin rate of rise, rate of decline, ESA responsiveness and hemoglobin variability. A single hemoglobin excursion may not require a dosing change. | |||
*Do not increase the dose more frequently than once every 4 weeks. Decreases in dose can occur more frequently. Avoid frequent dose adjustments. | |||
*If the hemoglobin rises rapidly (e.g., more than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period), reduce the dose of Epogen by 25% or more as needed to reduce rapid responses. | |||
*For patients who do not respond adequately, if the hemoglobin has not increased by more than 1 g/dL after 4 weeks of therapy, increase the dose by 25%. | |||
*For patients who do not respond adequately over a 12-week escalation period, increasing the Epogen dose further is unlikely to improve response and may increase risks. Use the lowest dose that will maintain a hemoglobin level sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions. Evaluate other causes of anemia. Discontinue Epogen if responsiveness does not improve. | |||
=====For patients with CKD on dialysis===== | |||
*Initiate Epogen treatment when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL. | |||
*If the hemoglobin level approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen. | |||
*The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. For pediatric patients, a starting dose of 50 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously is recommended. The intravenous route is recommended for patients on hemodialysis. | |||
=====For patients with CKD not on dialysis===== | |||
*Consider initiating Epogen treatment only when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL and the following considerations apply: | |||
*The rate of hemoglobin decline indicates the likelihood of requiring a RBC transfusion and, | |||
*Reducing the risk of alloimmunization and/or other RBC transfusion-related risks is a goal | |||
*If the hemoglobin level exceeds 10 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen, and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions. | |||
*The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. | |||
===== | =====Zidovudine-treated HIV-infected Patients===== | ||
* | *Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to zidovudine administered at ≤ 4200 mg/week in HIV-infected patients with endogenous serum erythropoietin levels of ≤ 500 mUnits/mL. | ||
*Starting Dose | |||
:*The recommended starting dose in adults is 100 Units/kg as an intravenous or subcutaneous injection 3 times per week. | |||
*Dose Adjustment | |||
:*If hemoglobin does not increase after 8 weeks of therapy, increase Epogen dose by approximately | |||
50 to 100 Units/kg at 4- to 8-week intervals until hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusions or 300 Units/kg. | |||
Withhold Epogen if hemoglobin exceeds 12 g/dL. Resume therapy at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin declines to less than 11 g/dL. | |||
Discontinue Epogen if an increase in hemoglobin is not achieved at a dose of 300 Units/kg for 8 weeks. | |||
=====Patients on Cancer Chemotherapy===== | |||
*Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies where anemia is due to the effect of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy. | |||
* Initiate Epogen in patients on cancer chemotherapy only if the hemoglobin is less than 10 g/dL, and if there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy. | |||
*Use the lowest dose of Epogen necessary to avoid RBC transfusions. | |||
*Recommended Starting Dose | |||
*Adults: | |||
:*150 Units/kg subcutaneously 3 times per week until completion of a chemotherapy course or | |||
:*40,000 Units subcutaneously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course. | |||
* | *Dose Reduction | ||
:*Reduce dose by 25% if: | |||
:*Hemoglobin increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period or | |||
:*Hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion. | |||
:*Withhold dose if hemoglobin exceeds a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion. Reinitiate at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin approaches a level where RBC transfusions may be required. | |||
*Dose Increase | |||
:*After the initial 4 weeks of Epogen therapy, if hemoglobin increases by less than 1 g/dL and remains below 10 g/dL, increase dose to: | |||
:*300 Units/kg three times per week in adults or | |||
:*60,000 Units weekly in adults | |||
:*900 Units/kg (maximum 60,000 Units) weekly in children | |||
*After 8 weeks of therapy, if there is no response as measured by hemoglobin levels or if RBC transfusions are still required, discontinue Epogen. | |||
=====Surgery Patients===== | |||
*Epogen is indicated to reduce the need for allogeneic RBC transfusions among patients with perioperative hemoglobin > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL who are at high risk for perioperative blood loss from elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery. Epogen is not indicated for patients who are willing to donate autologous blood pre-operatively. | |||
*300 Units/kg per day subcutaneously for 15 days total: administered daily for 10 days before surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery. | |||
*600 Units/kg subcutaneously in 4 doses administered 21, 14, and 7 days before surgery and on the day of surgery. | |||
*Deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis is recommended during Epogen therapy. | |||
* | =====Preparation and Administration===== | ||
*Do not shake. Do not use Epogen that has been shaken or frozen. | |||
*Protect vials from light. | |||
*Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use any vials exhibiting particulate matter or discoloration. | |||
*Discard unused portions of Epogen in preservative-free vials. Do not re-enter preservative-free vials. | |||
*Store unused portions of Epogen in multidose vials at 36°F to 46° F (2°C to 8°C). Discard 21 days after initial entry. | |||
*Do not dilute. Do not mix with other drug solutions except for admixing as described below: | |||
*Preservative-free Epogen from single-use vials may be admixed in a syringe with bacteriostatic 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, with benzyl alcohol 0.9% (bacteriostatic saline) in a 1:1 ratio using aseptic technique at the time of administration. Risks are associated with benzyl alcohol in neonates, infants, pregnant women, and nursing mothers. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 139: | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
Blood unit collection for autotransfusion | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Anemia - Congestive heart failure===== | |||
* Subcutaneous erythropoietin (average dose: 5227 units/week) and intravenous (IV) iron (average dose: 185 milligrams (mg)/month). | |||
=====Anemia due to radiation===== | |||
*Epoetin alfa 200 units/kilogram/day for 5 consecutive days per week for up to 7 weeks during radiotherapy. | |||
=====Anemia during the puerperium===== | |||
*Intravenous (IV) erythropoietin (EPO) 300 units/kilogram/day plus IV iron sucrose 200 milligrams (mg)/day on days 1 to 4 postpartum. | |||
===== | =====Anemia - Hepatitis C, In patients being treated with a combination of ribavirin and interferon alfa or ribavirin and peginterferon alfa===== | ||
* | *Epoetin alfa (Procrit(R)) 40,000 units subcutaneously once weekly. | ||
=====Anemia - Multiple myeloma===== | |||
*Erythropoietin (150 units/kilogram 3 times/week initially with adjustments every 3 weeks as needed). | |||
=====Anemia - Myelodysplastic syndrome===== | |||
*Erythropoietin alfa 150 international units/kilogram subcutaneously 3 times weekly for 26 weeks. | |||
=====Anemia - Myelofibrosis===== | |||
*Subcutaneous erythropoietin 10,000 units 3 days per week. | |||
===== | =====Anemia - Rheumatoid arthritis===== | ||
* | * 100 units/kilogram (kg) 3 times per week for eight weeks. | ||
=====Beta Thalassemia===== | |||
*150 international units/kilogram subcutaneously was administered 3 times per week for at least 12 weeks. | |||
=====Blood unit collection for autotransfusion===== | |||
*Epoetin alfa doses of 12,000 to 24,000 units subcutaneously once weekly or 300 to 600 units/kilogram twice weekly. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
=====Patients on Cancer Chemotherapy==== | |||
* | *Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies where anemia is due to the effect of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy | ||
* Pediatric Patients (5 to 18 years): | |||
:*600 Units/kg intravenously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 217: | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | ||
===== | =====Anemia of prematurity===== | ||
* IV erythropoietin dosing was 1250 units/kg/wk as 5 divided doses. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
| Line 163: | Line 225: | ||
|contraindications= | |contraindications= | ||
* | *Uncontrolled hypertension. | ||
*Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) that begins after treatment with Epogen or other erythropoietin protein drugs. | |||
*Serious allergic reactions to Epogen. | |||
*Epogen from multidose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in: | |||
:*Neonates, infants, pregnant women, and nursing mothers. Benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse events and death, particularly in pediatric patients. When therapy with Epogen is needed in neonates and infants, use single-dose vials; do not admix with bacteriostatic saline containing benzyl alcohol. | |||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 4 August 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
Overview
Epoetin is a that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of anemia due to chronic kidney disease, anemia due to zidovudine in hiv-infected patients, anemia due to chemotherapy in patients with cancer, reduction of allogeneic red blood cell transfusions in patients undergoing elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery.. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Evaluate the iron status in all patients before and during treatment and maintain iron repletion. Correct or exclude other causes of anemia (e.g., vitamin deficiency, metabolic or chronic inflammatory conditions, bleeding, etc.) before initiating Epogen
Chronic Kidney Disease
- Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease (CKD), including patients on dialysis and not on dialysis to decrease the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusion.
- In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL. No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, ESA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks. Individualize dosing and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Physicians and patients should weigh the possible benefits of decreasing transfusions against the increased risks of death and other serious cardiovascular adverse events [see Boxed Warning and Clinical Studies (14)].
For all patients with CKD
- When initiating or adjusting therapy, monitor hemoglobin levels at least weekly until stable, then monitor at least monthly. When adjusting therapy consider hemoglobin rate of rise, rate of decline, ESA responsiveness and hemoglobin variability. A single hemoglobin excursion may not require a dosing change.
- Do not increase the dose more frequently than once every 4 weeks. Decreases in dose can occur more frequently. Avoid frequent dose adjustments.
- If the hemoglobin rises rapidly (e.g., more than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period), reduce the dose of Epogen by 25% or more as needed to reduce rapid responses.
- For patients who do not respond adequately, if the hemoglobin has not increased by more than 1 g/dL after 4 weeks of therapy, increase the dose by 25%.
- For patients who do not respond adequately over a 12-week escalation period, increasing the Epogen dose further is unlikely to improve response and may increase risks. Use the lowest dose that will maintain a hemoglobin level sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions. Evaluate other causes of anemia. Discontinue Epogen if responsiveness does not improve.
For patients with CKD on dialysis
- Initiate Epogen treatment when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL.
- If the hemoglobin level approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen.
- The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. For pediatric patients, a starting dose of 50 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously is recommended. The intravenous route is recommended for patients on hemodialysis.
For patients with CKD not on dialysis
- Consider initiating Epogen treatment only when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL and the following considerations apply:
- The rate of hemoglobin decline indicates the likelihood of requiring a RBC transfusion and,
- Reducing the risk of alloimmunization and/or other RBC transfusion-related risks is a goal
- If the hemoglobin level exceeds 10 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen, and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions.
- The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously.
Zidovudine-treated HIV-infected Patients
- Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to zidovudine administered at ≤ 4200 mg/week in HIV-infected patients with endogenous serum erythropoietin levels of ≤ 500 mUnits/mL.
- Starting Dose
- The recommended starting dose in adults is 100 Units/kg as an intravenous or subcutaneous injection 3 times per week.
- Dose Adjustment
- If hemoglobin does not increase after 8 weeks of therapy, increase Epogen dose by approximately
50 to 100 Units/kg at 4- to 8-week intervals until hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusions or 300 Units/kg. Withhold Epogen if hemoglobin exceeds 12 g/dL. Resume therapy at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin declines to less than 11 g/dL. Discontinue Epogen if an increase in hemoglobin is not achieved at a dose of 300 Units/kg for 8 weeks.
Patients on Cancer Chemotherapy
- Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies where anemia is due to the effect of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy.
- Initiate Epogen in patients on cancer chemotherapy only if the hemoglobin is less than 10 g/dL, and if there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy.
- Use the lowest dose of Epogen necessary to avoid RBC transfusions.
- Recommended Starting Dose
- Adults:
- 150 Units/kg subcutaneously 3 times per week until completion of a chemotherapy course or
- 40,000 Units subcutaneously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course.
- Dose Reduction
- Reduce dose by 25% if:
- Hemoglobin increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period or
- Hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion.
- Withhold dose if hemoglobin exceeds a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion. Reinitiate at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin approaches a level where RBC transfusions may be required.
- Dose Increase
- After the initial 4 weeks of Epogen therapy, if hemoglobin increases by less than 1 g/dL and remains below 10 g/dL, increase dose to:
- 300 Units/kg three times per week in adults or
- 60,000 Units weekly in adults
- 900 Units/kg (maximum 60,000 Units) weekly in children
- After 8 weeks of therapy, if there is no response as measured by hemoglobin levels or if RBC transfusions are still required, discontinue Epogen.
Surgery Patients
- Epogen is indicated to reduce the need for allogeneic RBC transfusions among patients with perioperative hemoglobin > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL who are at high risk for perioperative blood loss from elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery. Epogen is not indicated for patients who are willing to donate autologous blood pre-operatively.
- 300 Units/kg per day subcutaneously for 15 days total: administered daily for 10 days before surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery.
- 600 Units/kg subcutaneously in 4 doses administered 21, 14, and 7 days before surgery and on the day of surgery.
- Deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis is recommended during Epogen therapy.
Preparation and Administration
- Do not shake. Do not use Epogen that has been shaken or frozen.
- Protect vials from light.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use any vials exhibiting particulate matter or discoloration.
- Discard unused portions of Epogen in preservative-free vials. Do not re-enter preservative-free vials.
- Store unused portions of Epogen in multidose vials at 36°F to 46° F (2°C to 8°C). Discard 21 days after initial entry.
- Do not dilute. Do not mix with other drug solutions except for admixing as described below:
- Preservative-free Epogen from single-use vials may be admixed in a syringe with bacteriostatic 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, with benzyl alcohol 0.9% (bacteriostatic saline) in a 1:1 ratio using aseptic technique at the time of administration. Risks are associated with benzyl alcohol in neonates, infants, pregnant women, and nursing mothers.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Epoetin in adult patients.
Blood unit collection for autotransfusion
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Anemia - Congestive heart failure
- Subcutaneous erythropoietin (average dose: 5227 units/week) and intravenous (IV) iron (average dose: 185 milligrams (mg)/month).
Anemia due to radiation
- Epoetin alfa 200 units/kilogram/day for 5 consecutive days per week for up to 7 weeks during radiotherapy.
Anemia during the puerperium
- Intravenous (IV) erythropoietin (EPO) 300 units/kilogram/day plus IV iron sucrose 200 milligrams (mg)/day on days 1 to 4 postpartum.
Anemia - Hepatitis C, In patients being treated with a combination of ribavirin and interferon alfa or ribavirin and peginterferon alfa
- Epoetin alfa (Procrit(R)) 40,000 units subcutaneously once weekly.
Anemia - Multiple myeloma
- Erythropoietin (150 units/kilogram 3 times/week initially with adjustments every 3 weeks as needed).
Anemia - Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Erythropoietin alfa 150 international units/kilogram subcutaneously 3 times weekly for 26 weeks.
Anemia - Myelofibrosis
- Subcutaneous erythropoietin 10,000 units 3 days per week.
Anemia - Rheumatoid arthritis
- 100 units/kilogram (kg) 3 times per week for eight weeks.
Beta Thalassemia
- 150 international units/kilogram subcutaneously was administered 3 times per week for at least 12 weeks.
Blood unit collection for autotransfusion
- Epoetin alfa doses of 12,000 to 24,000 units subcutaneously once weekly or 300 to 600 units/kilogram twice weekly.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
=Patients on Cancer Chemotherapy
- Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies where anemia is due to the effect of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy
- Pediatric Patients (5 to 18 years):
- 600 Units/kg intravenously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Epoetin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Anemia of prematurity
- IV erythropoietin dosing was 1250 units/kg/wk as 5 divided doses.
Contraindications
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
- Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) that begins after treatment with Epogen or other erythropoietin protein drugs.
- Serious allergic reactions to Epogen.
- Epogen from multidose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in:
- Neonates, infants, pregnant women, and nursing mothers. Benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse events and death, particularly in pediatric patients. When therapy with Epogen is needed in neonates and infants, use single-dose vials; do not admix with bacteriostatic saline containing benzyl alcohol.
Warnings
|
ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Epoetin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Epoetin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Epoetin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Epoetin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Epoetin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Epoetin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Epoetin in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Epoetin in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Epoetin in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Epoetin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Epoetin in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Epoetin in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Epoetin in the drug label.
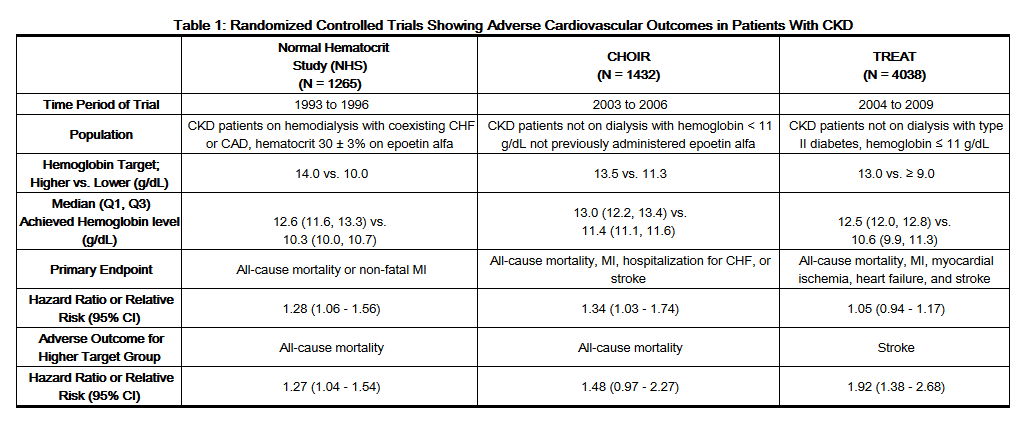
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Epoetin in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Epoetin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Epoetin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Epoetin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Epoetin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Epoetin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Epoetin |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Epoetin |Label Name=Epoetin11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Epoetin |Label Name=Epoetin11.png
}}