Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings: Difference between revisions
m (corrected my personal editor hyperlink) |
m (→Color Doppler) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Color Doppler=== | ===Color Doppler=== | ||
[[Color doppler]] is a type of ultrasound that visualizes flow direction and velocity. <ref name="“Radiopaedia”7">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/color-flow-doppler-ultrasound}}</ref> | [[Color doppler]] is a type of ultrasound that visualizes flow direction and velocity.<ref name="“Radiopaedia”7">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/color-flow-doppler-ultrasound}}</ref> | ||
*This study can be done to diagnose [[Endometrial polyp|endometrial polyps]] where it shows a single feeding vessel extending to and supplying the [[polyp]] <ref name="“Radiopaedia”2">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | *This study can be done to diagnose [[Endometrial polyp|endometrial polyps]] where it shows a single feeding vessel extending to and supplying the [[polyp]]<ref name="“Radiopaedia”2">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | ||
[[File:Endometrial Doppler.png|thumb|300x300px|PMID: 20955593|alt=|none|border]] | [[File:Endometrial Doppler.png|thumb|300x300px|PMID: 20955593|alt=|none|border]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Sonohysterography=== | ===Sonohysterography=== | ||
[[Sonohysterography]] is an ultrasound technique used to asses the uterine anatomical structure. It is most commonly utilized for purposes of assessing [[fertility]]. <ref name="“Radiopaedia”6">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sonohysterography}}</ref> | [[Sonohysterography]] is an ultrasound technique used to asses the uterine anatomical structure. It is most commonly utilized for purposes of assessing [[fertility]].<ref name="“Radiopaedia”6">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sonohysterography}}</ref> | ||
*Sonohysterography may be helpful in determining endometrial polyps which presents echogenic, smooth masses outlined by fluid <ref name="“Radiopaedia”3">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | *Sonohysterography may be helpful in determining endometrial polyps which presents echogenic, smooth masses outlined by fluid<ref name="“Radiopaedia”3">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | ||
===Hysterosalpingography=== | ===Hysterosalpingography=== | ||
*This study can be done to diagnose: | *This study can be done to diagnose: | ||
**[[Endometrial polyp|Endometrial polyps]]: may present as pedunculated masses on imaging <ref name="“Radiopaedia”4">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | **[[Endometrial polyp|Endometrial polyps]]: may present as pedunculated masses on imaging<ref name="“Radiopaedia”4">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp}}</ref> | ||
**[[Adenomyosis]]: diverticula extending into the myometrium <ref name="“Radiopaedia”22">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/adenomyosis}}</ref> | **[[Adenomyosis]]: diverticula extending into the myometrium<ref name="“Radiopaedia”22">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/adenomyosis}}</ref> | ||
[[File:Normal-hysterosalpingogram-2.PNG|none|thumb|300x300px|Case courtesy of Dr MT Niknejad, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 85288|alt=|border]] | [[File:Normal-hysterosalpingogram-2.PNG|none|thumb|300x300px|Case courtesy of Dr MT Niknejad, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 85288|alt=|border]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
===Nuclear Medicine=== | ===Nuclear Medicine=== | ||
*[[PET-CT]] may be done to detect [[Uterine cancer|uterine malignancie]]<nowiki/>s but it is less accurate than [[MRI]] and [[ultrasounds]] <ref name="“Radiopaedia”5">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-carcinoma}}</ref> | *[[PET-CT]] may be done to detect [[Uterine cancer|uterine malignancie]]<nowiki/>s but it is less accurate than [[MRI]] and [[ultrasounds]]<ref name="“Radiopaedia”5">{{cite web|url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-carcinoma}}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 01:23, 7 August 2022
|
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Dysfunctional uterine bleeding from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings |
|
FDA on Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings |
|
CDC on Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings |
|
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings in the news |
|
Blogs on Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Dysfunctional uterine bleeding other imaging findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Arooj Naz, M.B.B.S
Overview
Other imaging findings include colour doppler, sonohysterography, hysterosalpingography, and nuclear imaging (PET scan). These imaging modalities have proven useful for diagnosing polyps, endometrioma's and adenomyosis.
Other Imaging Findings
Color Doppler
Color doppler is a type of ultrasound that visualizes flow direction and velocity.[1]
- This study can be done to diagnose endometrial polyps where it shows a single feeding vessel extending to and supplying the polyp[2]

Sonohysterography
Sonohysterography is an ultrasound technique used to asses the uterine anatomical structure. It is most commonly utilized for purposes of assessing fertility.[3]
- Sonohysterography may be helpful in determining endometrial polyps which presents echogenic, smooth masses outlined by fluid[4]
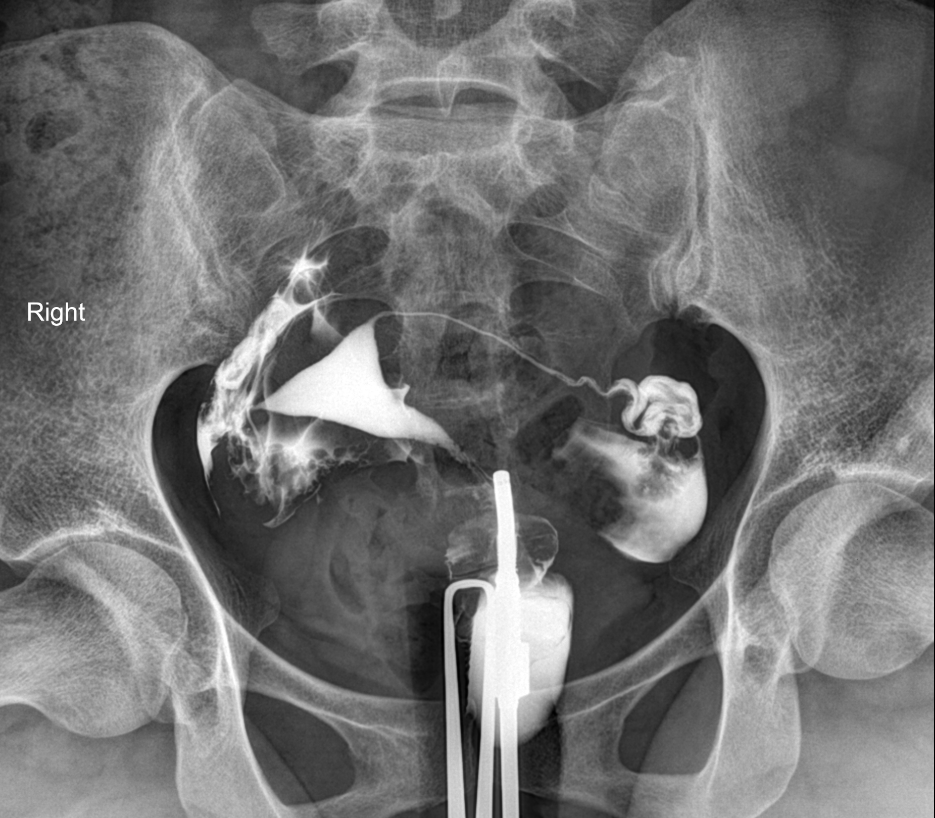
Hysterosalpingography
- This study can be done to diagnose:
- Endometrial polyps: may present as pedunculated masses on imaging[5]
- Adenomyosis: diverticula extending into the myometrium[6]
Nuclear Medicine
- PET-CT may be done to detect uterine malignancies but it is less accurate than MRI and ultrasounds[7]
References
- ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/color-flow-doppler-ultrasound. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sonohysterography. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-polyp. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/adenomyosis. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometrial-carcinoma. Missing or empty
|title=(help)